Abstract
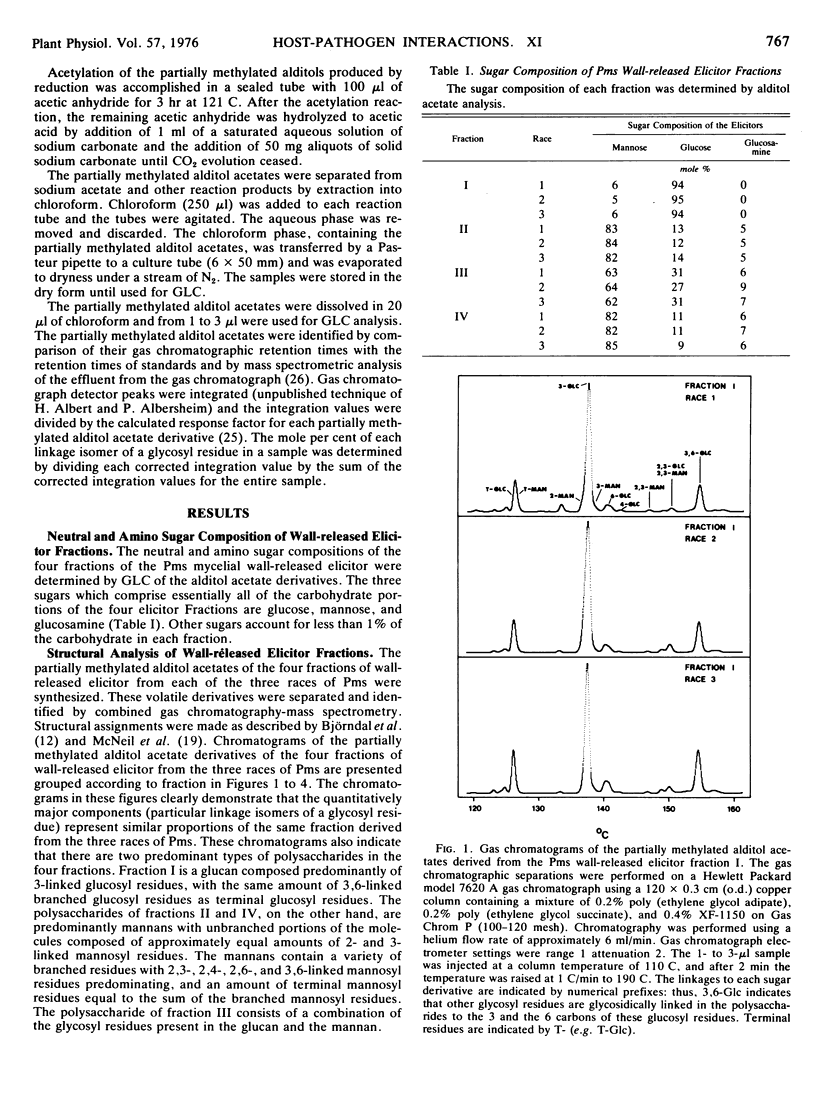
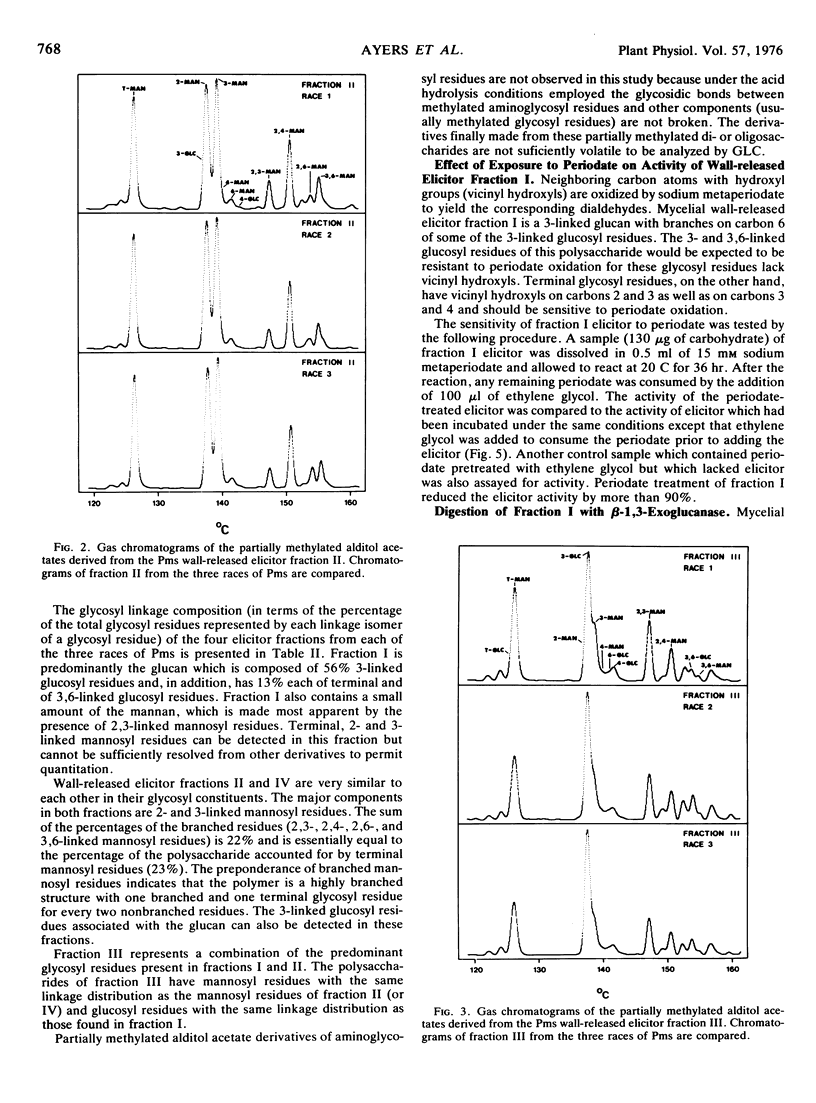
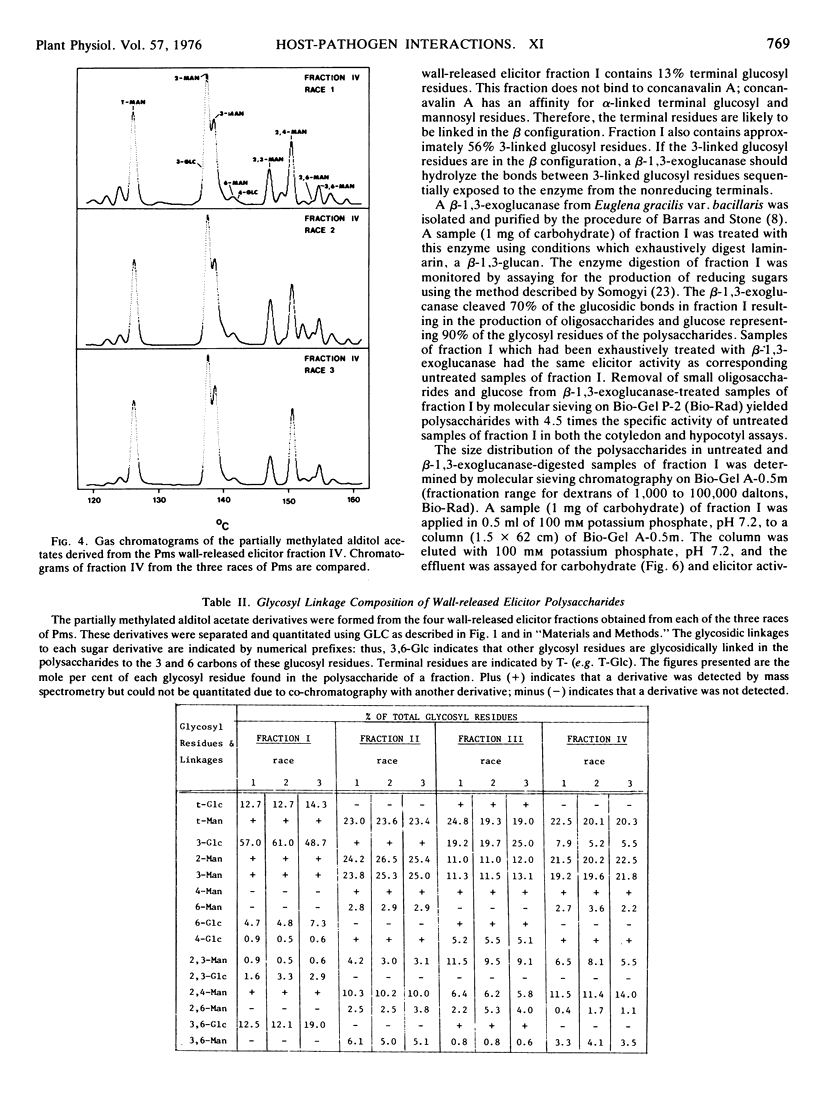
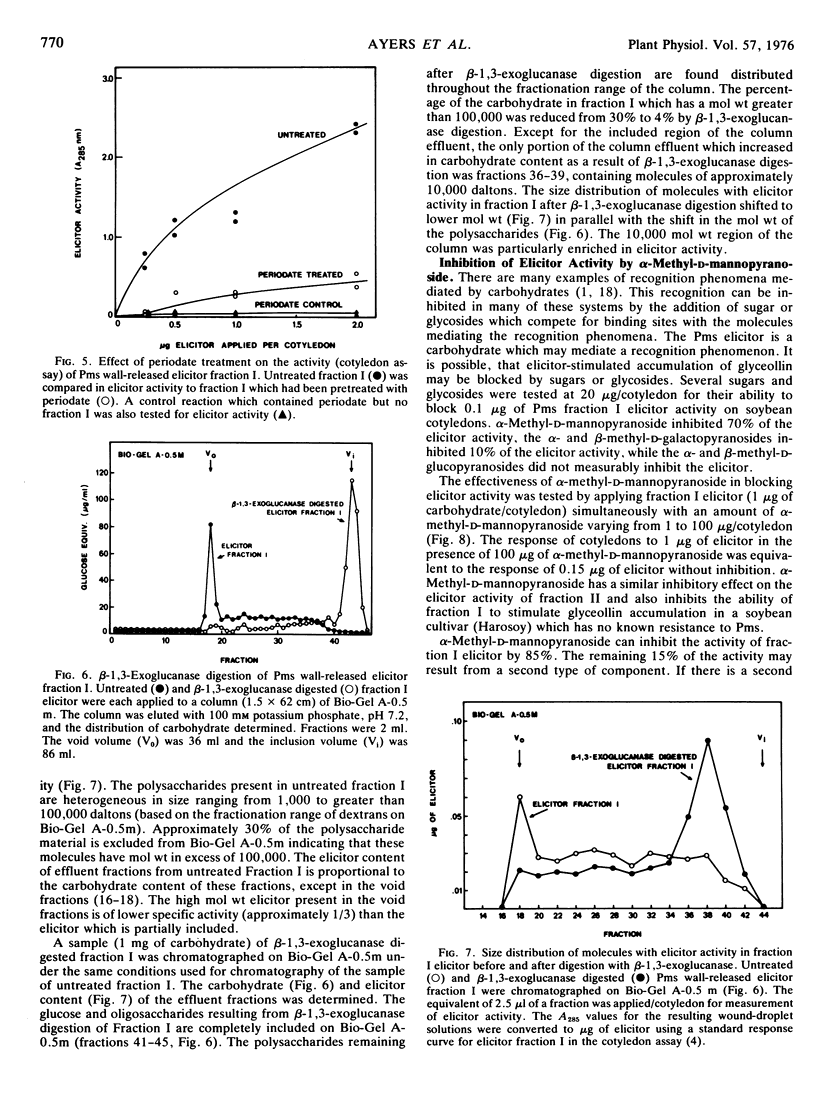
The structures of the four wall-released elicitor fractions isolated from the Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae mycelial walls have been examined. The results demonstrate that fraction I is primarily composed of a branched β-1,3-glucan, similar in structure to the extracellular elicitors described previously (Ayers, A., J. Ebel, F. Finelli, N. Burger, and P. Albersheim. 1976. Plant Physiol. 57: 751-759). Fractions II and IV are primarily composed of a highly branched mannan-containing glycoprotein, with fraction IV richer in protein than fraction II. Fraction III contains, attached to protein, a mixture of the two polysaccharide types found in fraction I and in fractions II and IV. The structural data presented here, in concert with the biological data presented in the previous two papers (Ayers et al. 1976. Plant Physiol. 57: 751-759; 760-765), demonstrate that the only compound produced by P. megasperma var. sojae which contains elicitor activity is the glucan. Evidence is presented that the terminal glycosyl residues of the glucan are required for elicitor activity. In addition, it is demonstrated that 90% of the glucan can be removed enzymically without any loss of biological activity. The active residue of the enzymic digestion