Abstract
Frequencies of 25 immunoglobulin heavy-chain and kappa light-chain variable (VH + V kappa) gene-family pairings expressed in splenic B-cell populations were determined by hybridization of VH- and V kappa-family-specific DNA probes to mitogen-induced B-cell colonies from C57BL/6 mice or hybridomas derived from BALB/c and NZB mice. Both analyses support the conclusion that VH and V kappa gene families pair without bias; as would be expected for random association, the frequencies of specific VH + V kappa pairs may be estimated by the product of the independent VH and V kappa frequencies. Based upon the frequencies at which 9 VH and 12 V kappa gene families are expressed, we calculated the expected usage for approximately 100 VH + V kappa family pairings in neonatal and adult C57BL/6 mice. Variability in the expression of such VH + V kappa pairings is considerable; pairs representing greater than 10% to less than 0.01% of the splenic B-cell population occur. This variability is most pronounced in the neonate, where 6 VH + V kappa family pairs account for nearly 40% of all mitogen-reactive B cells. As the neonate matures, the distribution of frequencies for VH + V kappa pairings becomes more nearly uniform. This process may underlie the patterned acquisition of humoral immune responsiveness.
Full text
PDF

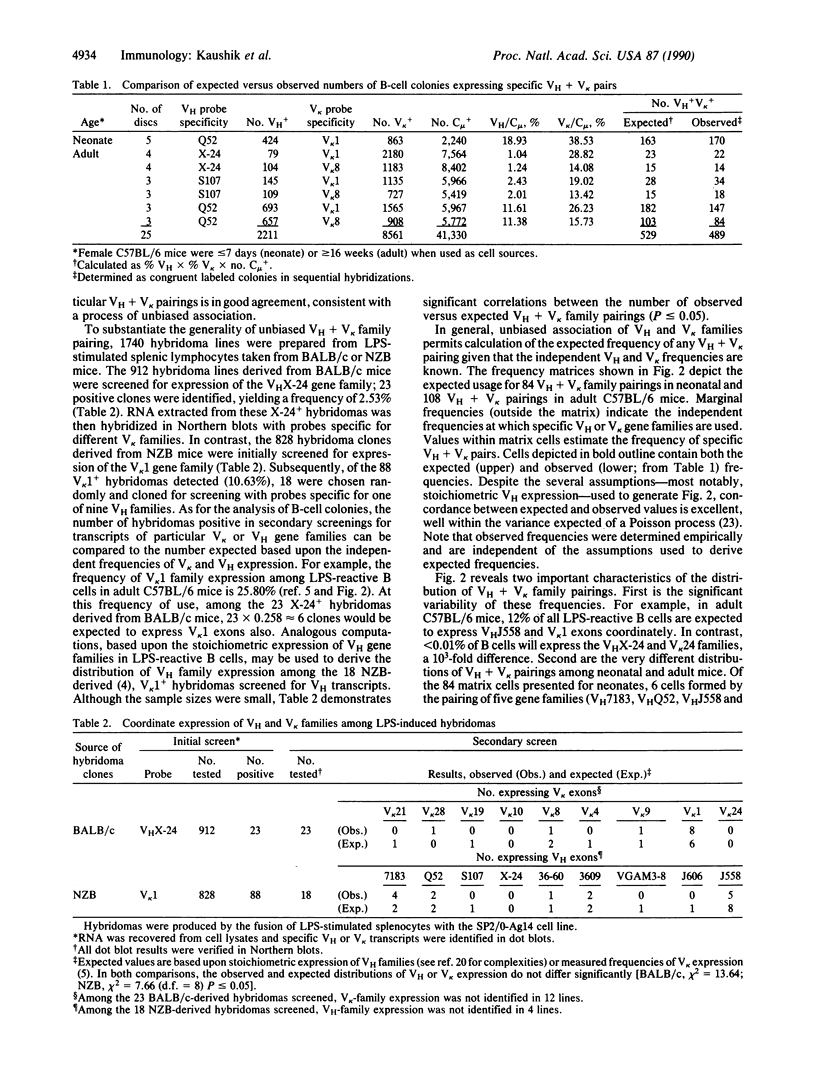


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., Yancopoulos G. D. Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1079–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.3317825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenstein T., Krawinkel U. Immunoglobulin VH region genes of the mouse are organized in overlapping clusters. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1351–1357. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissier M. C., Chiocchia G., Ronziere M. C., Herbage D., Fournier C. Arthritogenicity of minor cartilage collagens (types IX and XI) in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jan;33(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur P. H., Osman G. E., Mackle J. J., Lalor T. M. The organization of the mouse Igh-V locus. Dispersion, interspersion, and the evolution of VH gene family clusters. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2261–2278. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Hoostelaere L. A., Huppi K., Mock B., Mallett C., Potter M. The Ig kappa L chain allelic groups among the Ig kappa haplotypes and Ig kappa crossover populations suggest a gene order. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):652–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildrop R., Krawinkel U., Winter E., Rajewsky K. VH-gene expression in murine lipopolysaccharide blasts distributes over the nine known VH-gene groups and may be random. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Nov;15(11):1154–1156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T. Immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:499–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong H. D., Teale J. M. Comparison of the fetal and adult functional B cell repertoires by analysis of VH gene family expression. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):589–603. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong H. D., Teale J. M. VH gene family repertoire of resting B cells. Preferential use of D-proximal families early in development may be due to distinct B cell subsets. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2752–2760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasturi K., Monestier M., Mayer R., Bona C. Biased usage of certain Vk gene families by autoantibodies and their polymorphism in autoimmune mice. Mol Immunol. 1988 Feb;25(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik A., Schulze D. H., Bona C., Kelsoe G. Murine V kappa gene expression does not follow the VH paradigm. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1859–1864. