Abstract
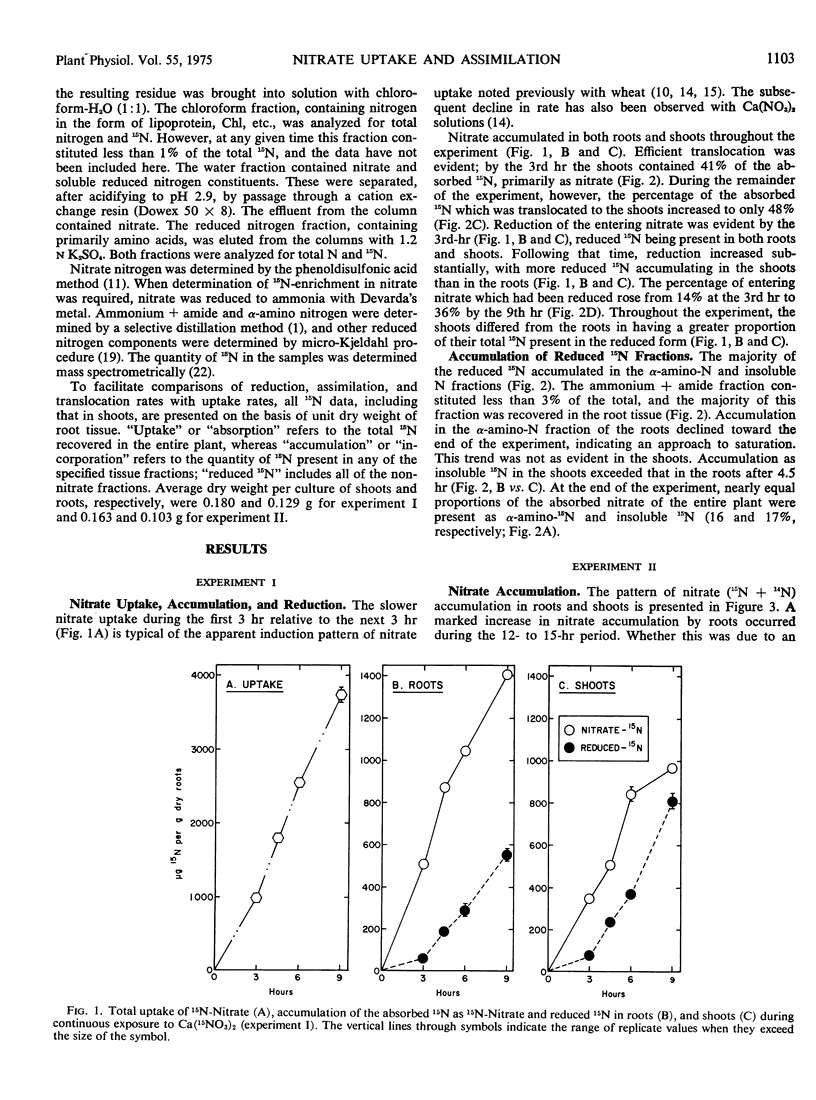
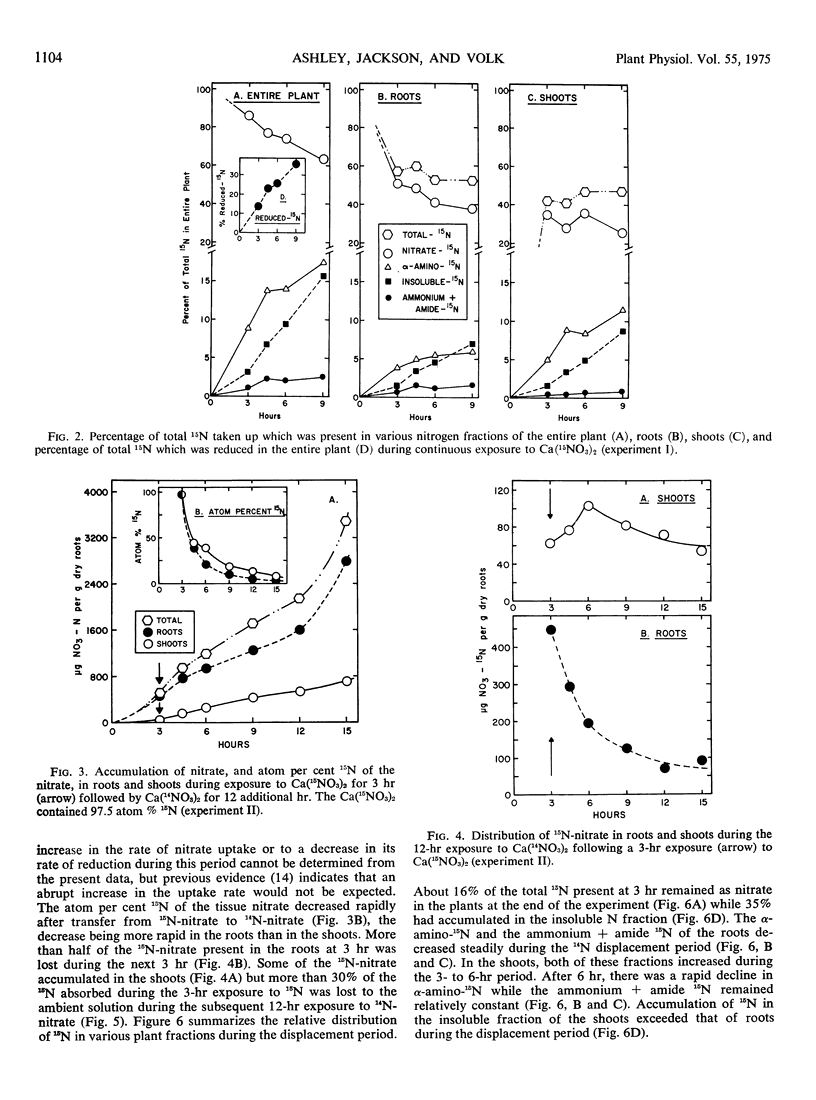
Nitrate uptake, reduction, and translocation were examined in intact, 14-day-old, nitrogen-depleted wheat (Triticum vulgare var. Knox) seedlings during a 9-hour exposure to 0.2 mm Ca (NO3)2. The nitrate uptake rate was low during the initial 3-hour period, increased during the 3- to 6-hour period, and then declined. By the 3rd hour, 14% of the absorbed nitrate had been reduced, and this increased to 36% by the 9th hour. Shoots accumulated reduced 15N more rapidly than roots and the ratio of reduced 15N to 15N-nitrate was higher in the shoots. A significant proportion of the total reduction occurred in the root system under these experimental conditions. Accumulation of 15N in ethanol-insoluble forms was evident in both roots and shoots by the 3rd hour and, after 4.5 hours, increased more rapidly in shoots than in roots.
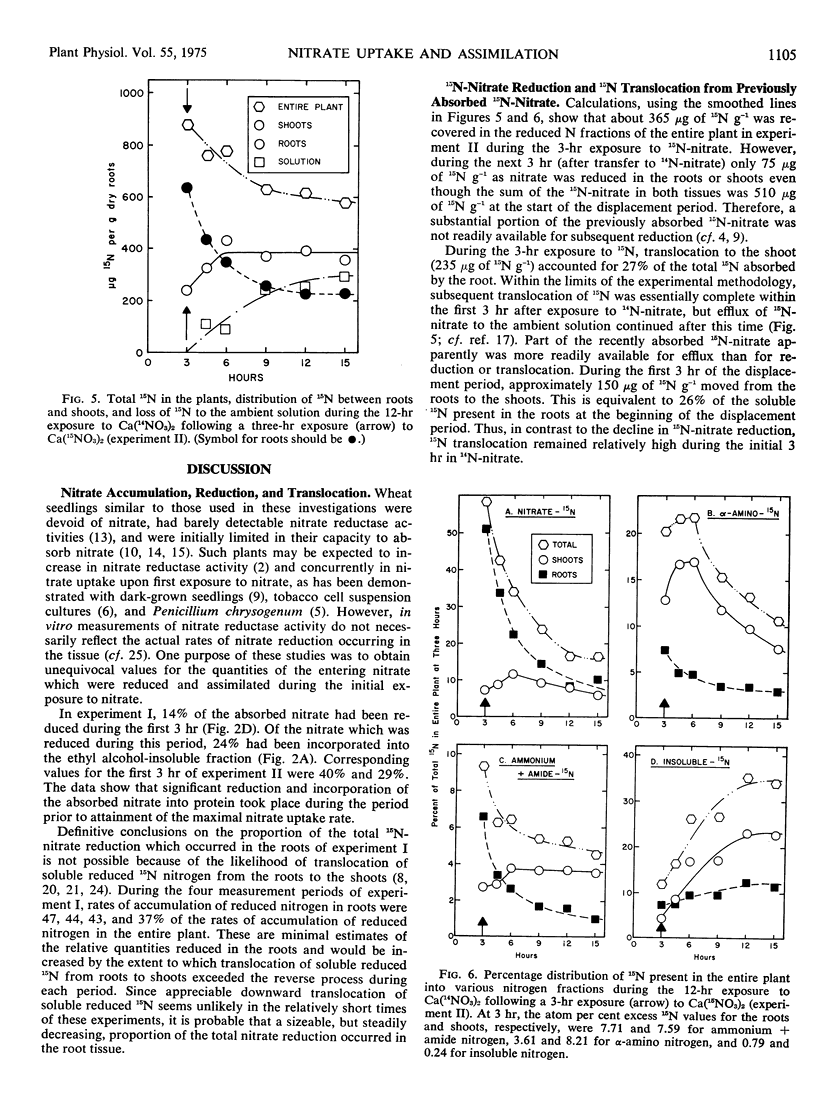
An experiment in which a 3-hour exposure to 0.2 mm Ca (15NO3)2 was followed by a 12-hour exposure to 0.2 mm Ca (14NO3)2 revealed a half-time of depletion of root nitrate of about 2.5 hours. A large proportion of this depletion, however, was due to loss of 15N-nitrate to the ambient 14N-nitrate solution. The remaining pool of 15N-nitrate