Abstract
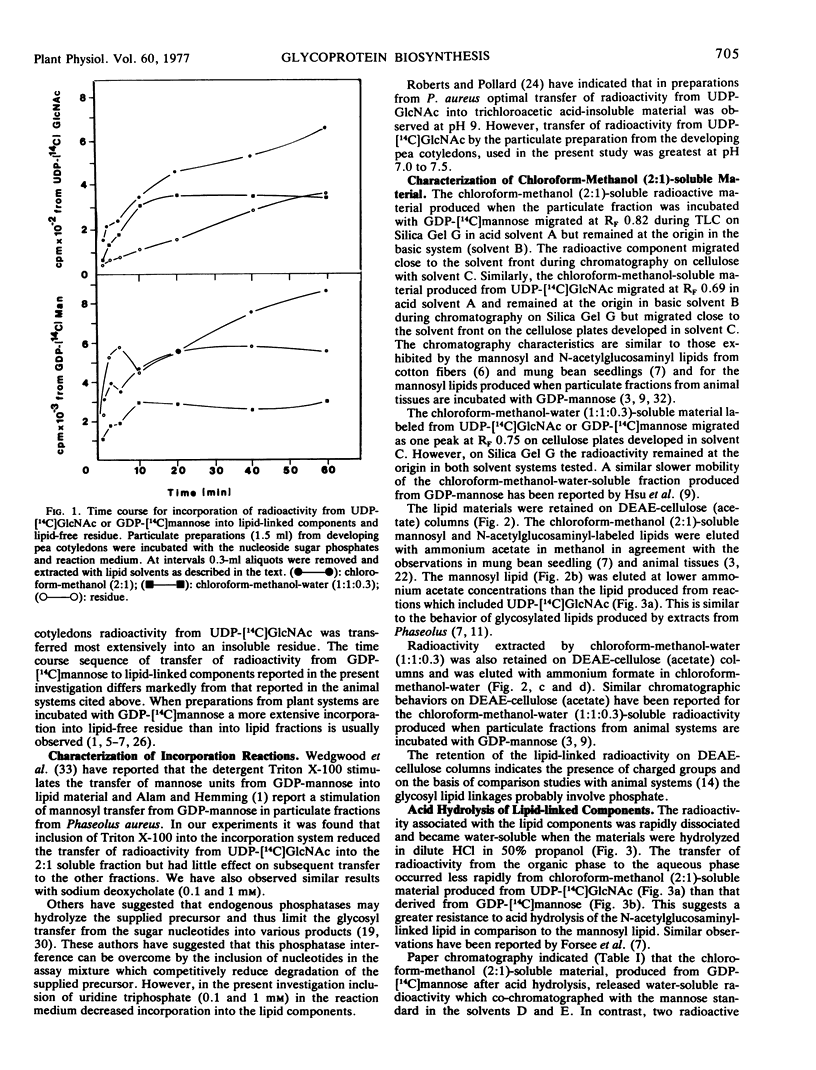
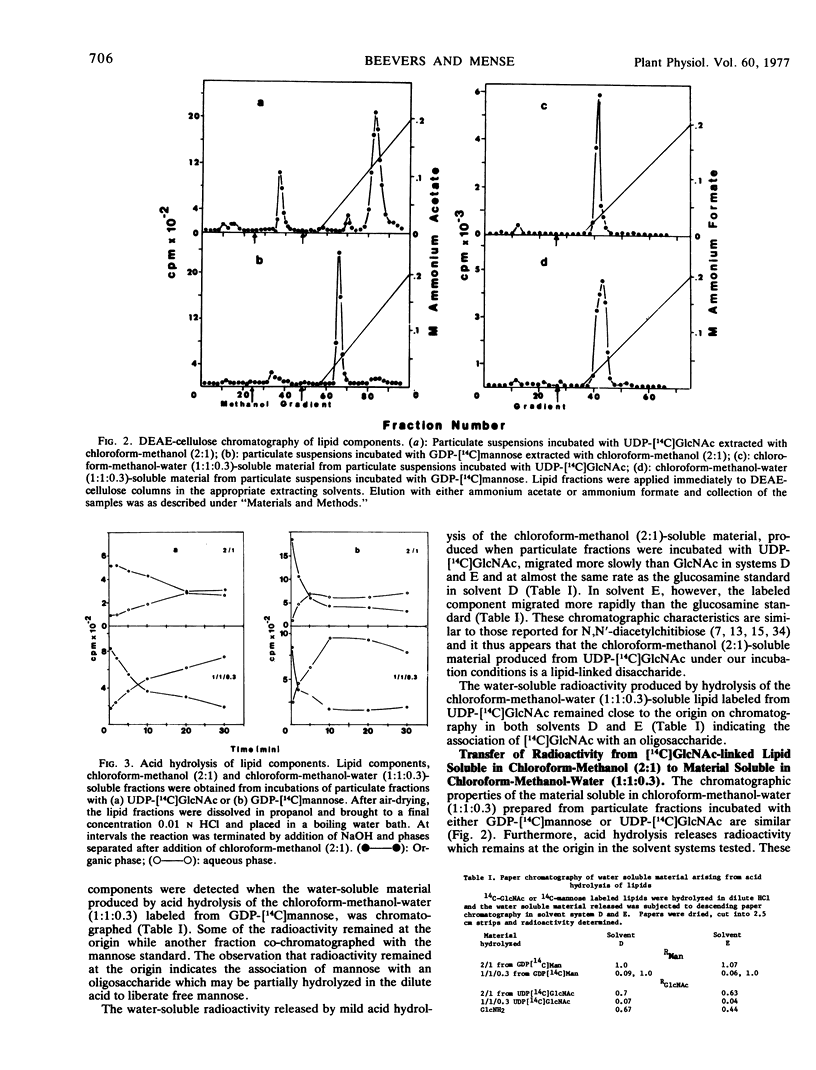
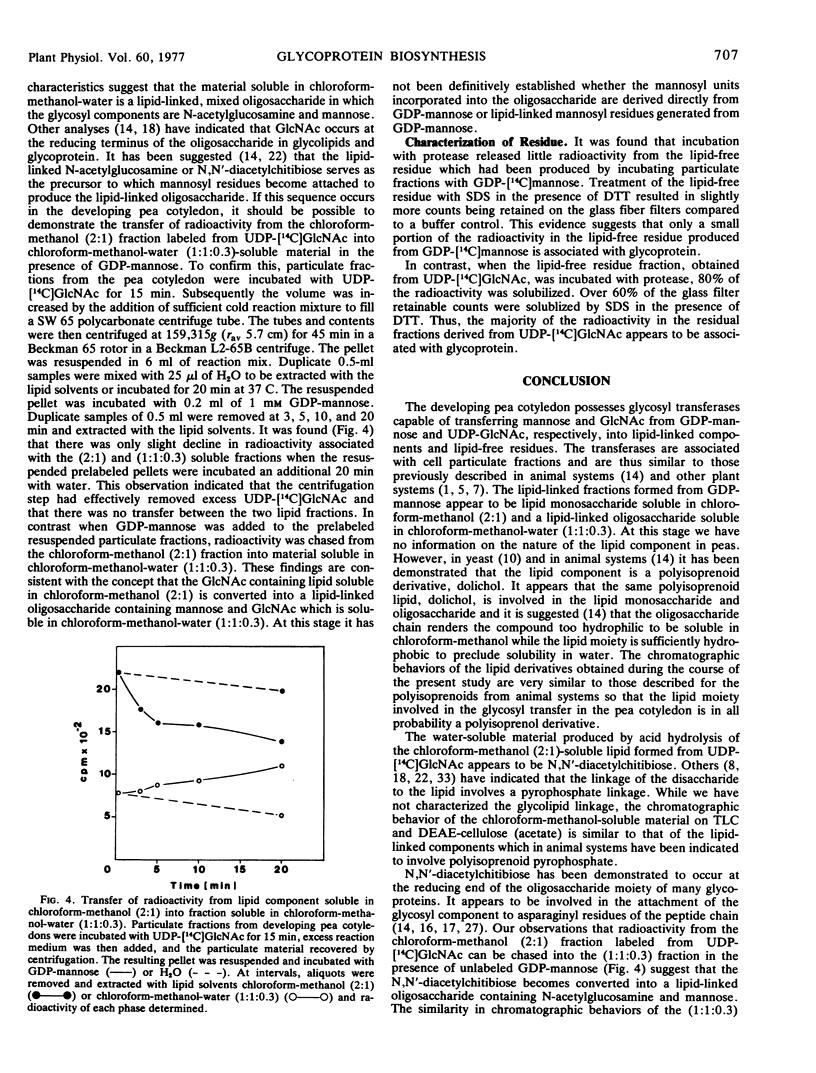
Particulate preparations from developing cotyledons of Pisum sativum L. cv. Burpeeana catalyze glycosyl transfer from UDP-[14C]N-acetylglucosamine and GDP-[14C]mannose. Radioactivity is transferred to lipid components soluble in chloroform-methanol (2:1) and chloroform-methanol-water (1:1:0.3) and into a water-insoluble and lipid-free residue.
The chloroform-methanol-soluble component formed from GDP-[14C]mannose appears to be a mannosyl lipid, whereas the chloroform-methanol-water-soluble fraction is probably a mixed oligosaccharide-lipid containing N-acetylglucosamine and mannose residues. The chloroform-methanol-soluble component formed from UDP-[14C]N-acetylglucosamine appears to be N,N′-diacetylchitibiosyl lipid, which may be incorporated with mannose to form the chloroform-methanol-water-soluble mixed oligosaccharide lipid.
