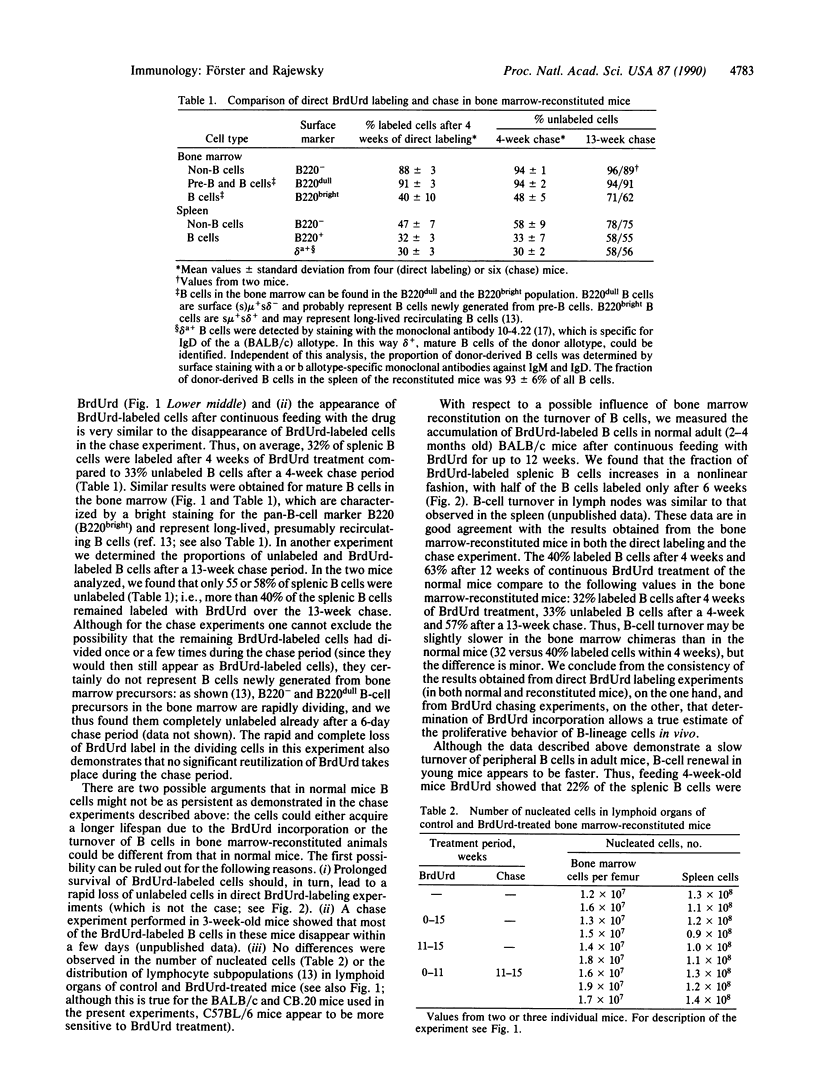
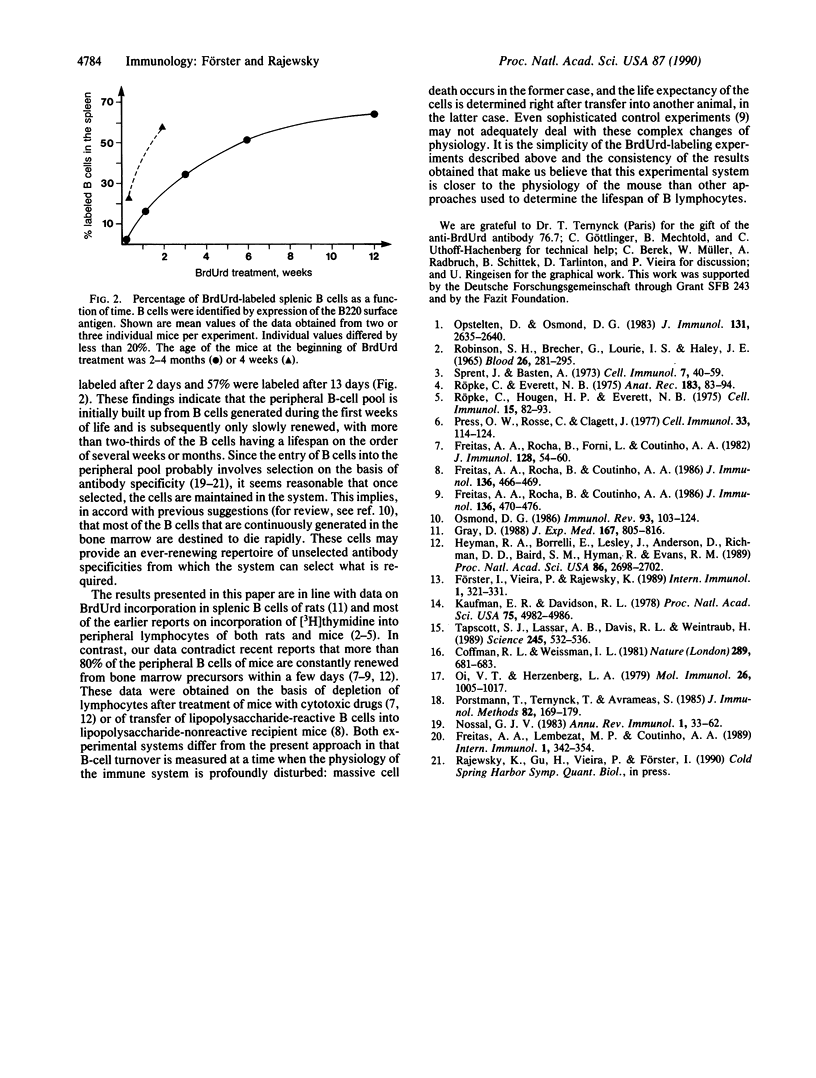
Abstract
We have reevaluated the in vivo lifespan of B lymphocytes based on incorporation of the thymidine analogue 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine into the DNA of dividing cells. To exclude potential alterations in the turnover of B-lineage cells due to the bromodeoxyuridine incorporation, we performed pulse-chase experiments comparing the appearance and disappearance of bromodeoxyuridine-labeled cells over long periods of time. The data consistently show that more than two-thirds of splenic B cells in adult (greater than 2 months old) mice have a lifetime of several weeks or months, whereas a more rapid turnover takes place in young (4 week old) mice. Thus, the peripheral B-cell pool is only slowly renewed after it has been initially built up early in life.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. B220: a B cell-specific member of th T200 glycoprotein family. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):681–683. doi: 10.1038/289681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Lembezat M. P., Coutinho A. Expression of antibody V-regions is genetically and developmentally controlled and modulated by the B lymphocyte environment. Int Immunol. 1989;1(4):342–354. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.4.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Rocha B., Coutinho A. A. Life span of B lymphocytes: the experimental basis for conflicting results. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):470–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Rocha B., Coutinho A. A. Two major classes of mitogen-reactive B lymphocytes defined by life span. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):466–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Rocha B., Forni L., Coutinho A. Population dynamics of B lymphocytes and their precursors: demonstration of high turnover in the central and peripheral lymphoid organs. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):54–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förster I., Vieira P., Rajewsky K. Flow cytometric analysis of cell proliferation dynamics in the B cell compartment of the mouse. Int Immunol. 1989;1(4):321–331. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Borrelli E., Lesley J., Anderson D., Richman D. D., Baird S. M., Hyman R., Evans R. M. Thymidine kinase obliteration: creation of transgenic mice with controlled immune deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2698–2702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman E. R., Davidson R. L. Bromodeoxyuridine mutagenesis in mammalian cells: mutagenesis is independent of the amount of bromouracil in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4982–4986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Herzenberg L. A. Localization of murine Ig-1b and Ig-1a (IgG 2a) allotypic determinants detected with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1979 Dec;16(12):1005–1017. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opstelten D., Osmond D. G. Pre-B cells in mouse bone marrow: immunofluorescence stathmokinetic studies of the proliferation of cytoplasmic mu-chain-bearing cells in normal mice. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2635–2640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmond D. G. Population dynamics of bone marrow B lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1986 Oct;93:103–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porstmann T., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. Quantitation of 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine incorporation into DNA: an enzyme immunoassay for the assessment of the lymphoid cell proliferative response. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Sep 3;82(1):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press O. W., Rosse C., Clagett J. The distribution of rapidly and slowly renewed T, B, and "null" lymphocytes in mouse bone marrow, thymus, lymph nodes, and spleen. Cell Immunol. 1977 Sep;33(1):114–124. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON S. H., BRECHER G., LOURIE I. S., HALEY J. E. LEUKOCYTE LABELING IN RATS DURING AND AFTER CONTINUOUS INFUSION OF TRITIATED THYMIDINE: IMPLICATIONS FOR LYMPHOCYTE LONGEVITY AND DNA REUTILIZATION. Blood. 1965 Sep;26:281–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röpke C., Hougen H. P., Everett N. B. Long-lived T and B lymphocytes in the bone marrow and thoracic duct lymph of the mouse. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jan;15(1):82–93. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J., Basten A. Circulating T and B lymphocytes of the mouse. II. Lifespan. Cell Immunol. 1973 Apr;7(1):40–59. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90181-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Lassar A. B., Davis R. L., Weintraub H. 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine blocks myogenesis by extinguishing expression of MyoD1. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):532–536. doi: 10.1126/science.2547249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



