Abstract
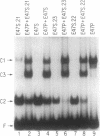
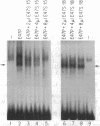
A common DNA binding and dimerization domain containing an apparent "helix-loop-helix" (HLH) structure was recognized recently in a number of regulatory proteins, including the E47 and E12 proteins that bind to the kappa E2 motif in immunoglobulin kappa gene enhancer. The effect of site-directed mutagenesis on E47 protein multimerization and DNA binding was examined. Mutations in either putative helix domain disrupted protein dimerization and DNA binding. No DNA binding was observed when mutations were introduced in the basic region, but these mutants were able to dimerize. These basic region mutants were not able to bind to DNA as heterodimers with the wild-type E47 proteins, demonstrating that two functional basic regions are required for binding to DNA. Therefore the basic region mutants are "transdominant."
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso M. C., Cabrera C. V. The achaete-scute gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster comprises four homologous genes. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2585–2591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Identification of a myocyte nuclear factor that binds to the muscle-specific enhancer of the mouse muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2627–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caudy M., Vässin H., Brand M., Tuma R., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. daughterless, a Drosophila gene essential for both neurogenesis and sex determination, has sequence similarities to myc and the achaete-scute complex. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klämbt C., Knust E., Tietze K., Campos-Ortega J. A. Closely related transcripts encoded by the neurogenic gene complex enhancer of split of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):203–210. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellentin J. D., Smith S. D., Cleary M. L. lyl-1, a novel gene altered by chromosomal translocation in T cell leukemia, codes for a protein with a helix-loop-helix DNA binding motif. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss L. G., Moss J. B., Rutter W. J. Systematic binding analysis of the insulin gene transcription control region: insulin and immunoglobulin enhancers utilize similar transactivators. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2620–2627. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse B., Stoetzel C., Gorostiza-Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F. Sequence of the twist gene and nuclear localization of its protein in endomesodermal cells of early Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2175–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]