Abstract
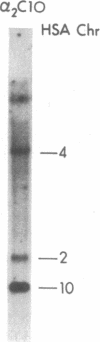
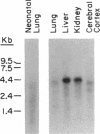
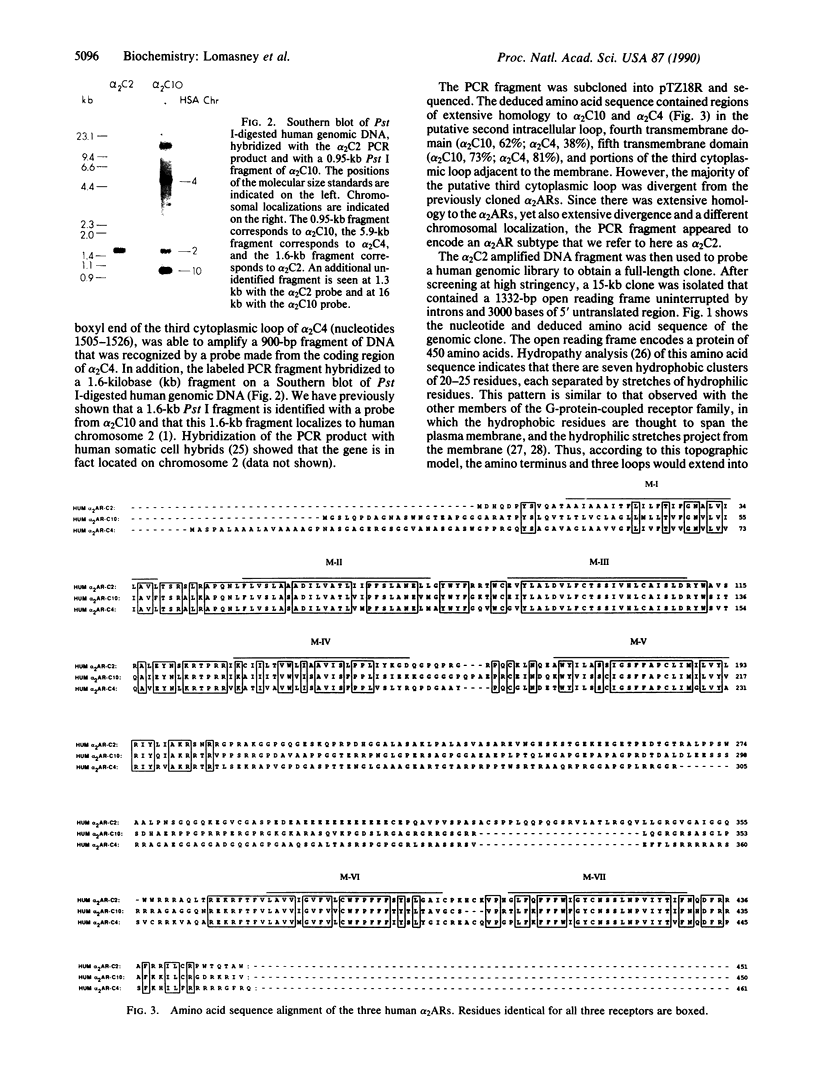
Pharmacologic, biochemical, and genetic analyses have demonstrated the existence of multiple alpha 2-adrenergic receptor (alpha 2AR) subtypes. We have cloned a human alpha 2AR by using the polymerase chain reaction with oligonucleotide primers homologous to conserved regions of the previously cloned alpha 2ARs, the genes for which are located on human chromosomes 4 (C4) and 10 (C10). The deduced amino acid sequence encodes a protein of 450 amino acids whose putative topology is similar to that of the family of guanine nucleotide-binding protein-coupled receptors, but whose structure most closely resembles that of the alpha 2ARs. Competition curve analysis of the binding properties of the receptor expressed in COS-7 cells with a variety of adrenergic ligands demonstrates a unique alpha 2AR pharmacology. Hybridization with somatic cell hybrids shows that the gene for this receptor is located on chromosome 2. Northern blot analysis of various rat tissues shows expression in liver and kidney. The unique pharmacology and tissue localization of this receptor suggest that this is an alpha 2AR subtype not previously identified by classical pharmacological or ligand binding approaches.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benovic J. L., Regan J. W., Matsui H., Mayor F., Jr, Cotecchia S., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17251–17253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Heterogeneity of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 May;22(5):835–843. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Ray-Prenger C., Murphy T. J. Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: antagonist binding in tissues and cell lines containing only one subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):600–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptors: pharmacological and molecular biological evidence converge. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Oct;9(10):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Hancock A. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Validation and statistical analysis of a computer modeling method for quantitative analysis of radioligand binding data for mixtures of pharmacological receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):5–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Bouvier M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The multiple membrane spanning topography of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Localization of the sites of binding, glycosylation, and regulatory phosphorylation by limited proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14282–14288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. A family of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2657–2664. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Briend-Sutren M. M., Patey G., Tate K., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.2570461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frielle T., Collins S., Daniel K. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning of the cDNA for the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7920–7924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Dixon R. A., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Sigal I. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of catecholamine release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jul 1;23(13):1793–1800. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier S. M., Homcy C. J., Patenaude C., Graham R. M. Identification of structurally distinct alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14491–14496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. J., Bylund D. B. Characterization of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the OK cell, an opossum kidney cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):571–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Bouvier M. Palmitoylation of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Mutation of Cys341 in the carboxyl tail leads to an uncoupled nonpalmitoylated form of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7564–7569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Wilkie T. M., Simon M. I. Diversity of the G-protein family: sequences from five additional alpha subunits in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7407–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Lipfert L., Malbon C. C., Bahouth S. Site-directed anti-peptide antibodies define the topography of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14424–14431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Landau N. R., Baltimore D., Francke U. The terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase gene is located on human chromosome 10 (10q23----q24) and on mouse chromosome 19. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(3-4):121–126. doi: 10.1159/000132309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]