is a highly branched 3- and 3,6-linked glucan containing about 4% mannosyl residues. The results presented suggest that the mannosyl residues of the glucan, which represent only about 1% of the undegraded glucan, are likely to participate in the active site of this molecule. The role of elicitors and phytoalexins in host-pathogen interactions is discussed. Evidence for the existence of and possible identity of another factor, which determines race specificity of host-pathogen interactions, is summarized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson-Prouty A. J., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: VIII. Isolation of a Pathogen-synthesized Fraction Rich in Glucan That Elicits a Defense Response in the Pathogen's Host. Plant Physiol. 1975 Aug;56(2):286–291. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Finelli F., Berger N., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: IX. Quantitative Assays of Elicitor Activity and Characterization of the Elicitor Present in the Extracellular Medium of Cultures of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):751–759. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Valent B., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: X. Fractionation and Biological Activity of an Elicitor Isolated from the Mycelial Walls of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):760–765. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou C. E. Some aspects of the structure, immunochemistry, and genetic control of yeast mannans. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;40(0):239–270. doi: 10.1002/9780470122853.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barras D. R., Stone B. A. Beta-1,3-glucan hydrolases from Euglena gracilis. II. Purification and properties of the beta-1,3-glucan exo-hydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 4;191(2):342–353. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman D. F., Van Etten H. D. Susceptibility to Enzymatic Degradation of Cell Walls From Bean Plants Resistant and Susceptible to Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Plant Physiol. 1969 May;44(5):641–648. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.5.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. M., Albersheim P. A gas chromatographic method for the determination of aldose and uronic Acid constituents of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jun;49(6):926–936. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.6.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T. Specific elicitors of plant phytoalexin production: detenninants of race specificity in pathogens? Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):74–75. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4171.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis H., Sharon N. The biochemistry of plant lectins (phytohemagglutinins). Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42(0):541–574. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil M., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: VII. Barley Aleurone Cells. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jan;55(1):64–68. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschke W. C., Ballou C. E. Characterization of a yeast mannan containing N-acetyl-D-glucosamine as an immunochemical determinant. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 26;11(20):3807–3816. doi: 10.1021/bi00770a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandford P. A., Conrad H. E. The structure of the Aerobacter aerogenes A3(S1) polysaccharide. I. A reexamination using improved procedures for methylation analysis. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1508–1517. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K. W., Keegstra K., Bauer W. D., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: I. The Macromolecular Components of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells with a Detailed Analysis of the Pectic Polysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):158–173. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Ballou C. E. Structure and immunochemistry of Hansenula wingei Y-2340 mannan. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2420–2427. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


