Abstract
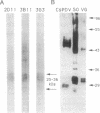
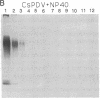
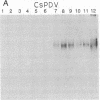
Endoparasitic wasps of lepidopteran insects must induce changes in host immunity and development to survive. Depending on the species, this may require wasp venom proteins and/or a polydnavirus. We describe an immunological and genetic relationship between the Campoletis sonorensis polydnavirus and the wasp's venom gland. Monoclonal antibodies raised against venom glands recognized epitopes conserved on several polydnavirus proteins and on multiple wasp oviduct and venom proteins. The viral envelope proteins had molecular masses of 16, 20, 45, and 50 kDa, while a complex of at least five immunoreactive venom-gland and soluble oviduct proteins ranged in size from 24 to 36 kDa. Since the conserved epitopes were present on the viral envelope, neutralization assays were performed. Monoclonal antibodies added to purified virus blocked the normal viral inhibition of host growth and development. To determine whether venom mRNA and viral genes were also related, venom-related cDNA clones were isolated from the wasp oviduct with a venom-gland cDNA probe. Venom-related viral clones were then identified and selected from a viral genomic library and from a parasitized Heliothis virescens cDNA library. Venom-related mRNAs were expressed in the venom gland, the oviduct, and the parasitized host. We propose that the immunological relationship between venom and viral proteins, and the hybridization of venom and viral genes, may reflect an evolutionary relationship in which venom gene homologs were incorporated into the viral genome, thereby allowing viral expression of venom-related genes and enhancing parasite survival.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedwin O. The particulate basis of the resistance of a parasitoid to the defence reactions of its insect host. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Aug 1;205(1159):267–270. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blissard G. W., Theilmann D. A., Summers M. D. Segment W of Campoletis sonorensis virus: expression, gene products, and organization. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):78–89. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blissard G. W., Vinson S. B., Summers M. D. Identification, Mapping, and In Vitro Translation of Campoletis sonorensis Virus mRNAs from Parasitized Heliothis virescens Larvae. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):318–327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.318-327.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Fredrickson T. Cell proliferative response to vaccinia virus is mediated by VGF. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):182–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90635-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson K. M., Vinson S. B., Stoltz D. B., Summers M. D. Virus in a parasitoid wasp: suppression of the cellular immune response in the parasitoid's host. Science. 1981 Feb 6;211(4482):582–583. doi: 10.1126/science.7455695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. A., Blissard G. W., Summers M. D., Vinson S. B. Expression of Campoletis sonorensis Virus in the Parasitized Host, Heliothis virescens. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):74–78. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.74-78.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. A., Summers M. D. Campoletis sonorensis Endoparasitic Wasps Contain Forms of C. sonorensis Virus DNA Suggestive of Integrated and Extrachromosomal Polydnavirus DNAs. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):552–562. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.552-562.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A. Identification of a viral gene encoding a ubiquitin-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):409–413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitano Y., Okada N., Adachi J. TPA-induced alteration of actin organization in cultured human keratinocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Dec;167(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Moss B. Vaccinia virus encodes a secretory polypeptide structurally related to complement control proteins. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):176–178. doi: 10.1038/335176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krell P. J., Summers M. D., Vinson S. B. Virus with a Multipartite Superhelical DNA Genome from the Ichneumonid Parasitoid Campoletis sonorensis. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):859–870. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.859-870.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. N., Vinson S. B. Correlating the initiation of virus replication with a specific pupal developmental phase of an ichneumonid parasitoid. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;231(2):387–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00222189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly D. R., Miller L. K. A baculovirus blocks insect molting by producing ecdysteroid UDP-glucosyl transferase. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1110–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.2505387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizki R. M., Rizki T. M. Selective destruction of a host blood cell type by a parasitoid wasp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6154–6158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Guzo D., Cook D. Studies on polydnavirus transmission. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Krell P., Summers M. D., Vinson S. B. Polydnaviridae - a proposed family of insect viruses with segmented, double-stranded, circular DNA genomes. Intervirology. 1984;21(1):1–4. doi: 10.1159/000149497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann D. A., Summers M. D. Identification and comparison of Campoletis sonorensis virus transcripts expressed from four genomic segments in the insect hosts Campoletis sonorensis and Heliothis virescens. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):329–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann D. A., Summers M. D. Molecular analysis of Campoletis sonorensis virus DNA in the lepidopteran host Heliothis virescens. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1961–1969. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann D. A., Summers M. D. Physical Analysis of the Campoletis sonorensis Virus Multipartite Genome and Identification of a Family of Tandemly Repeated Elements. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2589–2598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2589-2598.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweeten K. A., Bulla L. A., Consigli R. A. Characterization of an extremely basic protein derived from granulosis virus nucleocapsids. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):866–876. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.866-876.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb B. A., Riddiford L. M. Regulation of expression of arylphorin and female-specific protein mRNAs in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Dev Biol. 1988 Dec;130(2):682–692. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Zheng S. L., Rosen B. I., Knight N., Gourley N. E., Ramig R. F. Protection between different serotypes of bovine rotavirus in gnotobiotic calves: specificity of serum antibody and coproantibody responses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1052–1058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1052-1058.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]