Abstract
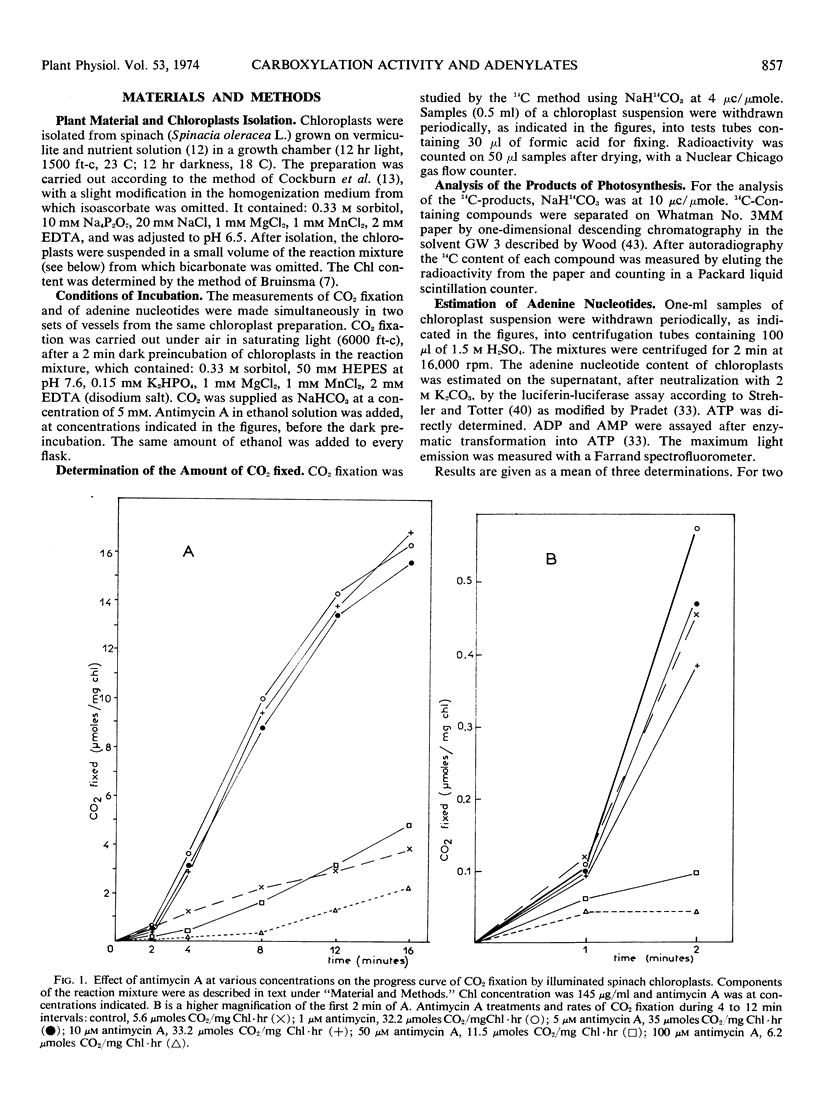
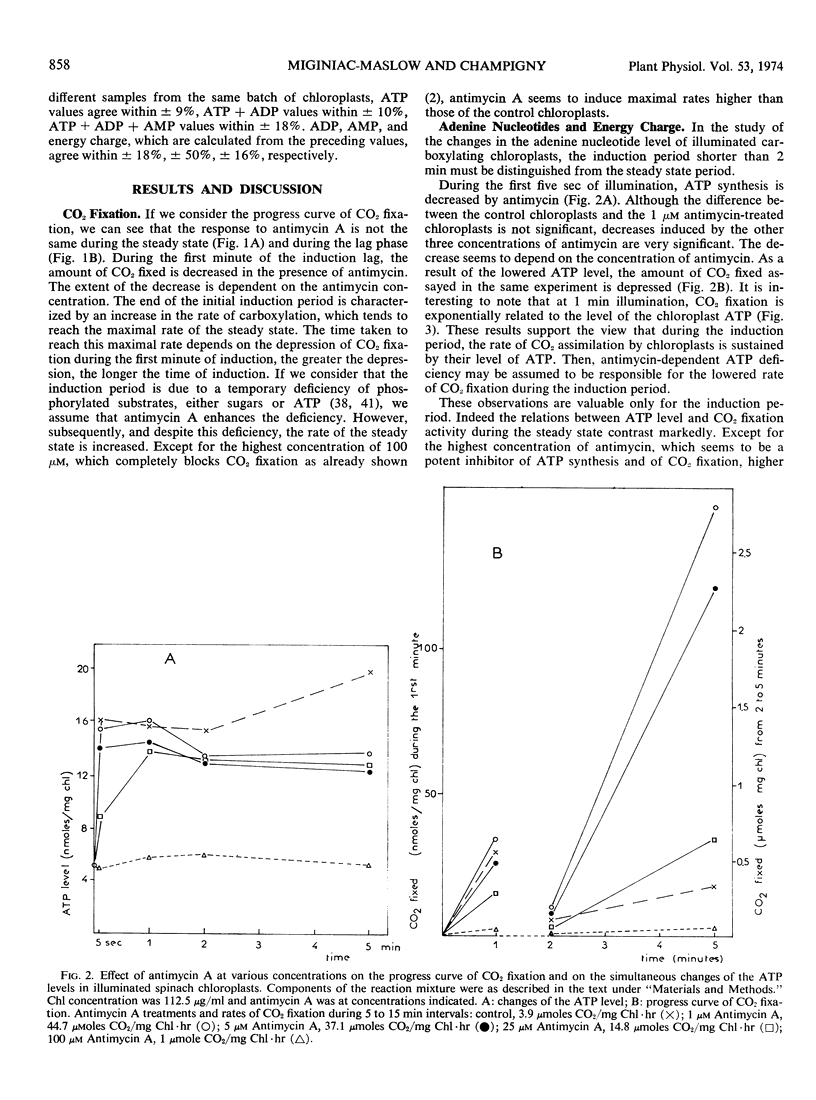
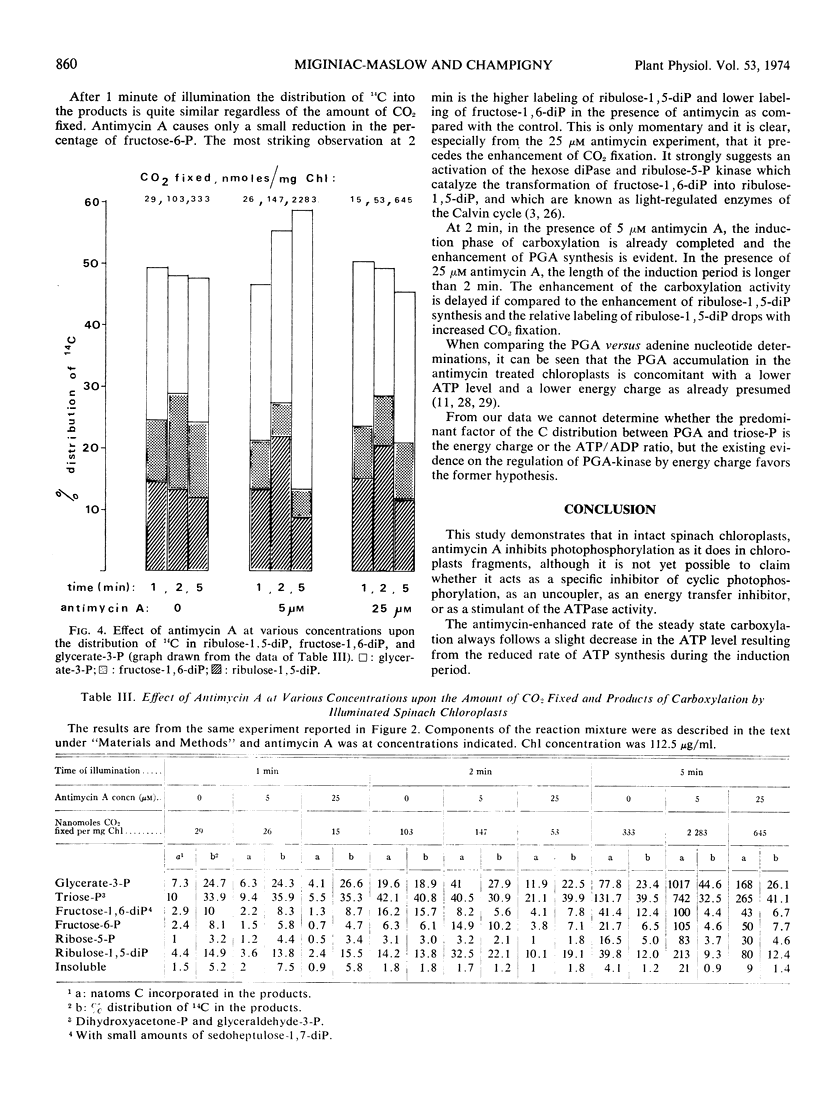
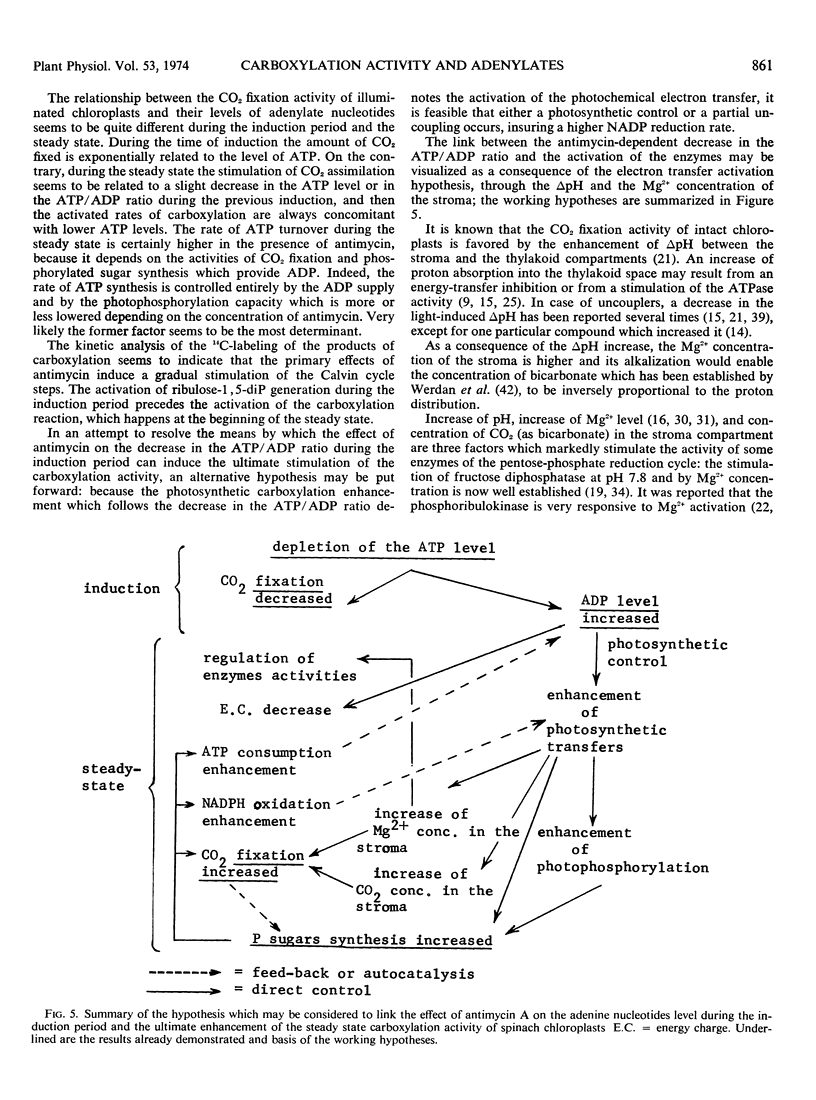
The changes in the levels of intact spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) chloroplast adenine nucleotides during the time course of light-dependent CO2 fixation were determined with respect to the effect of antimycin A. This study demonstrated that antimycin A lowered the rate of ATP formation during the induction period of carboxylation. While the steady state levels of ATP and the energy-charge value also decreased in the presence of antimycin, the concomitant increase of the CO2 fixation activities insured higher ATP turnover rates. Changes in the labeling of CO2 fixation products during the lag phase suggested a stepwise activation of the Calvin cycle, with fructose 1,6-diphosphate, and ribulose 5-phosphate kinase being activated before ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. The possible mechanisms of the enhancement of CO2 fixation activity by antimycin A in relation to its action on photophosphorylation during the lag phase are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson D. E., Fall L. Adenosine triphosphate conservation in biosynthetic regulation. Escherichia coli phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3241–3242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberger E. S., Black C. C., Fewson C. A., Gibbs M. Inhibitor Studies on Carbon Dioxide Fixation, Adenosine Triphosphate Formation, & Triphosphopyridine Nucleotide Reduction by Spinach Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1963 Jul;38(4):483–487. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.4.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassham J. A., Sharp P., Morris I. The effect of Mg2+ concentration on the pH optimum and Michaelis constants of the spinach chloroplast ribulosediphosphate carboxylase (carboxydismutase). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 28;153(4):898–900. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassham J. A. The control of photosynthetic carbon metabolism. Science. 