Abstract
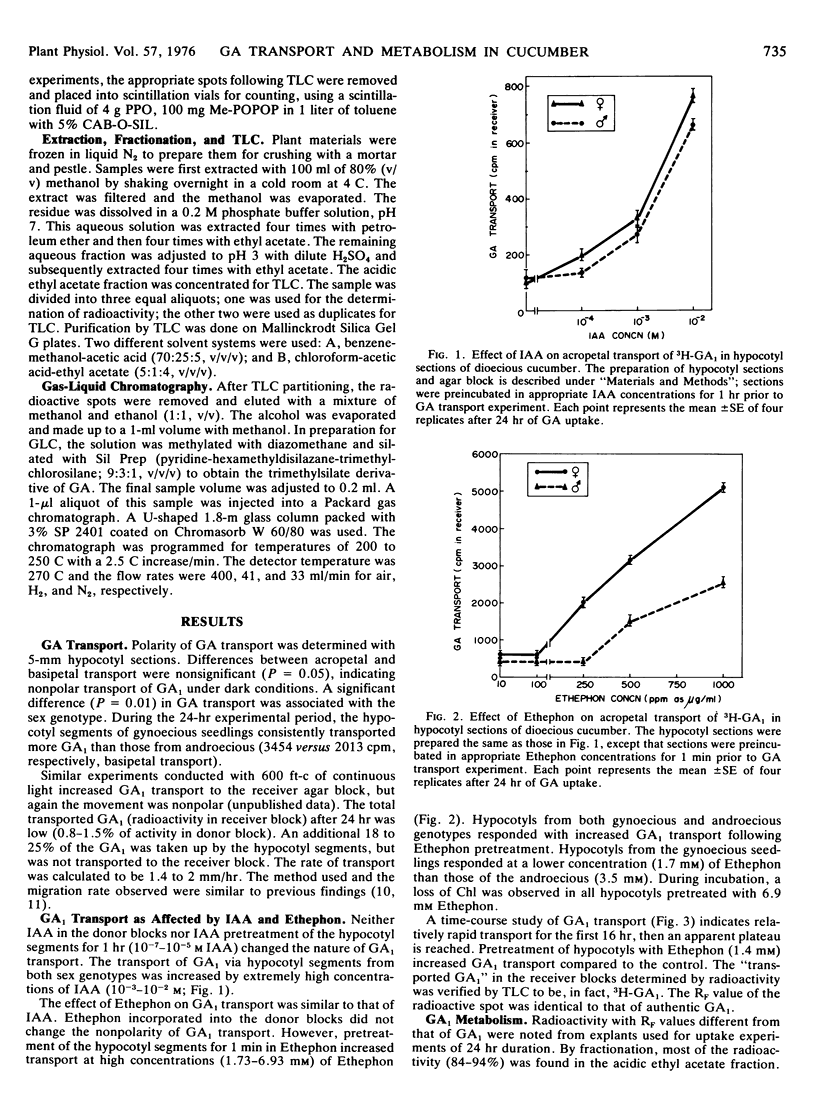
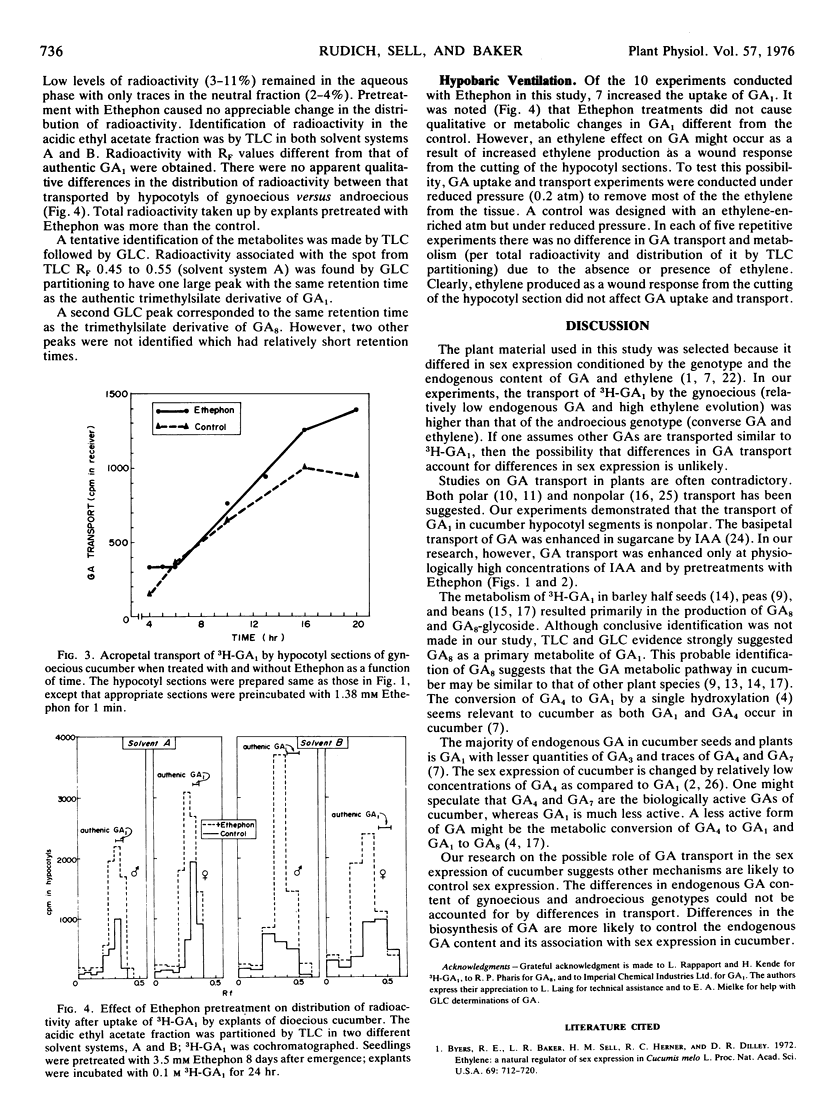
The transport of 3H-GA1 through hypocotyl segments of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) was found to be nonpolar. The transport of 3H-GA1 was increased by pretreatment with relatively high concentrations of either IAA or Ethephon (2-chloroethylphosphonic acid). Hypocotyl segments from plants of a gynoecious genotype transported more 3H-GA1 than those of an androecious. The metabolism of 3H-GA1 in hypocotyl segments was neither related to the sex genotype of the cucumber plant nor influenced by pretreatment with Ethephon. The primary metabolite of GA1 was suggested to be GA8. Two other suspected metabolites were not identified. Differences in the endogenous GA of gynoecious and androecious plants could not be accounted for by transport differences.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byers R. E., Baker L. R., Sell H. M., Herner R. C., Dilley D. R. Ethylene: A Natural Regulator of Sex Expression of Cucumis melo L. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):717–720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galun E., Izhar S., Atsmon D. Determination of Relative Auxin Content in Hermaphrodite and Andromonoecious Cucumis sativus L. Plant Physiol. 1965 Mar;40(2):321–326. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill D. D., Jr, Baker L. R., Sell H. M. Isolation of novel conjugated gibberellins from Cucumis sativus seed. Can J Biochem. 1973 Dec;51(12):1647–1653. doi: 10.1139/o73-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kende H. Preparation of radioactive gibberellin a(1) and its metabolism in dwarf peas. Plant Physiol. 1967 Nov;42(11):1612–1618. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.11.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve D. R., Crozier A. Metabolism of H-Gibberellin A(1) and H-Gibberellin A(4) by Phaseolus coccineus Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jan;55(1):42–44. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudich J., Halevy A. H., Kedar N. Ethylene evolution from cucumber plants as related to sex expression. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jun;49(6):998–999. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.6.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudich J., Halevy A. H., Kedar N. The level of phytohormones in monoecious and gynoecious cucumbers as affected by photoperiod and ethephon. Plant Physiol. 1972 Nov;50(5):585–590. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.5.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


