Abstract
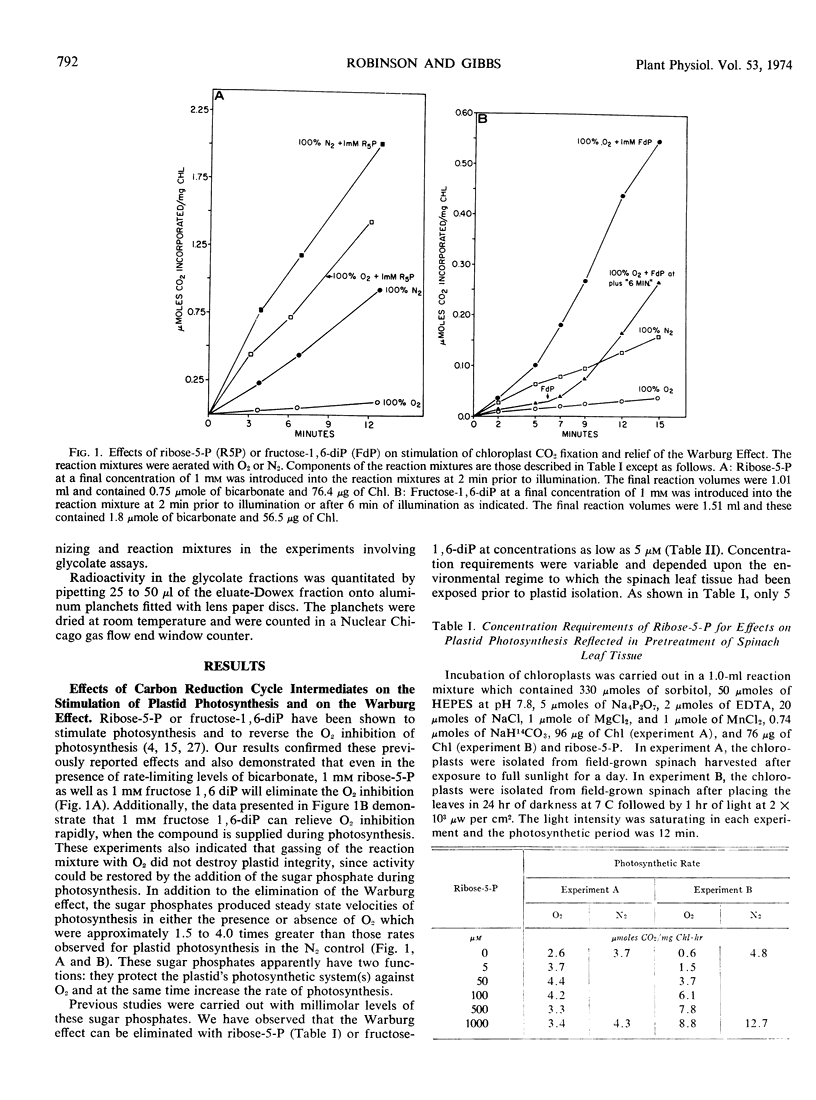
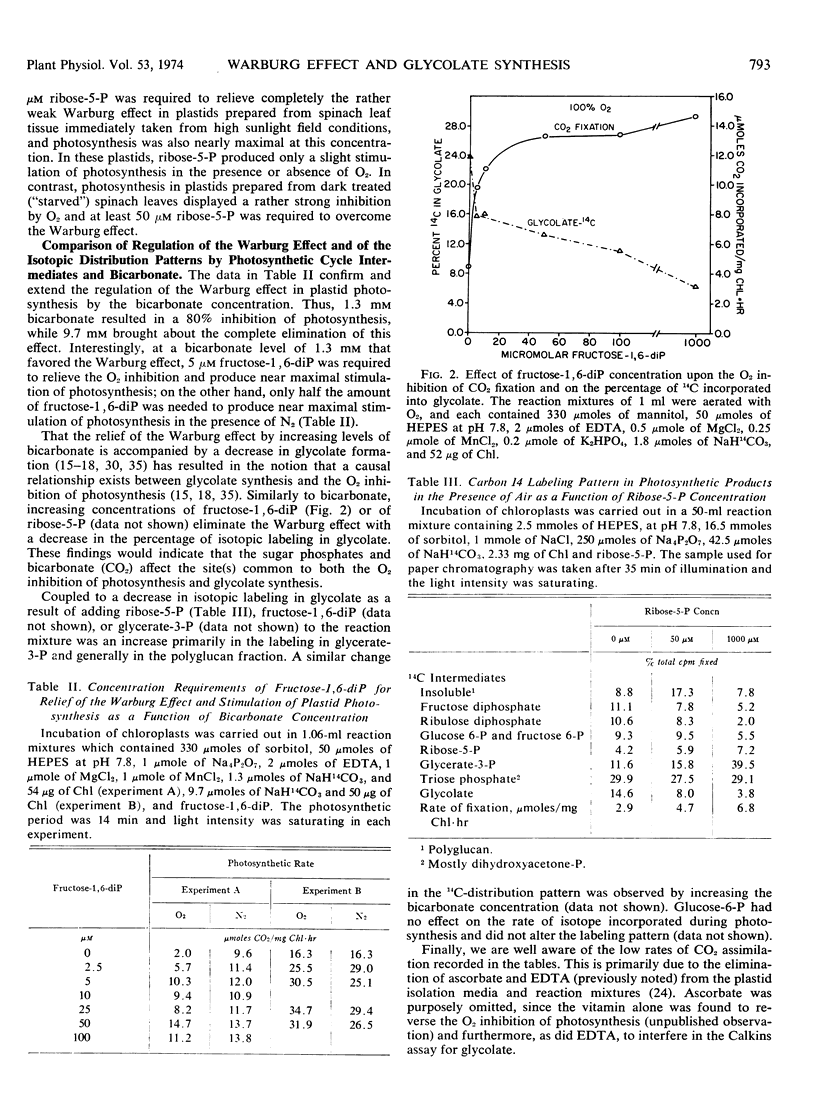
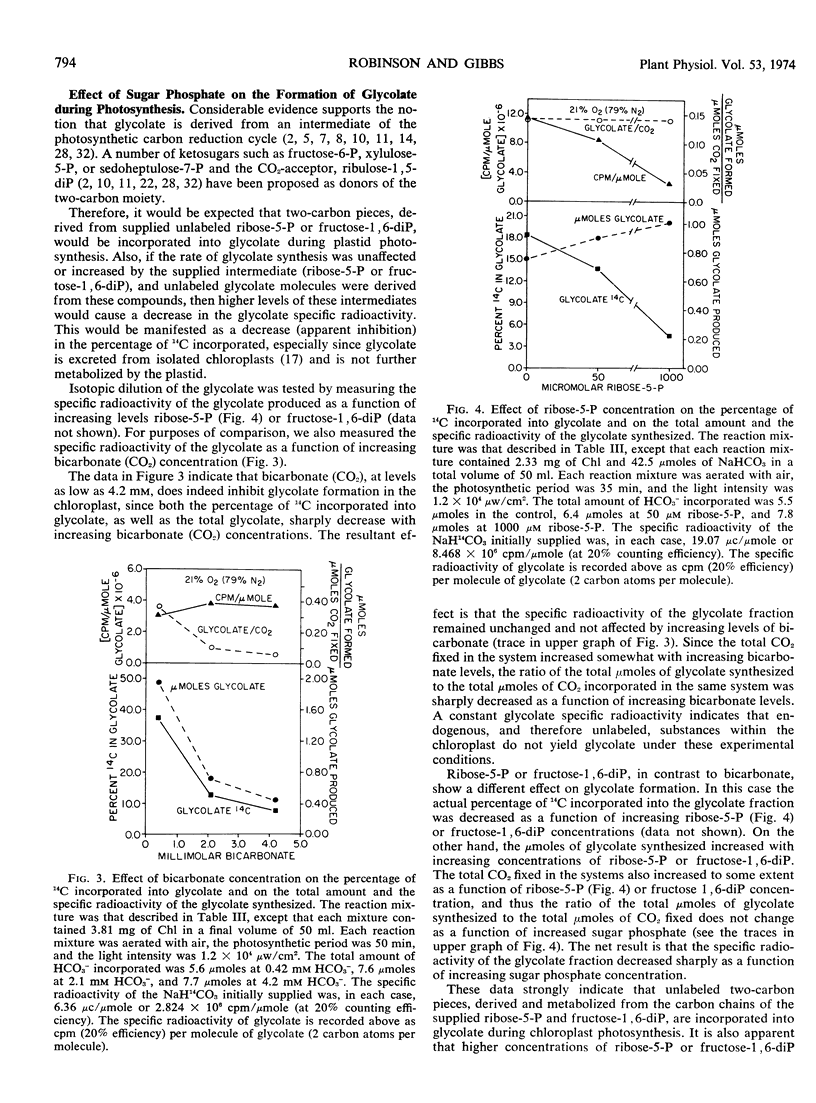
Increasing levels of CO2 have been shown to stimulate the rate of photosynthesis, eliminate the oxygen inhibition of photosynthesis (Warburg effect), and decrease glycolate formation in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Ribose 5-phosphate and fructose 1,6-diphosphate at concentrations of 5 to 10 μm also stimulate the rate of plastid photosynthesis and eliminate the Warburg effect. In contrast to the effect of high CO2 levels, these sugar phosphates have little effect on glycolate formation. Evidence is presented to show that the level of intermediates of the photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle may influence the Warburg effect in vivo. It is postulated that the formation of glycolate is not the causal factor of the Warburg effect.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews T. J., Lorimer G. H., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. I. Synthesis of phosphoglycolate by fraction-1 protein of leaves. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):11–18. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BASSHAM J. A., KIRK M. The effect of oxygen on the reduction of CO2 to glycolic acid and other products during photosynthesis by Chlorella. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Nov 27;9:376–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldry C. W., Walker D. A., Bucke C. Calvin-cycle intermediates in relation to induction phenomena in photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation by isolated chloroplasts. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):642–646. doi: 10.1042/bj1010642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberger E. S., Gibbs M. Effect of Phosphorylated Compounds and Inhibitors on CO(2) Fixation by Intact Spinach Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):919–926. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassham J. A., Kirk M. Sequence of Formation of Phosphoglycolate and Glycolate in Photosynthesizing Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Plant Physiol. 1973 Nov;52(5):407–411. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.5.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes G., Ogren W. L., Hageman R. H. Phosphoglycolate production catalyzed by ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):716–722. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90475-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes G., Ogren W. L. Oxygen inhibition and other properties of soybean ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2171–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucke C., Walker D. A., Baldry C. W. Some effects of sugars and sugar phosphates on carbon dioxide fixation by isolated chloroplasts. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):636–641. doi: 10.1042/bj1010636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellyard P. W., Gibbs M. Inhibition of photosynthesis by oxygen in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1969 Aug;44(8):1115–1121. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.8.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. G., Bassham J. A. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latzko E., von Garnier R., Gibbs M. Effect of photosynthesis, photosynthetic inhibitors and oxygen on the activity of ribulose 5-phosphate kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970;39(6):1140–1144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90678-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Andrews T. J., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. II. Further proof of reaction products and mechanism of action. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):18–23. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson C. O., Myers J. Photosynthetic Production of Hydrogen Peroxide by Anacystis nidulans. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):104–109. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut Z., Gibbs M. Glycolate formation in intact spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1970 Apr;45(4):470–474. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.4.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. E., TOLBERT N. E. Phosphoglycolic acid phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1285–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacter B., Eley J. H., Gibbs M. Involvement of Photosynthetic Carbon Reduction Cycle Intermediates in CO(2) Fixation and O(2) Evolution by Isolated Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1971 Dec;48(6):707–711. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.6.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shain Y., Gibbs M. Formation of glycolate by a reconstituted spinach chloroplast preparation. Plant Physiol. 1971 Sep;48(3):325–330. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER J. S., BRITTAIN E. G. Oxygen as a factor in photosynthesis. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1962 Feb;37:130–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1962.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELITCH I. The role of glycolic acid oxidase in the respiration of leaves. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1299–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelitch I., Walker D. A. The Role of Glycolic Acid Metabolism in Opening of Leaf Stomata. Plant Physiol. 1964 Sep;39(5):856–862. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.5.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


