Abstract
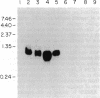
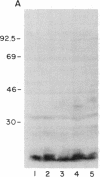
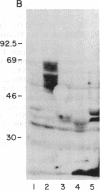
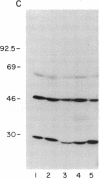
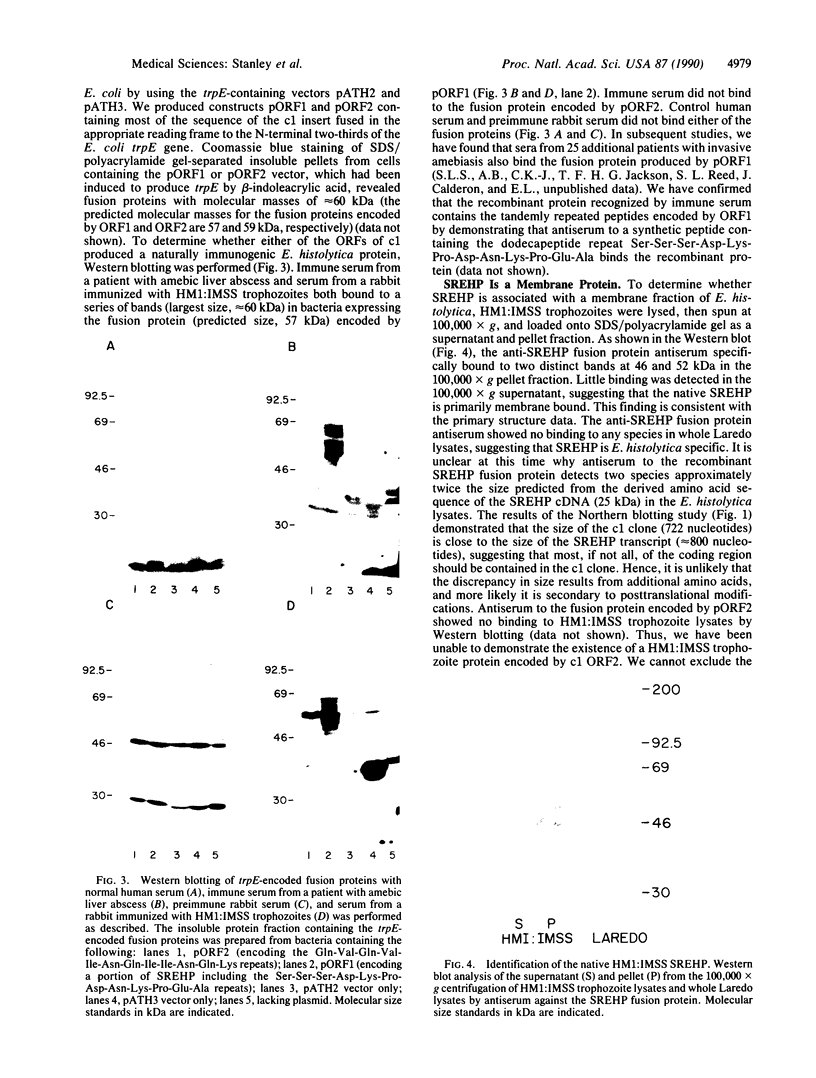
Entamoeba histolytica causes amebic dysentery and amebic liver abscess, major causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. We have used differential hybridization screening to isolate an E. histolytica-specific cDNA clone. The cDNA was found to encode a serine-rich E. histolytica protein (SREHP) containing multiple tandem repeats. The structural motif of SREHP resembles some of the repetitive antigens of malarial species, especially the circumsporozoite proteins. A recombinant trpE fusion protein containing the tandem repeats of SREHP was recognized by immune serum from a patient with amebiasis, demonstrating that SREHP is a naturally immunogenic protein. An antiserum raised against the recombinant fusion protein specifically bound to two distinct bands with apparent molecular masses of 46 and 52 kDa in a crude preparation of E. histolytica trophozoite membranes. This antiserum also inhibited E. histolytica trophozoite adhesion to Chinese hamster ovary cells in vitro. The ability to isolate E. histolytica-specific genes, and to express those genes in Escherichia coli, may be important in studying the molecular basis of E. histolytica pathogenesis and for the future development of vaccines.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Techniques of axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae. J Parasitol. 1968 Oct;54(5):1047–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galinski M. R., Arnot D. E., Cochrane A. H., Barnwell J. W., Nussenzweig R. S., Enea V. The circumsporozoite gene of the Plasmodium cynomolgi complex. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90434-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E., Hartmann D. P. Protection against amebic liver abscess in hamsters by means of immunization with amebic antigen and some of its fractions. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Sep;29(5):779–784. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. R., Strauss J. H. Processing the nonstructural polyproteins of Sindbis virus: study of the kinetics in vivo by using monospecific antibodies. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):998–1007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.998-1007.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuckeroth R. O., Birkenmeier E. H., Levin M. S., Gordon J. I. Analysis of the tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and linkage relationships of a rodent gene encoding heart fatty acid binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9709–9717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Anders R. F. Repetitive proteins and genes of malaria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:181–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M. Protective immunity to amebic infection demonstrated in guinea pigs. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 May;23(3):355–360. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Becker A., Stanley S. L., Jr Chinese hamster ovary cells deficient in N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I activity are resistant to Entamoeba histolytica-mediated cytotoxicity. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):8–12. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.8-12.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Becker A., Stanley S. L., Jr Use of Chinese hamster ovary cells with altered glycosylation patterns to define the carbohydrate specificity of Entamoeba histolytica adhesion. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1725–1730. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Demmer L. A., Sweetser D. A., Ong D. E., Gordon J. I. Rat cellular retinol-binding protein II: use of a cloned cDNA to define its primary structure, tissue-specific expression, and developmental regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5779–5783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern C. F., Keister D. B., Caspar P. A. Experimental amebiasis. III. A rapid in vitro assay for virulence of Entamoeba histolytica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Sep;27(5):882–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki L. S., Svec P., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V., Godson G. N. Structure of the plasmodium knowlesi gene coding for the circumsporozoite protein. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90538-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez M. A., Hernández F., Santos L., Valdez A., Orozco E. Entamoeba histolytica: molecules involved in the target cell-parasite relationship. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Nov;37(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWARTZWELDER J. C., AVANT W. H. Immunity to amebic infection in dogs. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1952 Jul;1(4):567–575. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1952.1.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Horstmann R. D., Knobloch J., Arnold H. H. Genomic DNA differences between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5118–5122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Broome S., Lomedico P., Tizard R., Naber S. P., Chick W. L., Gilbert W. A bacterial clone synthesizing proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3727–3731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]