Abstract
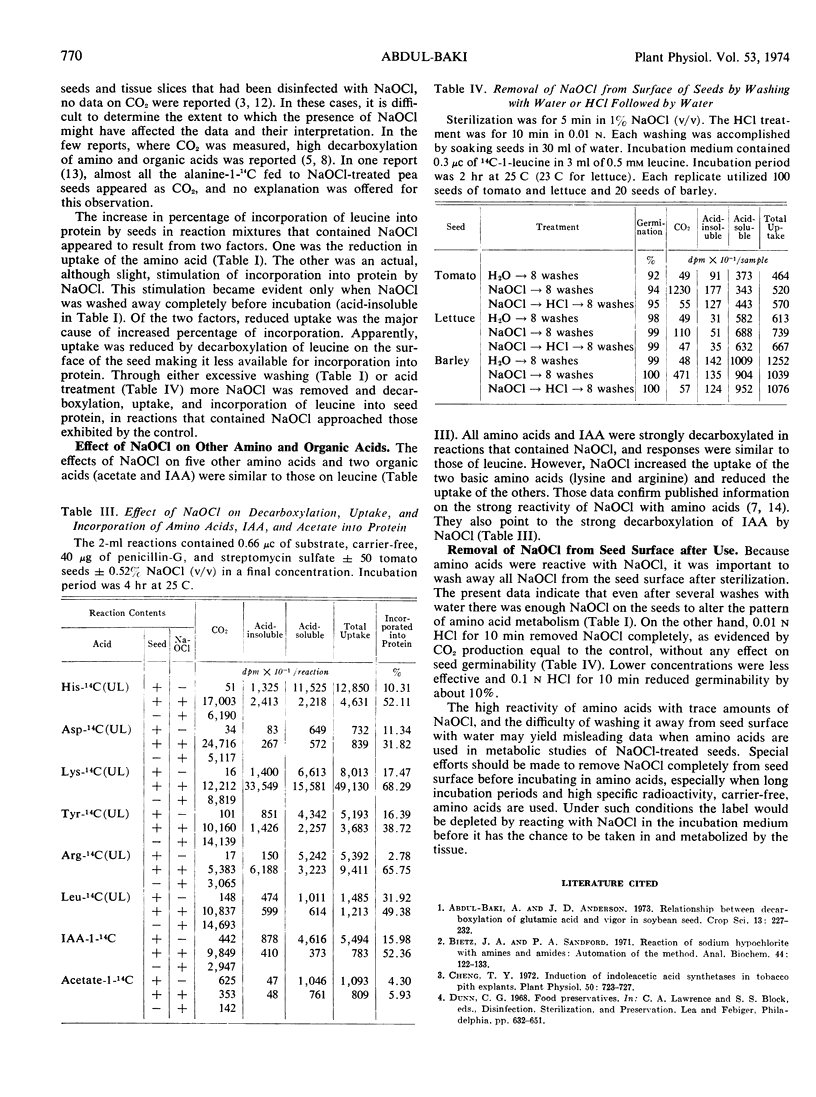
Seeds sterilized with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) retained sufficient amounts to interfere with studies of amino acid metabolism of the sterilized seeds during germination. Repeated washing in water did not remove NaOCl completely. However, soaking the seeds for 10 min in 0.01 n HCl removed NaOCl completely, without reducing germinability.