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsoe G. Cloning of mitogen- and antigen-reactive B lymphocytes on filter paper disks: phenotypic and genotypic analysis of B cell colonies. Methods Enzymol. 1987;150:287–304. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)50086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsoe G., Miceli R., Cerny J., Schulze D. H. Mapping of antibody specificities to VH gene families. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(5):288–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00352838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofler R., Duchosal M. A., Dixon F. J. Complexity, polymorphism, and connectivity of mouse Vk gene families. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(2):65–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00395853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler A. M., Kearney J. F., Kuehl M., Gearhart P. J. Early rearrangements of genes encoding murine immunoglobulin kappa chains, unlike genes encoding heavy chains, use variable gene segments dispersed throughout the locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6744–6747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydyard P. M., Grossi C. E., Cooper M. D. Ontogeny of B cells in the chicken. I. Sequential development of clonal diversity in the bursa. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):79–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser T., Gefter M. L. Isolation of hybridomas expressing a specific heavy chain variable region gene segment by using a screening technique that detects mRNA sequences in whole cell lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2470–2474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monestier M., Manheimer-Lory A., Bellon B., Painter C., Dang H., Talal N., Zanetti M., Schwartz R., Pisetsky D., Kuppers R. Shared idiotypes and restricted immunoglobulin variable region heavy chain genes characterize murine autoantibodies of various specificities. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):753–759. doi: 10.1172/JCI112637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter C. J., Monestier M., Chew A., Bona-Dimitriu A., Kasturi K., Bailey C., Scott V. E., Sidman C. L., Bona C. A. Specificities and V genes encoding monoclonal autoantibodies from viable motheaten mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1137–1153. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. T., Jr, Blakeslee D., Angala E. Acquired immunity in opossum (Didelphis virginiana) embryos. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2148–2153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERSTEIN A. M., UHR J. W., KRANER K. L., LUKES R. J. Fetal response to antigenic stimulus. II. Antibody production by the fetal lamb. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:799–812. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze D. H., Kelsoe G. Genotypic analysis of B cell colonies by in situ hybridization. Stoichiometric expression of three VH families in adult C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):163–172. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin W. K., Rowlands D. T., Jr Determinants of the hierarchy of humoral immune responsiveness during ontogeny. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1549–1554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teale J. M., Morris E. G. Comparison of V kappa gene family expression in adult and fetal B cells. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2768–2772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor-Kobrin C., Bonilla F. A., Barak Z., Bona C. Structural correlates of a regulatory idiotope. Immunol Rev. 1989 Aug;110:151–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Malynn B. A., Alt F. W. Developmentally regulated and strain-specific expression of murine VH gene families. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):417–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]