Abstract
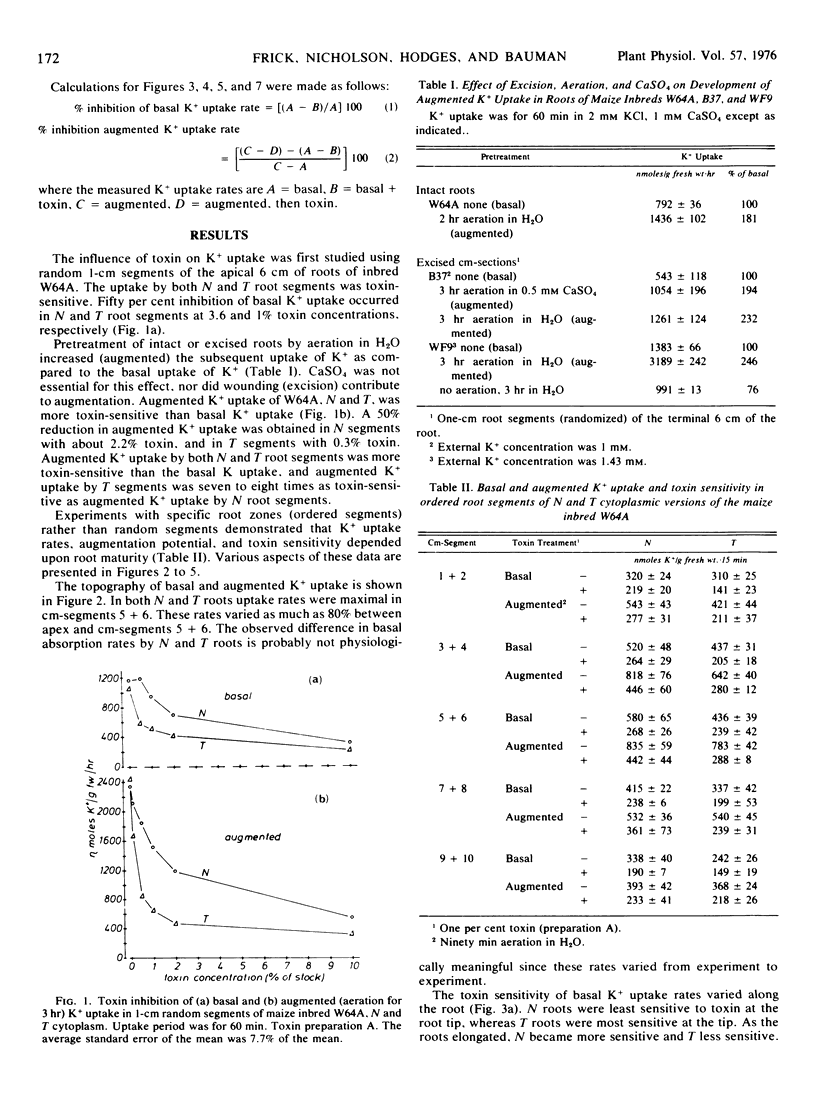
The effect of a toxin extract of Helminthosporium maydis, race T on K+ (86Rb) uptake by excised root segments of normal (N) and Texas cytoplasmic male-sterile (T) versions of corn inbred W64A was investigated. The uptake of K+ was inhibited in both N and T roots by the toxin. This was true for both basal (freshly excised) and augmented (pretreated with aeration) K+ uptake. Augmented uptake was more toxin-sensitive than basal uptake (irrespective of cytoplasm type), and the augmented uptake in T roots was seven to eight times more toxin-sensitive than in N roots.
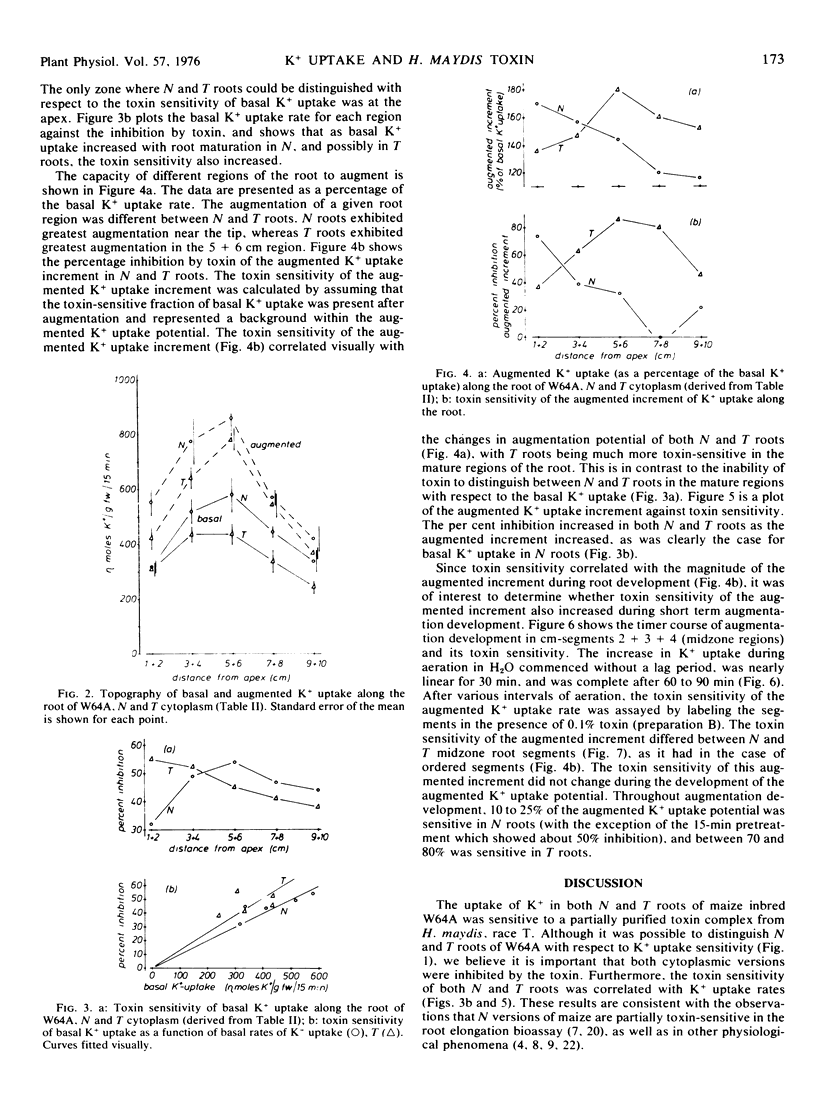
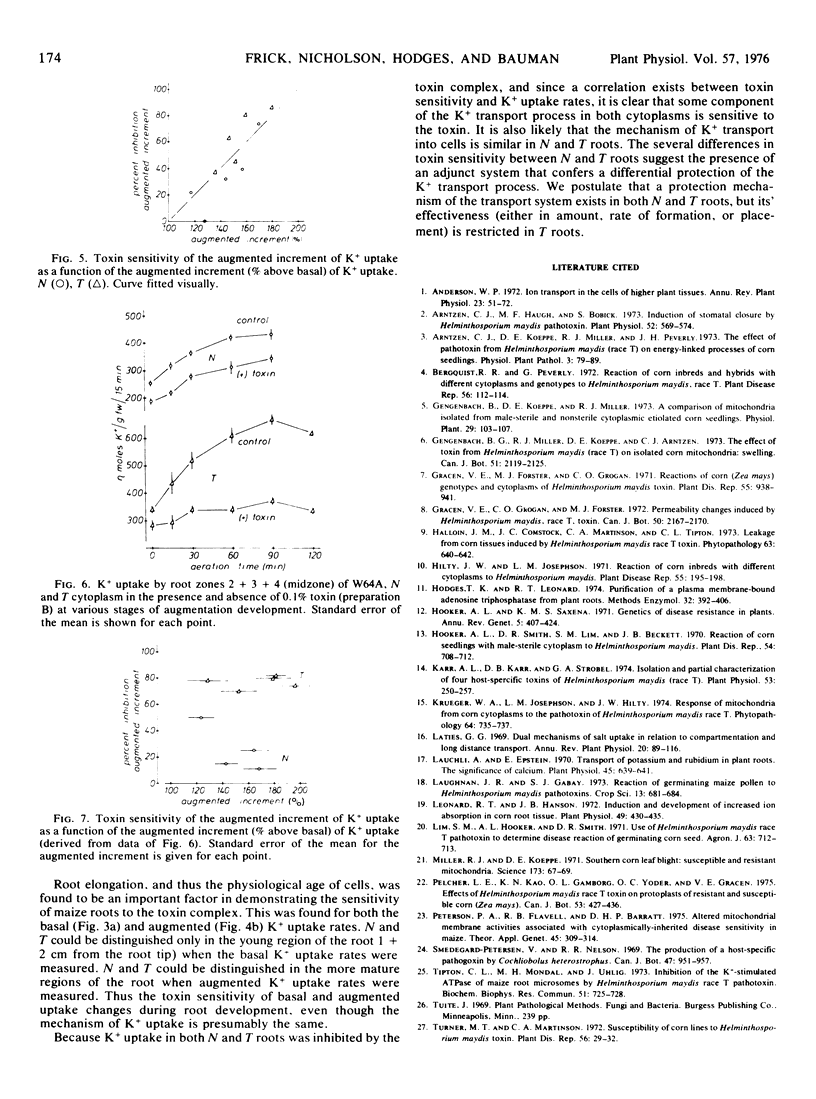
Specific zones of roots differed in their basal and augmented K+ uptake rates as well as their toxin sensitivities. The root apex of T was more sensitive to toxin than the apex of N roots when basal K+ uptake was measured. In mature zones of the root, T was more sensitive than N when augmented rates were measured. During the development of the augmented K+ uptake capacity in either N or T roots, the sensitivity to the toxin did not change; uptake in N roots was inhibited by 10 to 25% and uptake in T roots was inhibited by 70 to 80%.
The difference in toxin sensitivity of K+ uptake between N and T roots may be due to N possessing a protective mechanism which is deficient in T.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arntzen C. J., Haugh M. F., Bobick S. Induction of Stomatal Closure by Helminthosporium maydis Pathotoxin. Plant Physiol. 1973 Dec;52(6):569–574. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.6.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooker A. L., Saxena K. M. Genetics of disease resistance in plants. Annu Rev Genet. 1971;5:407–424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.05.120171.002203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr A. L., Karr D. B., Strobel G. A. Isolation and Partial Characterization of Four Host-specific Toxins of Helminthosporium maydis (Race T). Plant Physiol. 1974 Feb;53(2):250–257. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.2.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hanson J. B. Induction and development of increased ion absorption in corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):430–435. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuchli A., Epstein E. Transport of potassium and rubidium in plant roots: the significance of calcium. Plant Physiol. 1970 May;45(5):639–641. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.5.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Koeppe D. E. Southern corn leaf blight: susceptible and resistant mitochondria. Science. 1971 Jul 2;173(3991):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3991.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipton C. L., Mondal M. H., Uhlig J. Inhibition of the K + -stimulated ATPase of maize root microsomes by Helminthosporium maydis race T pathotoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 2;51(3):725–728. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