The oligosaccharide lipid appears to function as a precursor for the transfer of the oligosaccharide to the peptide moiety in the formation of the glycoproteins. The bulk of the radioactivity, arising from UDP-[14C]N-acetylglucosamine, incorporated into the insoluble residue, is associated with glycoprotein. In contrast only a small percentage of radioactivity in the insoluble residue, arising from GDP-[14C]mannose incorporation, appears to be associated with glycoprotein. The majority of the radioactivity found in the residue fraction labeled from GDP-[14C]mannose appears to be associated with oligomannosyl residues.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basha S. M., Beevers L. Glycoprotein Metabolism in the Cotyledons of Pisum sativum during Development and Germination. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):93–97. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J., Elbein A. D. Biosynthesis and characterization of lipid-linked sugars and glycoproteins in aorta. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6904–6915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson M. C., Delmer D. P. Glycoprotein synthesis in plants: I. Role of lipid intermediates. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):341–347. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsee W. T., Elbein A. D. Glycoprotein biosynthesis in plants. Demonstration of lipid-linked oligosaccharides of mannose and N-acetylglucosamine. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9283–9293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsee W. T., Valkovich G., Elbein A. D. Glycoprotein biosynthesis in plants. Formation of lipid-linked oligosaccharides of mannose and N-acetylglucosamine by mung bean seedlings. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jun;174(2):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghalambor M. A., Warren C. D., Jeanloz R. W. Biosynthesis of a P1-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucosyl P2-polyisoprenyl pyrophosphate by calf pancreas microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan 23;56(2):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90857-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu A. F., Baynes J. W., Heath E. C. The role of a dolichol-oligosaccharide as an intermediate in glycoprotein biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2391–2395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung P., Tanner W. Identification of the lipid intermediate in yeast mannan biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 1;37(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Fartaczek F., Tanner W., Kauss H. Formation of polyprenol-linked mono- and oligosaccharides in Phaseolus aureus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Aug;175(2):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90529-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Tanner W. Membrane-bound mannosyl transferase in yeast glycoprotein biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 20;350(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leloir L. F., Staneloni R. J., Carminatti H., Behrens N. H. The biosynthesis of a N,N'-diacetylchitobiose containing lipid by liver microsomes. A probable dolichol pyrophosphate derivative. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 19;52(4):1285–1292. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90640-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas J. J., Waechter C. J. Polyisoprenoid glycolipids involved in glycoprotein biosynthesis. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Apr 28;11(2):67–78. doi: 10.1007/BF01792788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas J. J., Waechter J., Lennarz W. J. The participation of lipid-linked oligosaccharide in synthesis of membrane glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):1992–2002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:673–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar J. A proposed pathway of plasma glycoprotein synthesis. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Jan 31;6(1):3–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01731862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar J., Chao H., Ikehara Y. Phosphoryl-N-acetylglucosamine transfer to a lipid acceptor of liver microsomal preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 1;239(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mookerjea S., Yung J. W. Studies on uridine diphosphate-galactose pyrophosphatase and uridine diphosphate-galactose: glycoprotein galactosyltransferase activities in microsomal membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jan;166(1):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G. J., Harrison J., Hemming F. W. The mannosylation of dolichol-diphosphate oligosaccharides in relation to the formation of oligosaccharides and glycoproteins in pig-liver endoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 1;58(1):223–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G. J., Hemming F. W. The transfer of mannose to dolichol diphosphate oligosaccharides in pig liver endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;152(2):191–199. doi: 10.1042/bj1520191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palamarczyk G., Hemming F. W. The formation of mono-N-acetylhexosamine derivatives of dolichol diphosphate by pig liver microsomal fractions. Biochem J. 1975 May;148(2):245–251. doi: 10.1042/bj1480245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Oka T., Schimke R. T. Modulation of ovalbumin synthesis by estradiol-17 beta and actinomycin D as studied in explants of chick oviduct in culture. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):724–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. M., Pollard W. E. The Incorporation of d-Glucosamine into Glycolipids and Glycoproteins of Membrane Preparations from Phaseolus aureus Hypocotyls. Plant Physiol. 1975 Mar;55(3):431–436. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Axelos M., Péaud-Lenoël C. Biosynthesis of mannan and mannolipids from GDP-Man by membrane fractions of sycamore cell cultures. Biochimie. 1976;58(10):1195–1211. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Lennarz W. J. Utilization of exogenous GDP-mannose for the synthesis of mannose-containing lipids and glycoproteins by oviduct cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2511–2519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacz J. S., Herscovics A., Warren C. D., Jeanloz R. W. Mannosyltransferase activity in calf pancreas microsomes. Formation from guanosine diphosphate-D-(14C)mannose of a 14C-labeled mannolipid with properties of dolichyl mannopyranosyl phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6372–6381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessey D. A., Zakim D. Characterization of the reaction of GDP-mannose with dolichol phosphate in liver membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May 6;53(2):499–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waechter C. J., Kennedy J. L., Harford J. B. Lipid intermediates involved in the assembly of membrane-associated glycoproteins in calf brain white matter. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jun;174(2):726–737. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedgwood J. F., Strominger J. L., Warren C. D. Transfer of sugars from nucleoside diphosphosugar compounds to endogenous and synthetic dolichyl phosphate in human lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6316–6324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedgwood J. F., Warren C. D., Jeanloz R. W., Strominger J. L. Enzymatic utilization of P1-di-N-acetylchitobiosyl P2-dolichyl pyrophosphate and its chemical synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5022–5026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatta P., Zakim D., Vessey D. A. Incorporation of N-acetyl glucosamine into lipid linked oligosaccharides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):1014–1019. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