was only slowly available for reduction. Total 15N translocation to the shoot was relatively efficient during the first 3 hours after transfer to Ca (14NO3)2 but it essentially ceased after that time in spite of significant pools of 15N-nitrate and α-amino-15N remaining in the root tissue.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blevins D. G., Hiatt A. J., Lowe R. H. The Influence of Nitrate and Chloride Uptake on Expressed Sap pH, Organic Acid Synthesis, and Potassium Accumulation in Higher Plants. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jul;54(1):82–87. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari T. E., Yoder O. C., Filner P. Anaerobic nitrite production by plant cells and tissues: evidence for two nitrate pools. Plant Physiol. 1973 Mar;51(3):423–431. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith J., Livoni J. P., Norberg C. L., Segel I. H. Regulation of Nitrate Uptake in Penicillium chrysogenum by Ammonium Ion. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):362–367. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer Y. M., Filner P. Regulation of the nitrate assimilation pathway in cultured tobacco cells. 3. The nitrate uptake system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 23;230(2):362–372. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. A., Flesher D., Hageman R. H. Nitrate Uptake by Dark-grown Corn Seedlings: Some Characteristics of Apparent Induction. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):120–127. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. A., Volk R. J., Jackson W. A. Simultaneous Influx and Efflux of Nitrate during Uptake by Perennial Ryegrass. Plant Physiol. 1973 Feb;51(2):267–272. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks A., Wallace W., Stevens D. Synthesis and turnover of nitrate reductase in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1972 Dec;50(6):649–654. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.6.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace W. The distribution and characteristics of nitrate reductase and glutamate dehydrogenase in the maize seedling. Plant Physiol. 1973 Sep;52(3):191–196. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.3.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder O. C., Scheffer R. P. Effects of Helminthosporium carbonum Toxin on Nitrate Uptake and Reduction by Corn Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1973 Dec;52(6):513–517. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.6.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


