Abstract
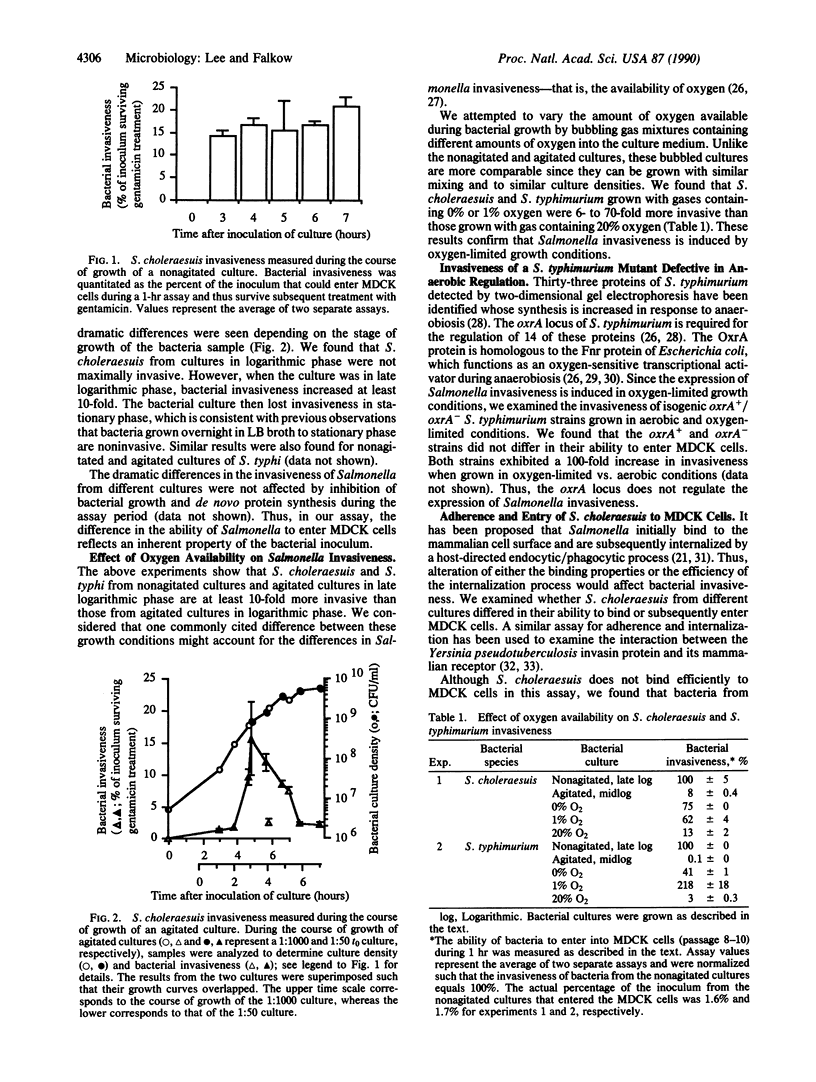
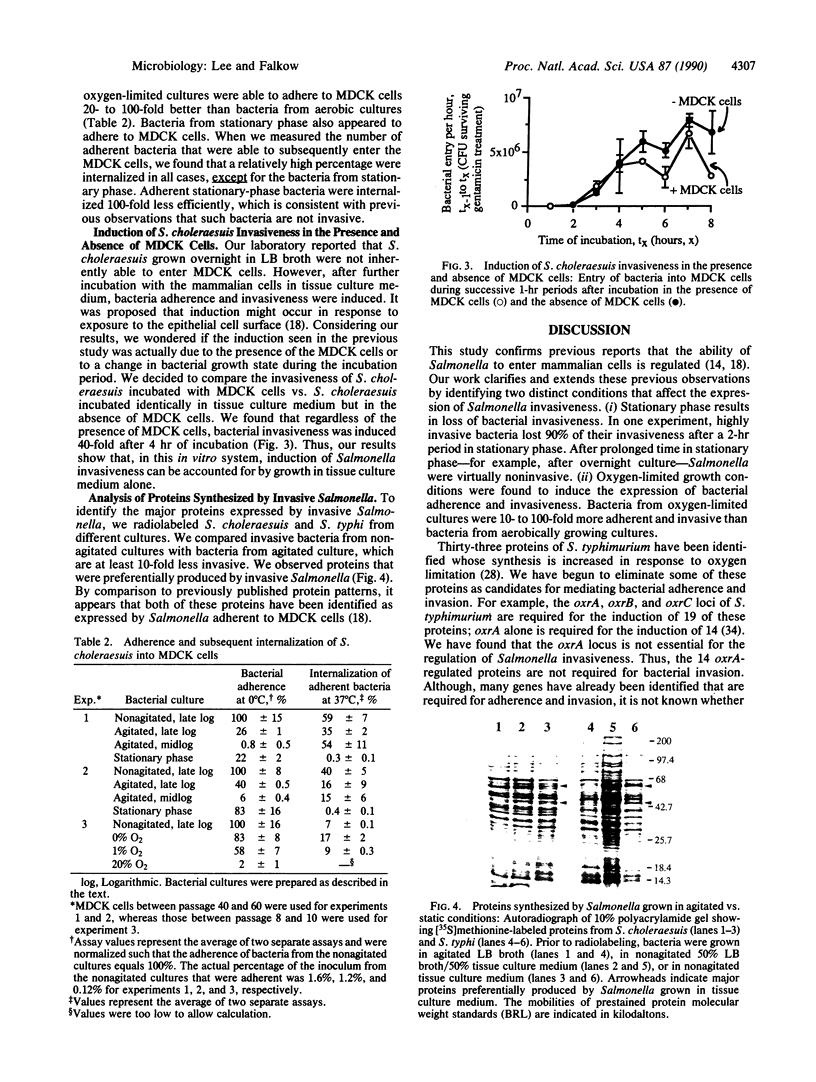
We have examined the effect of different growth conditions on the ability of Salmonella to interact with Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Two growth conditions that affect the expression of Salmonella adherence and invasiveness have been identified. First, bacteria lose their invasiveness in the stationary phase of growth. Second, bacteria growing in oxygen-limited growth conditions are induced for adherence and invasiveness, whereas those growing aerobically are relatively nonadherent and noninvasive. Salmonella from cultures aerated with gas mixtures containing 0% or 1% oxygen were 6- to 70-fold more adherent and invasive than those from cultures aerated with a gas mixture containing 20% oxygen. The Salmonella typhimurium oxrA gene that is required for the anaerobic induction of many proteins is not involved in the regulation of Salmonella invasiveness. We speculate that oxygen limitation might be an environmental cue that triggers the expression of Salmonella invasiveness within the intestinal lumen and other tissues.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aliabadi Z., Park Y. K., Slonczewski J. L., Foster J. W. Novel regulatory loci controlling oxygen- and pH-regulated gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):842–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.842-851.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson D. I., Roth J. R. Redox regulation of the genes for cobinamide biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6734–6739. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6734-6739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baloda S. B., Faris A., Krovacek K. Cell-surface properties of enterotoxigenic and cytotoxic Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium: studies on hemagglutination, cell-surface hydrophobicity, attachment to human intestinal cells and fibronectin-binding. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(5):447–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Collins F. M. The route of enteric infection in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1189–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Fry J., Rock E. P., Falkow S. Passage of Salmonella through polarized epithelial cells: role of the host and bacterium. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;11:99–107. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_11.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Heffron F., Falkow S. Epithelial cell surfaces induce Salmonella proteins required for bacterial adherence and invasion. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):940–943. doi: 10.1126/science.2919285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Starnbach M. N., Francis C. L., Stocker B. A., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of TnphoA mutants of Salmonella that are unable to pass through a polarized MDCK epithelial cell monolayer. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):757–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Jansen W. H., Maas H. M., Le Minor L., Beaud R. An unusual H antigen (Z66) in strains of Salmonella typhi. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 May-Jun;132(3):331–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B., Simons K. A functional assay for proteins involved in establishing an epithelial occluding barrier: identification of a uvomorulin-like polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):457–468. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffernan E. J., Fierer J., Chikami G., Guiney D. Natural history of oral Salmonella dublin infection in BALB/c mice: effect of an 80-kilobase-pair plasmid on virulence. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1254–1259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Mammalian cell adhesion functions and cellular penetration of enteropathogenic Yersinia species. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1449–1453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Richardson L. A. The attachment to, and invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: the contribution of mannose-sensitive and mannose-resistant haemagglutinating activities. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):361–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Richardson L. A., Uhlman D. The invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: reversible and irreversible bacterial attachment and the role of bacterial motility. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):351–360. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosla C., Bailey J. E. Heterologous expression of a bacterial haemoglobin improves the growth properties of recombinant Escherichia coli. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):633–635. doi: 10.1038/331633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Edebo L. Association of viable and inactivated Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR 10 with HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):851–857. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.851-857.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M., Mårdén P., Jones G. W. The transient phase between growth and nongrowth of heterotrophic bacteria, with emphasis on the marine environment. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:25–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist B. L., Lebenthal E., Lee P. C., Stinson M. W., Merrick J. M. Adherence of Salmonella typhimurium to small-intestinal enterocytes of the rat. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3044–3050. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3044-3050.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nnalue N. A., Stocker B. A. Some galE mutants of Salmonella choleraesuis retain virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):635–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.635-640.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector M. P., Aliabadi Z., Gonzalez T., Foster J. W. Global control in Salmonella typhimurium: two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of starvation-, anaerobiosis-, and heat shock-inducible proteins. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):420–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.420-424.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. Inactivation of the FNR protein of Escherichia coli by targeted mutagenesis in the N-terminal region. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):701–707. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch K. L., Lenk J. B., Gamble B. L., Miller C. G. Oxygen regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):673–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.673-680.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):109–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavendale A., Jardine C. K., Old D. C., Duguid J. P. Haemagglutinins and adhesion of Salmonella typhimurium to HEp2 and HeLa cells. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Aug;16(3):371–380. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trageser M., Unden G. Role of cysteine residues and of metal ions in the regulatory functioning of FNR, the transcriptional regulator of anaerobic respiration in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P., Waldvogel F. A. Gentamicin antibacterial activity in the presence of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):743–749. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis T. S., Starkey W. G., Stephen J., Haddon S. J., Osborne M. P., Candy D. C. The nature and role of mucosal damage in relation to Salmonella typhimurium-induced fluid secretion in the rabbit ileum. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Aug;22(1):39–49. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worton K. J., Candy D. C., Wallis T. S., Clarke G. J., Osborne M. P., Haddon S. J., Stephen J. Studies on early association of Salmonella typhimurium with intestinal mucosa in vivo and in vitro: relationship to virulence. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Aug;29(4):283–294. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-4-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]