Abstract
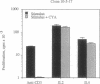
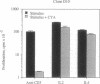
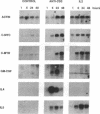
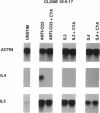
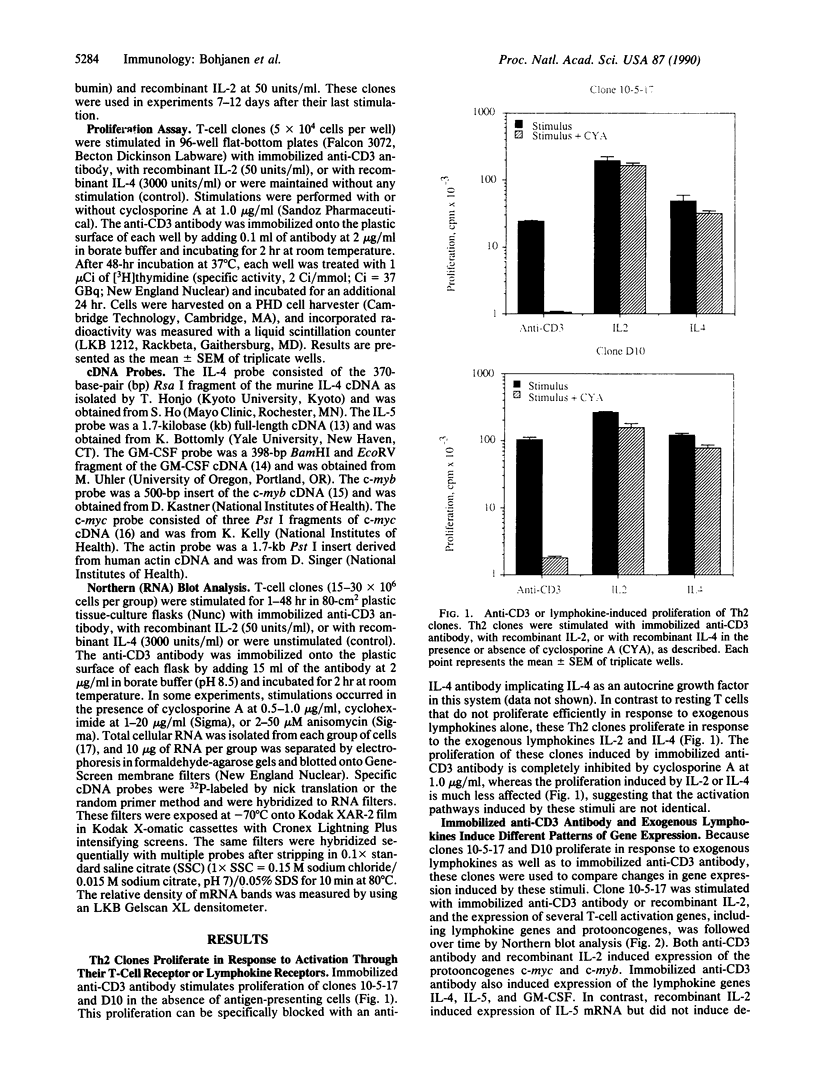
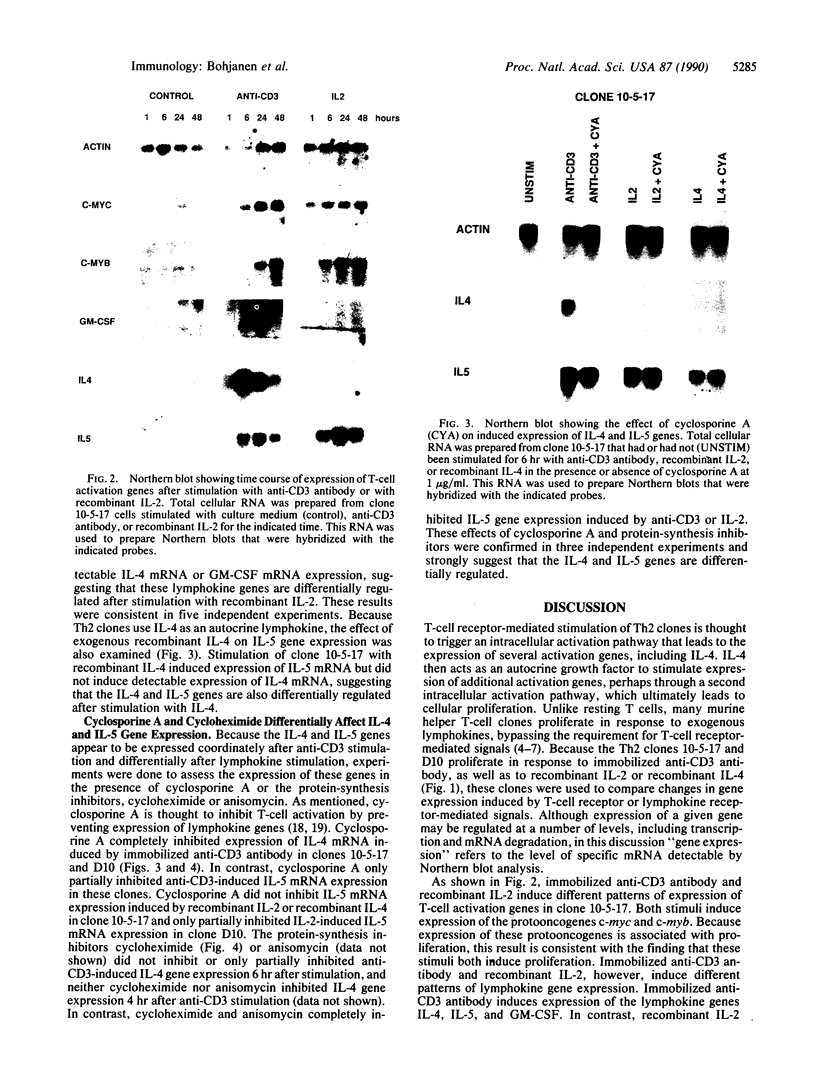
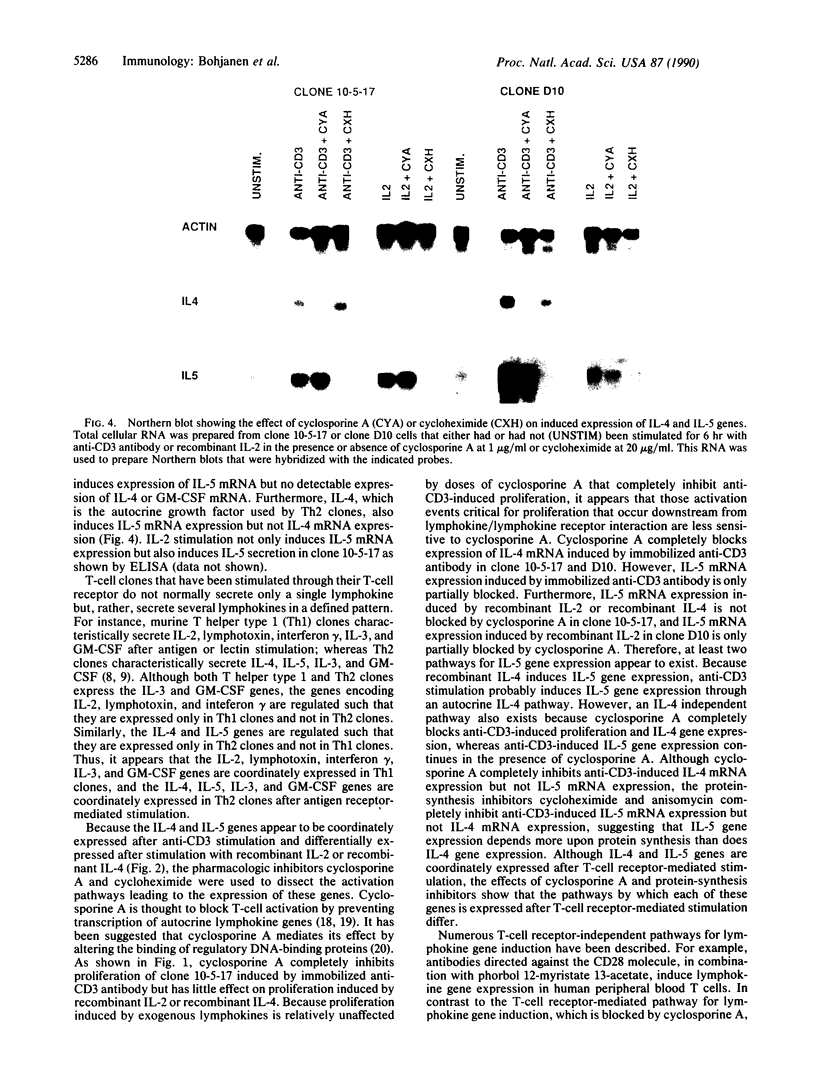
Murine T helper type 2 clones were stimulated with immobilized anti-CD3 antibody or with recombinant lymphokines to compare the expression of T-cell activation genes induced by these stimuli. Immobilized anti-CD3 antibody, recombinant interleukin 2 (IL-2), and recombinant interleukin 4 (IL-4) all induced proliferation of the T helper type 2 clones 10-5-17 and D10. Proliferation of these clones induced by anti-CD3 antibody was completely inhibited by cyclosporine A, whereas cyclosporine A had little effect on proliferation induced by recombinant IL-2 or recombinant IL-4. Both immobilized anti-CD3 antibody, and recombinant IL-2 induced the expression of the protooncogenes c-myc and c-myb. Immobilized anti-CD3 antibody also induced expression of the lymphokine genes IL-4, interleukin 5 (IL-5), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. In contrast, recombinant IL-2 induced IL-5 mRNA expression but did not induce detectable expression of IL-4 or granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNA. Likewise, recombinant IL-4 induced expression of IL-5 but not IL-4 mRNA. Thus, the IL-4 and IL-5 genes appear to be differentially regulated after stimulation with recombinant lymphokines. Effects of cyclosporine A and the protein synthesis inhibitors cycloheximide and anisomycin on IL-4 and IL-5 gene expression suggest that these genes are activated by different pathways after anti-CD3 stimulation. Cyclosporine A completely inhibited anti-CD3-induced expression of IL-4 mRNA but not of IL-5 mRNA, and protein-synthesis inhibitors completely inhibited induction of IL-5 mRNA but not of IL-4 mRNA. Together, our data show that T-cell receptor-mediated and lymphokine receptor-mediated signals induce different patterns of lymphokine gene expression and provide strong evidence that the IL-4 and IL-5 genes are differently regulated.