1971 May 7;172(3983):526–534. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3983.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsel J. L., Pradet A. Study of adenosine 5'-mono-,di- and triphosphates in plant tissues. IV. Regulation of the level of nucleotides, in vivo, by adenylate kinase: theoretical and experimental study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 20;162(2):230–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Schürmann P. A regulatory mechanism for CO 2 assimilation in plant photosynthesis: activation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by fructose 6-phosphate and deactivation by fructose 1,6-diphosphate. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 15;23(2):157–159. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeli C. Proton translocation induced by ATPase activity in chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 16;7(3):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champigny M. L., Miginiac-Maslow M. Relations entre l'assimilation photosynthétique de CO 2 et la photophosphorylation des chloroplastes isolés. I. Stimulation de la fixation de CO 2 par l'antimycine A, antagoniste de son inhibition par le phosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 15;234(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn W., Walker D. A., Baldry C. W. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Reversal of orthophosphate inhibition by Calvin-cycle intermediates. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(1):89–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1070089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilley R. A. The effect of various energy-conversion states of chloroplasts on proton and electron transport. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Mar;137(1):270–283. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilley R. A., Vernon L. P. Ion and water transport processes related to the light-dependent shrinkage of spinach chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Aug;111(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drechsler Z., Nelson N., Neumann J. Antimycin A as an uncoupler and electron transport inhibitor in photoreactions of chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Sep 16;189(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ J., WEISSBACH A., HORECKER B. L., SMYRNIOTIS P. Z. Spinach phosphoribulokinase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):769–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt W. H., Werdan K., Milovancev M., Geller G. Alkalization of the chloroplast stroma caused by light-dependent proton flux into the thylakoid space. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 31;314(2):224–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izawa S., Connolly T. N., Winget G. D., Good N. E. Inhibition and uncoupling of photophosphorylation in chloroplasts. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1966;19:169–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. G. Activation of CO 2 fixation in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 15;234(3):360–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90203-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Avron M. Energy transfer inhibition and ion movements in isolated chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1971 May 11;20(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latzko E., von Garnier R., Gibbs M. Effect of photosynthesis, photosynthetic inhibitors and oxygen on the activity of ribulose 5-phosphate kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970;39(6):1140–1144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90678-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miginiac-Maslow M., Champigny M. L. Relations entre l'assimilation photosynthétique du CO 2 et la photophosphorylation des chloroplastes isolès. II. L'utilisation de l'ATP dans l'assimilation photosynthétique du CO 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 15;234(3):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miginiac-Maslow M. Etude de la photophosphorylation endogène des chloroplastes isolés d'epinard. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 15;234(3):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobel P. S. Light-induced changes in the ionic content of chloroplasts in Pisum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 14;172(1):134–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacold I., Anderson L. E. Energy charge control of the Calvin cycle enzyme 3-phosphoglyceric acid kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 5;51(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90519-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Biggs M. L., Greenberg E. The effect of magnesium ion concentration on the pH optimum of the spinach leaf alkaline fructose diphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2292–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves S. G., Hall D. O. The stoichiometry (ATP-2e- ratio) of non-cyclic photophosphorylation in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 26;314(1):66–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STREHLER B. L., TOTTER J. R. Firefly luminescence in the study of energy transfer mechanisms. I. Substrate and enzyme determination. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Sep;40(1):28–41. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacter B. Z., Gibbs M., Champigny M. L. Effect of antimycin a on photosynthesis of intact spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1971 Oct;48(4):443–446. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.4.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacter B., Bassham J. A. Antimycin A Stimulation of Rate-limiting Steps of Photosynthesis in Isolated Spinach Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):411–416. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürmann P., Buchanan B. B., Arnon D. I. Role of cyclic photophosphorylation in photosynthetic carbon dioxide assimilation by isolated chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 20;267(1):111–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdan K., Heldt H. W. Accumulation of bicarbonate in intact chloroplasts following a pH gradient. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 14;283(3):430–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


