Abstract
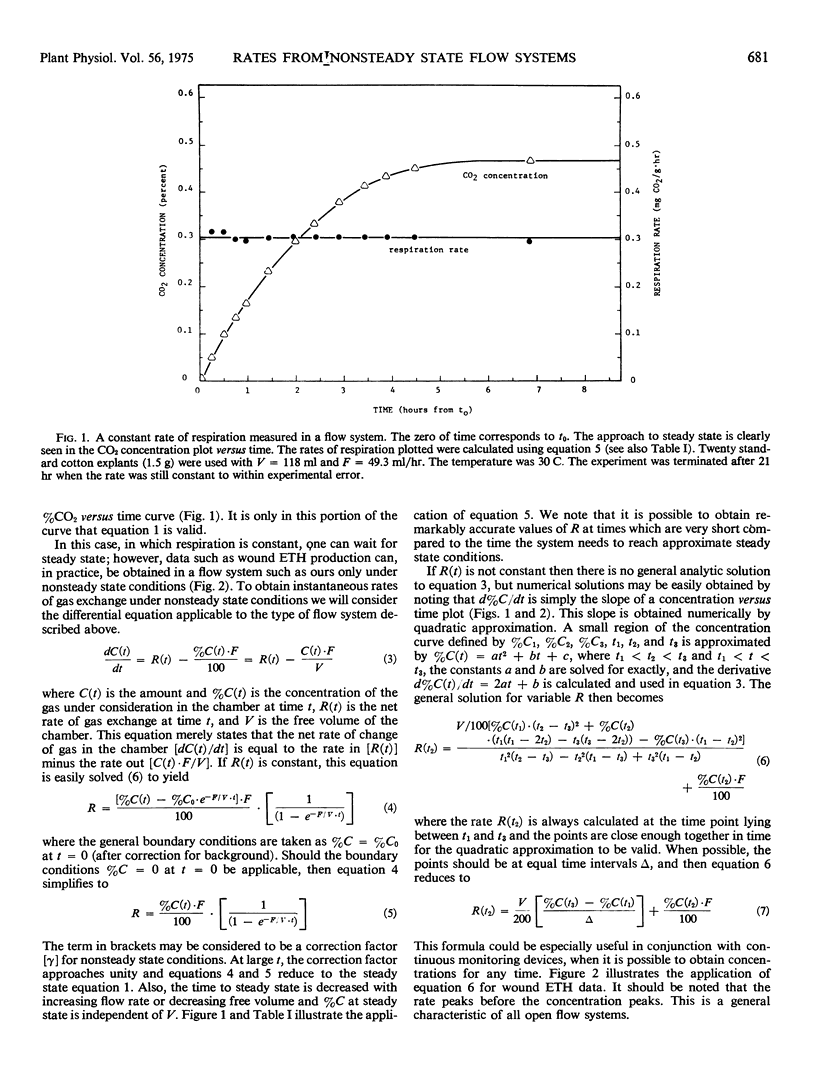
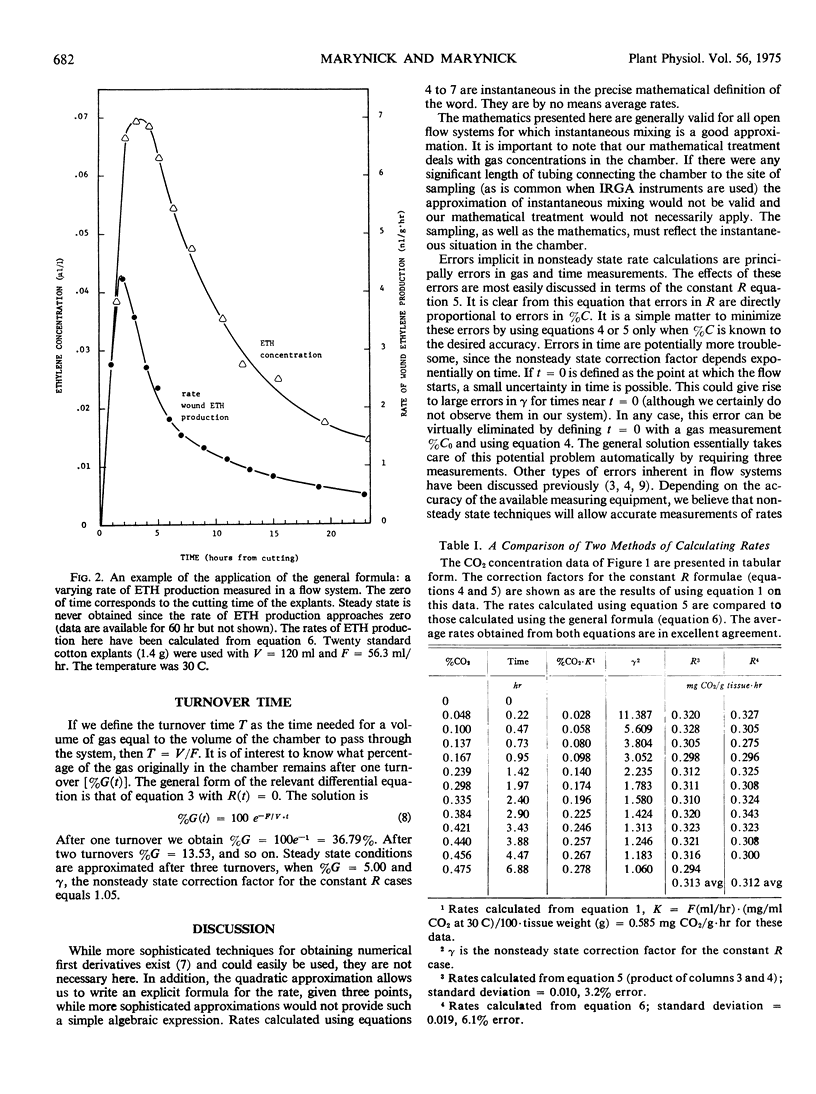
The problem of determining gas exchange rates from flow system data under nonsteady state conditions is analyzed. A correction factor is presented for obtaining constant rates under nonsteady state conditions. A general formula for obtaining any rate under nonsteady state conditions is also given. Turnover time is defined and discussed in terms of the mathematics presented. The origins of nonsteady states and steady states in flow systems are discussed, as are some of the experimental advantages of working under nonsteady state conditions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Young R. E., Biale J. B. Carbon Dioxide Effects on Fruit Respiration. I. Measurement of Oxygen Uptake in Continuous Gas Flow. Plant Physiol. 1962 May;37(3):409–415. doi: 10.1104/pp.37.3.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


