Abstract
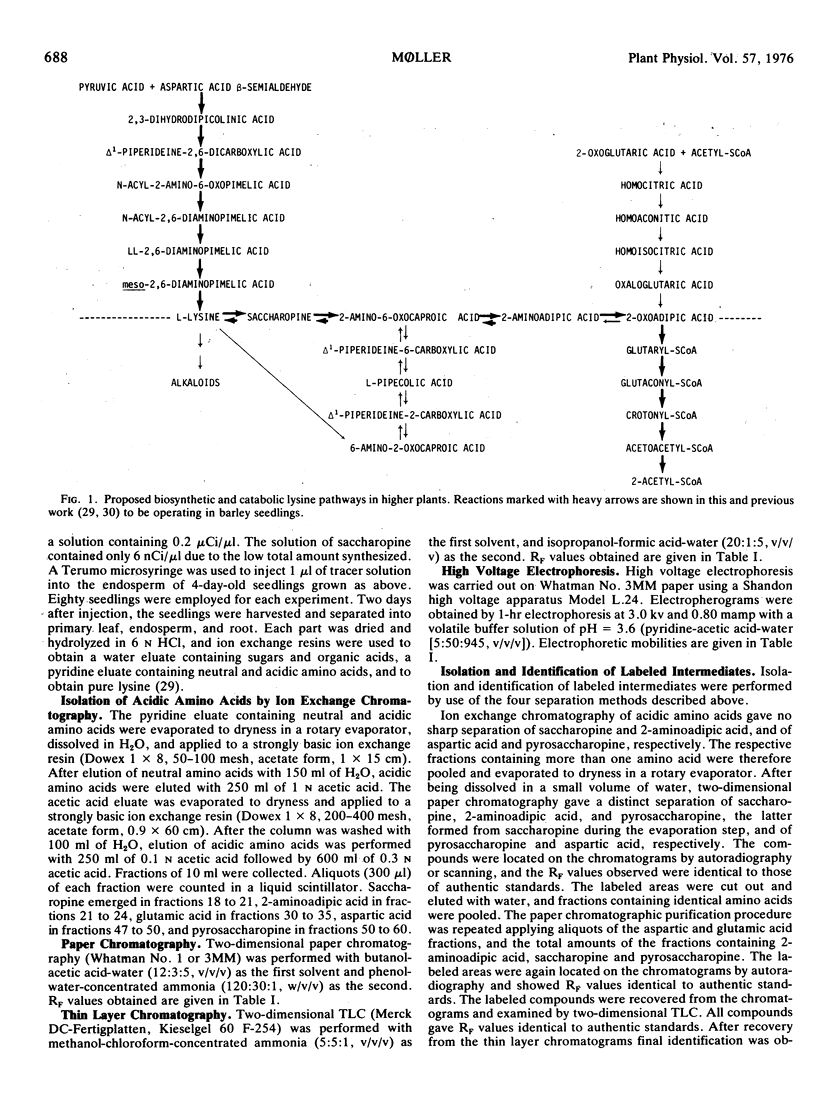
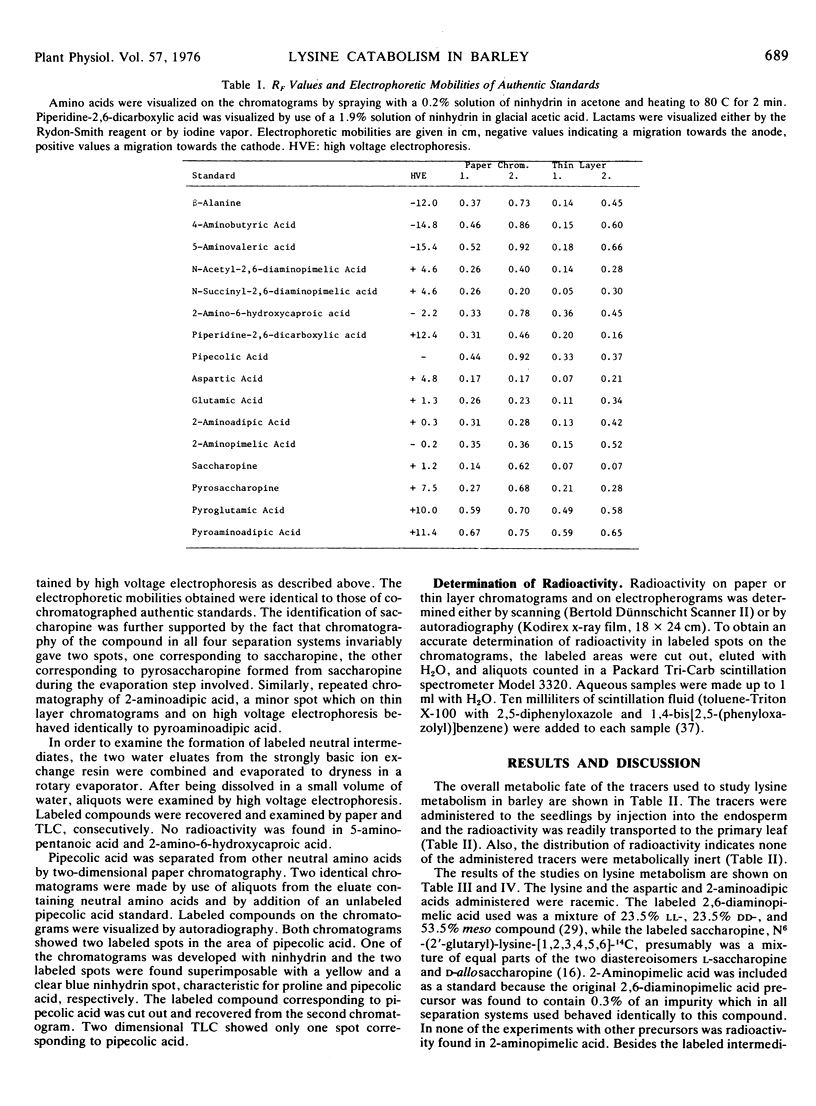
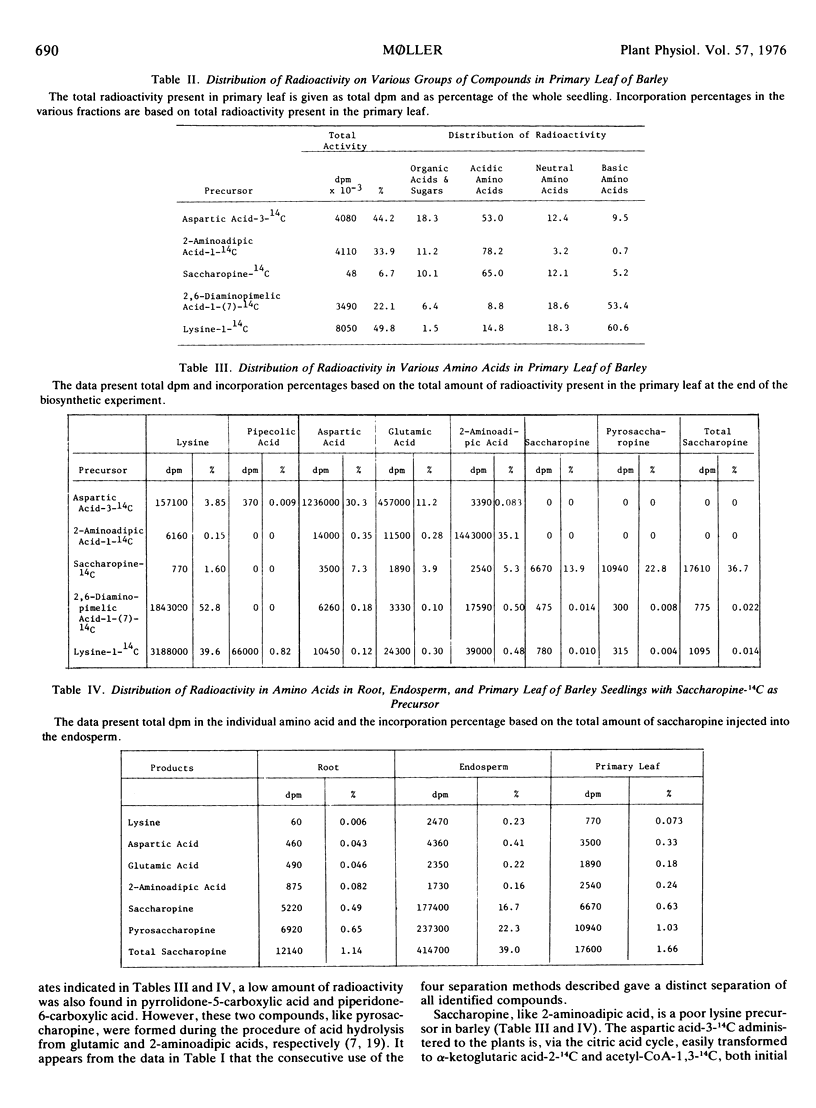
Lysine catabolism in seedlings of barley (Hordeum vulgare L. var. Emir) was studied by direct injection of the following tracers into the endosperm of the seedlings: aspartic acid-3-14C, 2-aminoadipic acid-1-14C, saccharopine-14C, 2,6-diaminopimelic acid-1-(7)-14C, and lysine-1-14C. Labeled saccharopine was formed only after the administration of either labeled 2,6-diaminopimelic acid or labeled lysine to the seedlings. The metabolic fate of the other tracers administered also supported a catabolic lysine pathway via saccharopine, and apparently proceeding by a reversal of some of the biosynthetic steps of the 2-aminoadipic acid pathway known from lysine biosynthesis in most fungi. Pipecolic acid seems not to be on the main pathway of l-lysine catabolism in barley seedlings.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betterton H., Fjellstedt T., Matsuda M., Ogur M., Tate R. Localization of the homocitrate pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):459–461. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellows F. C. Biosynthesis and degradation of saccharopine, an intermediate of lysine metabolism. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;136(2):321–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1360321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellows F. C., Lewis M. H. Lysine metabolism in mammals. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;136(2):329–334. doi: 10.1042/bj1360329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHOLSON R. K., NISHIZUKA Y., ICHIYAMA A., KAWAI H., NAKAMURA S., HAYAISHI O. New intermediates in the catabolism of tryptophan in