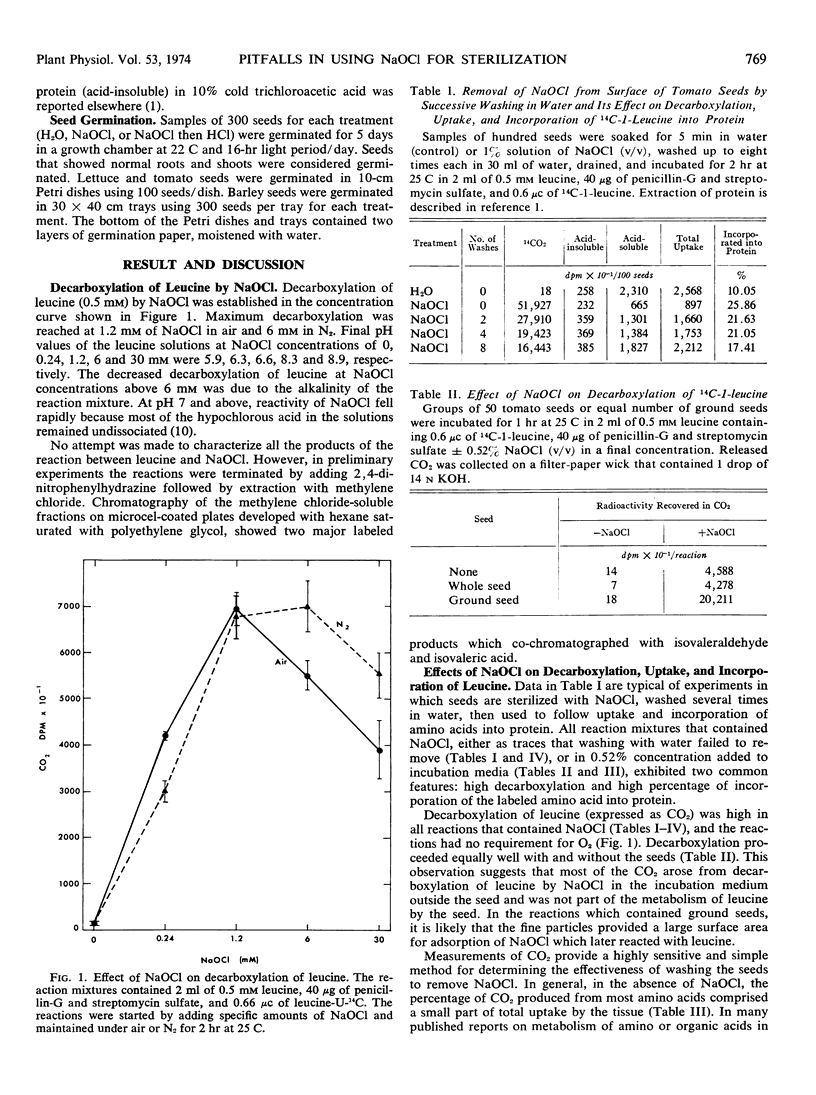
Residual NaOCl reacted with the amino acids and reduced their concentrations in the incubation media. This reaction resulted in high production of CO2 and low uptake of amino acids by the seeds. Decarboxylation of the amino acids occurred in the incubation medium outside the seed, was independent of the presence of seeds in the reaction, and therefore was not related to amino acid metabolism by the seeds. Effects of NaOCl on uptake, incorporation, and CO2 production from indoleacetic acid were similar to those of the amino acids studied.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bietz J. A., Sandford P. A. Reaction of sodium hypochlorite with amines and amides: automation of the method. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):122–133. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90353-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T. Y. Induction of indoleacetic Acid synthetases in tobacco pith explants. Plant Physiol. 1972 Dec;50(6):723–727. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.6.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernest L. C., Valdovinos J. G. Regulation of Auxin Levels in Coleus blumei by Ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1971 Oct;48(4):402–406. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.4.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayatsu H., Pan S., Ukita T. Reaction of sodium hypochlorite with nucleic acids and their constituents. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1971 Oct;19(10):2189–2192. doi: 10.1248/cpb.19.2189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. A., Verbeek R., Waters E. C., van Onckelen H. A. Embryoless Wheat Grain: A Natural System for the Study of Gibberellin-induced Enzyme Formation. Plant Physiol. 1973 Apr;51(4):641–645. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linask J., Laties G. G. Multiphasic absorption of glucose and 3-o-methyl glucose by aged potato slices. Plant Physiol. 1973 Feb;51(2):289–294. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa Y., Asahi T. Biochemical Studies on Development of Mitochondria in Pea Cotyledons during the Early Stage of Germination: Effects of Antibiotics on the Development. Plant Physiol. 1973 May;51(5):833–838. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.5.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa Y., Asahi T. Rapid Development of Mitochondria in Pea Cotyledons during the Early Stage of Germination. Plant Physiol. 1971 Dec;48(6):671–674. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozzolillo C., Paul K. B., Godin C. The Fate of l-Phenylalanine Fed to Germinating Pea Seeds, Pisum sativum (L.) var. Alaska, during Imbibition. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jan;47(1):119–123. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C., Murray M. G. Development of Pyrimidine-metabolizing Enzymes in Cotyledons of Germinating Peas. Plant Physiol. 1971 Nov;48(5):626–630. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.5.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandford P. A., Nafziger A. J., Jeanes A. Reaction of sodium hypochlorite with amines and amides. A new method for quantitating polysaccharides containing hexosamines. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90352-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandford P. A., Nafziger A. J., Jeanes A. Reaction of sodium hypochlorite with amines and amides: a new method for quantitating amino sugars in monomeric form. Anal Biochem. 1971 Aug;42(2):422–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