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow D. P., Bućan M., Lehrach H., Hogan B. L., Gough N. M. Close genetic and physical linkage between the murine haemopoietic growth factor genes GM-CSF and Multi-CSF (IL3). EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):617–623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherwinski H. M., Schumacher J. H., Brown K. D., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1229–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R. Contingent genetic regulatory events in T lymphocyte activation. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):355–361. doi: 10.1126/science.2783497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn D. E., Jin J. P., Lancki D. W., Fitch F. W. An alternative pathway of induction of lymphokine production by T lymphocyte clones. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3847–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Botran R., Sanders V. M., Mosmann T. R., Vitetta E. S. Lymphokine-mediated regulation of the proliferative response of clones of T helper 1 and T helper 2 cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):543–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Botran R., Sanders V. M., Oliver K. G., Chen Y. W., Krammer P. H., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Interleukin 4 mediates autocrine growth of helper T cells after antigenic stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9689–9693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herold K. C., Lancki D. W., Moldwin R. L., Fitch F. W. Immunosuppressive effects of cyclosporin A on cloned T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1315–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. D., Colombani P. M., Esa A. H. Cyclosporine and the immune response: basic aspects. Crit Rev Immunol. 1986;6(2):123–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Gillespie M. M., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B. T-cell proliferation involving the CD28 pathway is associated with cyclosporine-resistant interleukin 2 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4472–4481. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinashi T., Harada N., Severinson E., Tanabe T., Sideras P., Konishi M., Azuma C., Tominaga A., Bergstedt-Lindqvist S., Takahashi M. Cloning of complementary DNA encoding T-cell replacing factor and identity with B-cell growth factor II. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):70–73. doi: 10.1038/324070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupper T., Horowitz M., Lee F., Robb R., Flood P. M. Autocrine growth of T cells independent of interleukin 2: identification of interleukin 4 (IL 4, BSF-1) as an autocrine growth factor for a cloned antigen-specific helper T cell. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4280–4287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Hamberg S., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Abbas A. K. Heterogeneity of helper/inducer T lymphocytes. I. Lymphokine production and lymphokine responsiveness. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1774–1787. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman A. H., Kurt-Jones E. A., Abbas A. K. B-cell stimulatory factor 1 and not interleukin 2 is the autocrine growth factor for some helper T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):824–827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek T. R., Schmidt J. A., Shevach E. M. The murine IL 2 receptor. III. Cellular requirements for the induction of IL 2 receptor expression on T cell subpopulations. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2405–2413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Fahrlander P. D., Tesser P. M., Marcu K. B. Nucleotide sequence comparison of normal and translocated murine c-myc genes. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):423–425. doi: 10.1038/310423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taplits M. S., Henkart P. A., Hodes R. J. T helper cell cytoplasmic granules. Exocytosis in response to activation via the T cell receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida T., Sakane T. Intracellular activation signal requirements for the induction of IL-2 responsiveness in resting T cell subsets in humans. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3446–3449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]