Abstract
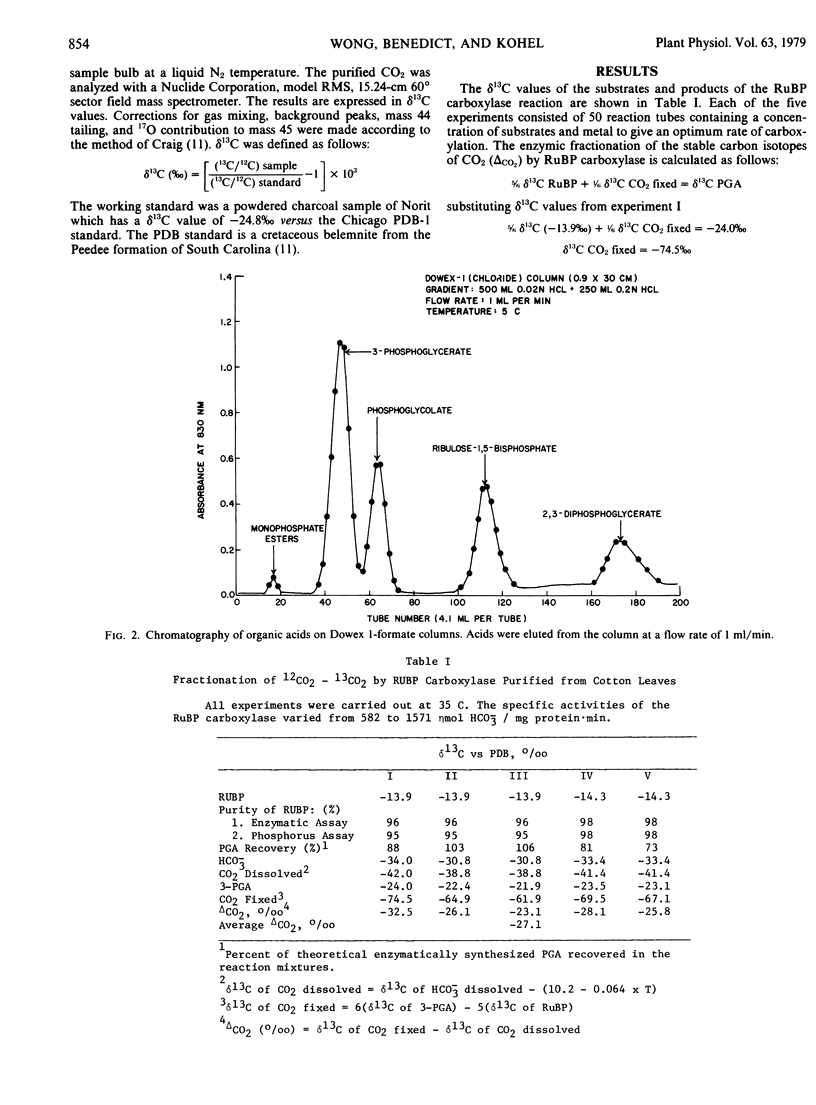
The enzymic fractionation of the stable carbon isotopes of CO2 (Δco2) was determined using a purified preparation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) carboxylase isolated from cotton (a C3 plant) leaves. The bicarbonate concentration in the reaction mixture saturated the enzyme and furnished an infinite pool of 12CO2 and 13CO2 for enzyme fractionation. The RuBP was 96 to 98% pure. The phosphoglycerate synthesized in the reaction mixtures was purified free of RuBP, phosphoglycolate, and other phosphate esters by column chromatography on Dowex 1-Cl− resin. The average Δco2 value of −27.1% was determined from five separate experiments. A discussion of the isotope fractionation associated with photosynthetic CO2 fixation in plants shows that the enzymic fractionation of stable carbon isotopes of CO2 by RuBP carboxylase is of major importance in determining the δ13C values of C3 plants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews T. J., Lorimer G. H., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. I. Synthesis of phosphoglycolate by fraction-1 protein of leaves. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):11–18. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Colorimetric assay methods for free and phosphorylated glyceric acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):469–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christeller J. T., Laing W. A. Isotope Discrimination by Ribulose 1,5-Diphosphate Carboxylase: No Effect of Temperature or HCO(3) Concentration. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):580–582. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estep M. F., Tabita F. R., Parker P. L., Van Baalen C. Carbon isotope fractionation by ribulose-1,5-bisophosphate carboxylase from various organisms. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):680–687. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Givan A. L., Criddle R. S. Ribulosediphosphate carboxylase from Chlamydomonas reinhardi: purification, properties and its mode of synthesis in the cell. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Mar;149(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. H., Heizmann P., Gelvin S., Walker L. L. Identification and Properties of the Messenger RNA Activity in Chlamydomonas reinhardi Coding for the Large Subunit of d-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):464–470. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. N., Epstein S. Two categories of c/c ratios for higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1971 Mar;47(3):380–384. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.3.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan T., Sackett W. M. Enzymatic fractionation of carbon isotopes by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from c(4) plants. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jun;51(6):1051–1054. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.6.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]