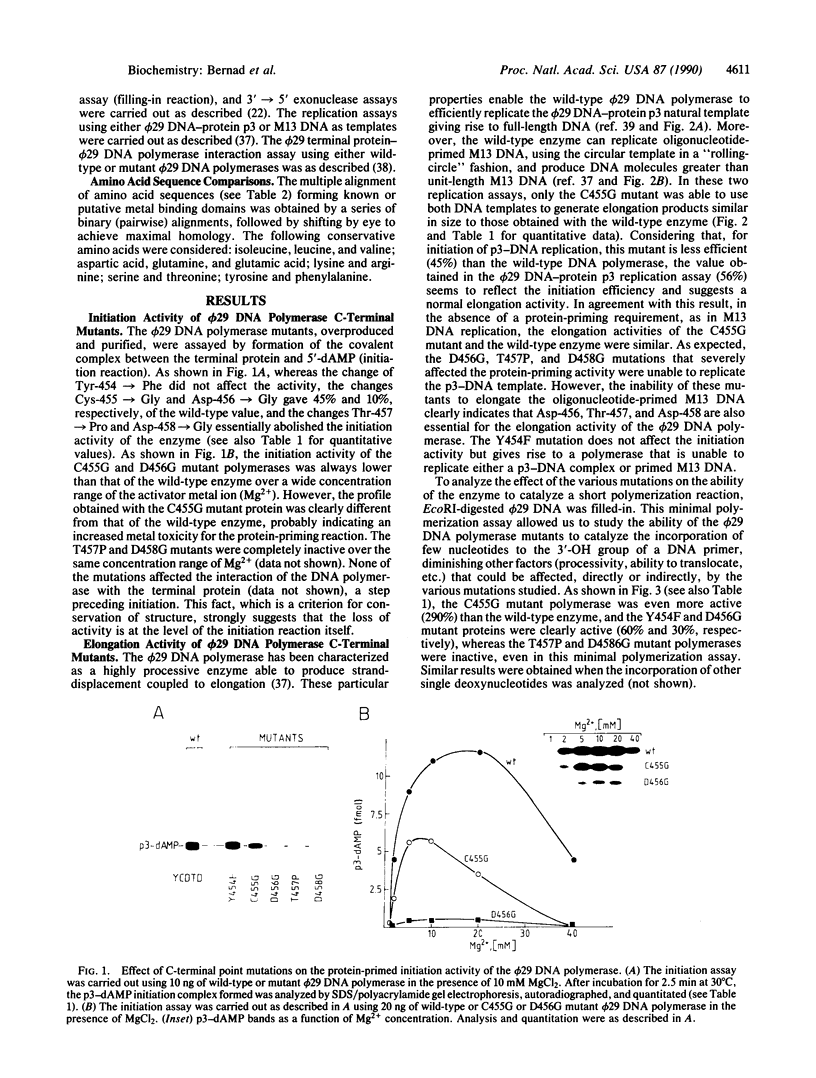
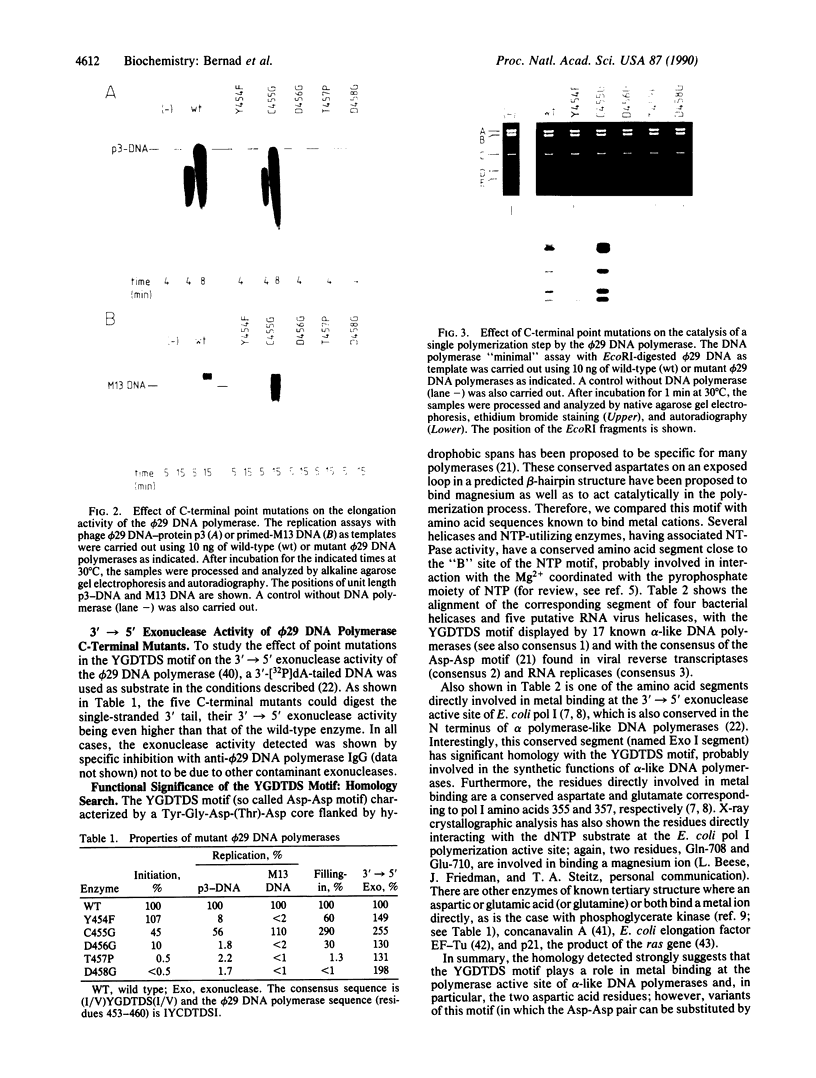
Abstract
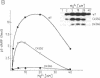
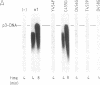
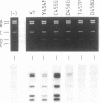
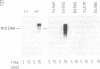
The alpha-like DNA polymerases from bacteriophage phi 29 and other viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes contain an amino acid consensus sequence that has been proposed to form part of the dNTP binding site. We have used site-directed mutants to study five of the six highly conserved consecutive amino acids corresponding to the most conserved C-terminal segment (Tyr-Gly-Asp-Thr-Asp-Ser). Our results indicate that in phi 29 DNA polymerase this consensus sequence, although irrelevant for the 3'----5' exonuclease activity, is essential for initiation and elongation. Based on these results and on its homology with known or putative metal-binding amino acid sequences, we propose that in phi 29 DNA polymerase the Tyr-Gly-Asp-Thr-Asp-Ser consensus motif is part of the dNTP binding site, involved in the synthetic activities of the polymerase (i.e., initiation and polymerization), and that it is involved particularly in the metal binding associated with the dNTP site.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P. A sequence motif in many polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9909–9916. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P. Analysis of sequence-similar pentapeptides in unrelated protein tertiary structures. Strategies for protein folding and a guide for site-directed mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):331–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernad A., Blanco L., Lázaro J. M., Martín G., Salas M. A conserved 3'----5' exonuclease active site in prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90883-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernad A., Zaballos A., Salas M., Blanco L. Structural and functional relationships between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4219–4225. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns M. M., Stenzler L., Tomley F. M., Campbell J., Boursnell M. E. Identification by a random sequencing strategy of the fowlpoxvirus DNA polymerase gene, its nucleotide sequence and comparison with other viral DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6563–6573. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco L., Bernad A., Lázaro J. M., Martín G., Garmendia C., Salas M. Highly efficient DNA synthesis by the phage phi 29 DNA polymerase. Symmetrical mode of DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8935–8940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco L., Prieto I., Gutiérrez J., Bernad A., Lázaro J. M., Hermoso J. M., Salas M. Effect of NH4+ ions on phi 29 DNA-protein p3 replication: formation of a complex between the terminal protein and the DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3983–3991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3983-3991.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco L., Salas M. Characterization and purification of a phage phi 29-encoded DNA polymerase required for the initiation of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5325–5329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco L., Salas M. Characterization of a 3'----5' exonuclease activity in the phage phi 29-encoded DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1239–1249. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco L., Salas M. Effect of aphidicolin and nucleotide analogs on the phage phi 29 DNA polymerase. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco L., Salas M. Replication of phage phi 29 DNA with purified terminal protein and DNA polymerase: synthesis of full-length phi 29 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6404–6408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulet A., Simon M., Faye G., Bauer G. A., Burgers P. M. Structure and function of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC2 gene encoding the large subunit of DNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire V., Freemont P. S., Sanderson M. R., Beese L., Friedman J. M., Joyce C. M., Steitz T. A. Genetic and crystallographic studies of the 3',5'-exonucleolytic site of DNA polymerase I. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):199–201. doi: 10.1126/science.2832946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Jones E. V., Moss B. Homology between DNA polymerases of poxviruses, herpesviruses, and adenoviruses: nucleotide sequence of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Friedman J. M., Beese L. S., Sanderson M. R., Steitz T. A. Cocrystal structure of an editing complex of Klenow fragment with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8924–8928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Chiou H. C., Hall J. D., Mount D. W., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Coen D. M. Sequence and mapping analyses of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene predict a C-terminal substrate binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7969–7973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. A novel superfamily of nucleoside triphosphate-binding motif containing proteins which are probably involved in duplex unwinding in DNA and RNA replication and recombination. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81226-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman K. D., Ainsworth C. F. Structure of concanavalin A at 2.4-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4910–4919. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidecker G., Messing J., Gronenborn B. A versatile primer for DNA sequencing in the M13mp2 cloning system. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermoso J. M., Méndez E., Soriano F., Salas M. Location of the serine residue involved in the linkage between the terminal protein and the DNA of phage phi 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7715–7728. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. A new superfamily of replicative proteins. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–23. doi: 10.1038/333022b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A. New views of the biochemistry of eucaryotic DNA replication revealed by aphidicolin, an unusual inhibitor of DNA polymerase alpha. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):647–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inciarte M. R., Viñuela E., Salas M. Transcription in vitro of phi29 DNA and EcoRI fragments by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec;71(1):77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi Y., Hirashima A. Interference with viral infection by defective RNA replicase. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3946–3949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3946-3949.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempken F., Meinhardt F., Esser K. In organello replication and viral affinity of linear, extrachromosomal DNA of the ascomycete Ascobolus immersus. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):523–530. doi: 10.1007/BF00332419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan N. N., Wright G. E., Dudycz L. W., Brown N. C. Butylphenyl dGTP: a selective and potent inhibitor of mammalian DNA polymerase alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3695–3706. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan N. N., Wright G. E., Dudycz L. W., Brown N. C. Elucidation of the mechanism of selective inhibition of mammalian DNA polymerase alpha by 2-butylanilinopurines: development and characterization of 2-(p-n-butylanilino)adenine and its deoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6331–6342. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S. C., Weston K., Tomlinson P., Barrell B. G. Sequence and transcription analysis of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.125-133.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D., Darby G. Related functional domains in virus DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):169–175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Saito T., Kim C. I., Ando T., Hirokawa H. Bacteriophage phi 29 DNA replication in vitro: participation of the terminal protein and the gene 2 product in elongation. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):381–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00436183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Clark B. F., la Cour T. F., Kjeldgaard M., Norskov-Lauritsen L., Nyborg J. A model for the tertiary structure of p21, the product of the ras oncogene. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):78–82. doi: 10.1126/science.3898366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastrana R., Lázaro J. M., Blanco L., García J. A., Méndez E., Salas M. Overproduction and purification of protein P6 of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29: role in the initiation of DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3083–3100. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peñalva M. A., Salas M. Initiation of phage phi 29 DNA replication in vitro: formation of a covalent complex between the terminal protein, p3, and 5'-dAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5522–5526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzagalli A., Valsasnini P., Plevani P., Lucchini G. DNA polymerase I gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence, mapping of a temperature-sensitive mutation, and protein homology with other DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3772–3776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto I., Lázaro J. M., García J. A., Hermoso J. M., Salas M. Purification in a functional form of the terminal protein of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1639–1643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomalski M. D., Wu J. G., Miller L. K. The location, sequence, transcription, and regulation of a baculovirus DNA polymerase gene. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):591–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe K., Leusch M., Ito J. Replication of bacteriophage phi 29 DNA in vitro: the roles of terminal protein and DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5374–5378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. C., Walker N. P., Shaw P. J., Bryant T. N., Wendell P. L., Fothergill L. A., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F. Sequence and structure of yeast phosphoglycerate kinase. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1635–1640. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. W., Wahl A. F., Yuan P. M., Arai N., Pearson B. E., Arai K., Korn D., Hunkapiller M. W., Wang T. S. Human DNA polymerase alpha gene expression is cell proliferation dependent and its primary structure is similar to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic replicative DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):37–47. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Thirup S., Clark B. F. Structural details of the binding of guanosine diphosphate to elongation factor Tu from E. coli as studied by X-ray crystallography. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2385–2388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]