mammalian liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:2043–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. N., Spenser I. D. Biosynthesis of the piperidine nucleus. The mode of incorporation of lysine into pipecolic acid and into piperidine alkaloids. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayaishi O. Crystalline oxygenases of pseudomonads. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Dec;30(4):720–731. doi: 10.1128/br.30.4.720-731.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashino K., Tsukada K., Lieberman I. Saccharopine, a product of lysine breakdown by mammalian liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 26;20(3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90361-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M., Bhattacharjee J. K. Biosynthesis of lysine in Rhodotorula glutinis: role of pipecolic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):103–110. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWY P. H. The conversion of lysine to pipecolic acid by Phaseolus vulgaris. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Nov;47(1):228–229. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea P. J., Miflin B. J. Alternative route for nitrogen assimilation in higher plants. Nature. 1974 Oct 18;251(5476):614–616. doi: 10.1038/251614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leistner E., Gupta R. N., Spenser I. D. A general method for the determination of precursor configuration in biosynthetic precursor-product relationships. Derivation of pipecolic acid from D-lysine, and of piperidine alkaloids from L-lysine. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Jun 13;95(12):4040–4047. doi: 10.1021/ja00793a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN P. J., SMITHIES W. R. Plant enzyme reactions leading to the formation of heterocyclic compounds. 1. The formation of unsaturated pyrrolidine and piperidine compounds. Biochem J. 1955 Sep;61(1):89–100. doi: 10.1042/bj0610089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEISTER A., RADHAKRISHNAN A. N., BUCKLEY S. D. Enzymatic synthesis of L-pipecolic acid and L-proline. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):789–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miflin B. J. The location of nitrite reductase and other enzymes related to amino Acid biosynthesis in the plastids of root and leaves. Plant Physiol. 1974 Oct;54(4):550–555. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.4.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller B. L. Lysine Biosynthesis in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Physiol. 1974 Oct;54(4):638–643. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.4.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. U., Leistner E. Conversion of D-lysine via L-pepecolic acid in Neurospora crassa. Z Naturforsch C. 1975 Mar-Apr;30(2):253–262. doi: 10.1515/znc-1975-3-419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS E. Studies of transamination. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Feb;48(2):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda H., Hayaishi O. Crystalline L-lysine oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 10;241(11):2733–2736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. C. Triton X-100 scintillant for carbon-14 labelled materials. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1968 Jul;19(7):557–563. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(68)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


