Abstract
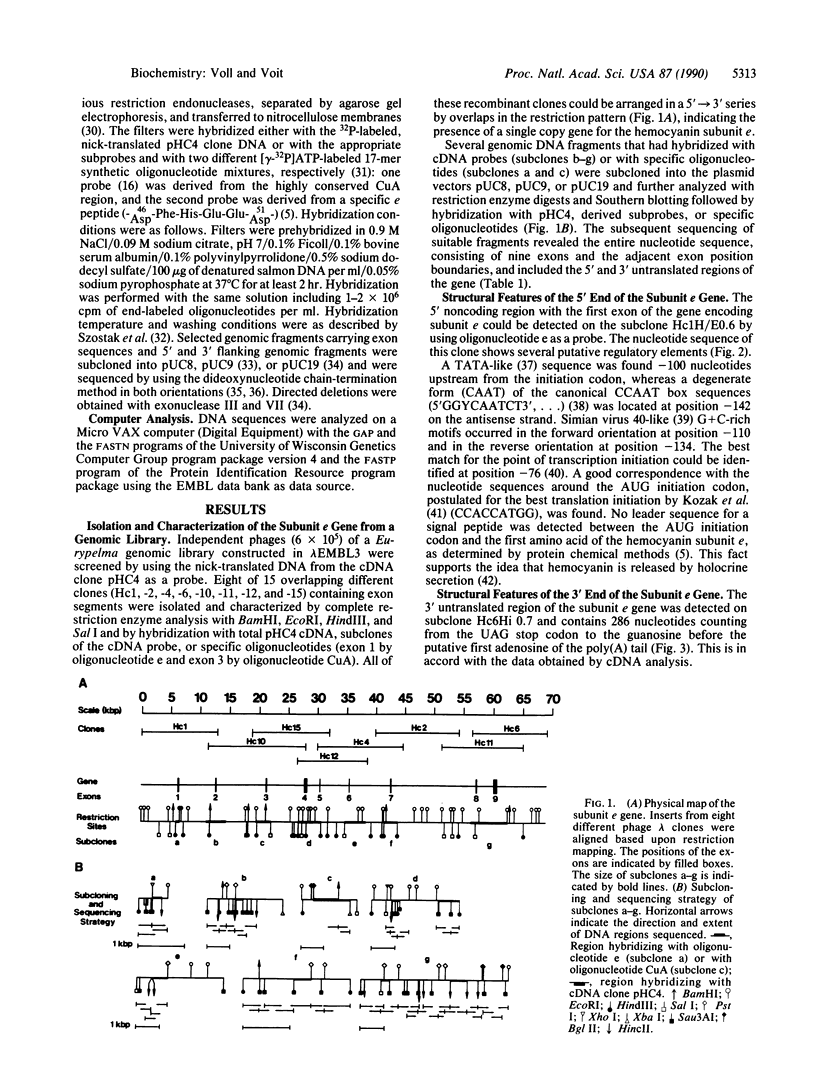
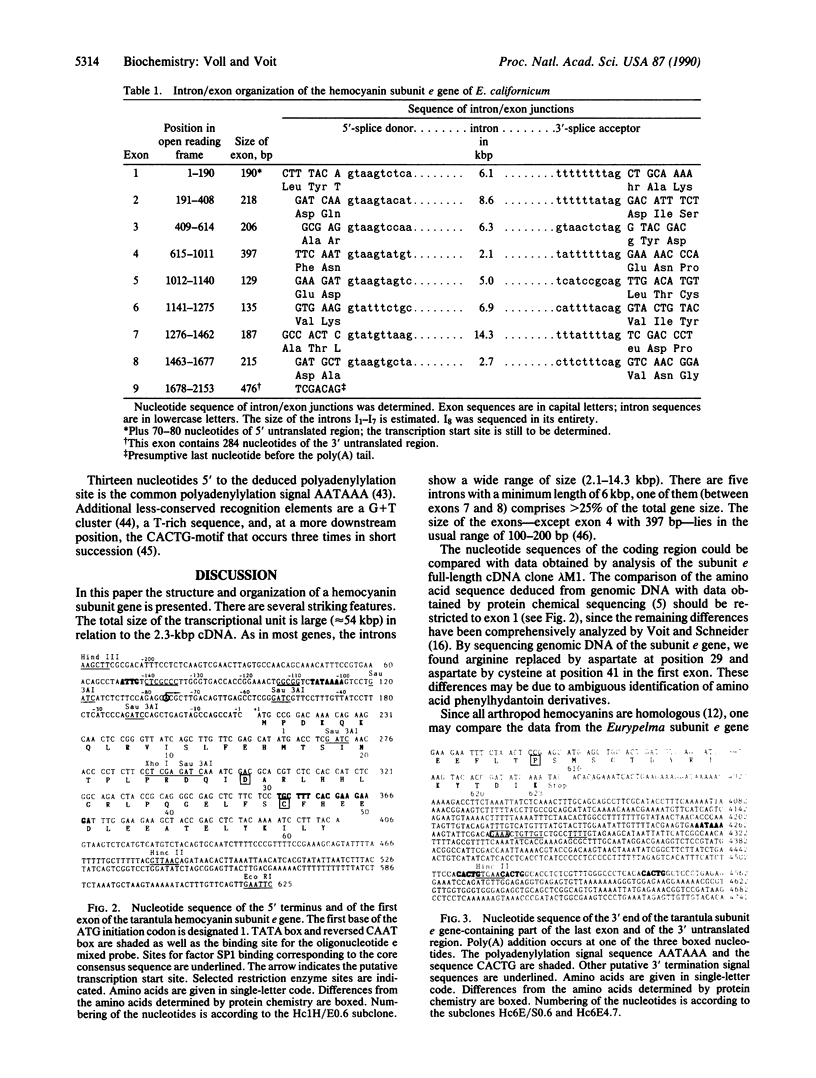
The gene for the hemocyanin subunit e of the tarantula Eurypelma californicum has been isolated from a genomic phage library by using a corresponding cDNA clone as a probe. The transcriptional unit spans a chromosomal region of about 55 kilobase pairs (kbp). The gene consists of nine exons that are separated by large introns. The intron/exon boundaries were determined by direct comparison of genomic and cDNA sequences. A putative promoter region ("TATA" box, reversed "CAAT" box) 100 bp 5' to the translational initiation codon strongly suggests the presence of a functional gene. The 3' flanking region carries the polyadenylylation signal (AATAAA) and several conserved structures for the 3' splicing of the pre-mRNA. A comparison of the gene architecture of the subunit e gene with the three-dimensional structure of the arthropod hemocyanin subunit shows a good correspondence with the division of the subunit into three domains (two exons coding for the first, three coding for the second, and four coding for the third domain). The relationship to molluscan hemocyanins, different tyrosinases, and the larval serum proteins is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bak H. J., Beintema J. J. Panulirus interruptus hemocyanin. The elucidation of the complete amino acid sequence of subunit a. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 1;169(2):333–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Sprang S., Fletterick R., Rutter W. J. Intron-exon splice junctions map at protein surfaces. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):180–182. doi: 10.1038/299180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker H., Sterner R. Nested allostery of arthropodan hemocyanin (Eurypelma californicum and Homarus americanus). The role of protons. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90027-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexel R., Siegmund S., Schneider H. J., Linzen B., Gielens C., Préaux G., Lontie R., Kellermann J., Lottspeich F. Complete amino-acid sequence of a functional unit from a molluscan hemocyanin (Helix pomatia). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Jun;368(6):617–635. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.1.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Sakurai H., Izumi S., Tomino S. Structure of the gene for the arylphorin-type storage protein SP 2 of Bombyx mori. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11020–11025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Genes-in-pieces revisited. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):823–824. doi: 10.1126/science.4001923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Hohn T. Activity of empty, headlike particles for packaging of DNA of bacteriophage lambda in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2372–2376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber M., Hintermann G., Lerch K. Primary structure of tyrosinase from Streptomyces glaucescens. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6038–6044. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jekel P. A., Bak H. J., Soeter N. M., Vereijken J. M., Beintema J. J. Panulirus interruptus hemocyanin. The amino acid sequence of subunit b and anomalous behaviour of subunits a and b on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of SDS. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 15;178(2):403–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang W. H. cDNA cloning of the Octopus dofleini hemocyanin: sequence of the carboxyl-terminal domain. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7276–7282. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch K. Amino acid sequence of tyrosinase from Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3635–3639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzen B., Soeter N. M., Riggs A. F., Schneider H. J., Schartau W., Moore M. D., Yokota E., Behrens P. Q., Nakashima H., Takagi T. The structure of arthropod hemocyanins. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):519–524. doi: 10.1126/science.4023698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewe R., Linzen B. Haemocyanins in spiders, I. Subunits and stability region of Dugesiella californica haemocyanin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Feb;354(2):182–188. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.1.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Ruppert S., Schmid E., Schütz G. Functional analysis of alternatively spliced tyrosinase gene transcripts. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2723–2730. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima H., Behrens P. Q., Moore M. D., Yokota E., Riggs A. F. Structure of hemocyanin II from the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. Sequences of the overlapping peptides, ordering the CNBr fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10526–10533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naora H., Deacon N. J. Relationship between the total size of exons and introns in protein-coding genes of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert S., Müller G., Kwon B., Schütz G. Multiple transcripts of the mouse tyrosinase gene are generated by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2715–2722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savel-Niemann A., Markl J., Linzen B. Hemocyanins in spiders. XXII. Range of allosteric interaction in a four-hexamer hemocyanin. Co-operativity and Bohr effect in dissociation intermediates. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):385–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90583-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schartau W., Eyerle F., Reisinger P., Geisert H., Storz H., Linzen B. Hemocyanins in spiders, XIX. Complete amino-acid sequence of subunit d from Eurypelma californicum hemocyanin, and comparison to chain e. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Oct;364(10):1383–1409. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. J., Drexel R., Feldmaier G., Linzen B., Lottspeich F., Henschen A. Hemocyanins in Spiders, XVIII. Complete amino-acid sequence of subunit e from Eurypelma californicum hemocyanin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Oct;364(10):1357–1381. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Parker R. C., Davidson N. Representation of DNA sequences in recombinant DNA libraries prepared by restriction enzyme partial digestion. Gene. 1982 Sep;19(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Stiles J. I., Tye B. K., Chiu P., Sherman F., Wu R. Hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:419–428. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit R., Schneider H. J. Tarantula hemocyanin mRNA. In vitro translation, cDNA cloning and nucleotide sequence corresponding to subunit e. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;159(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willott E., Wang X. Y., Wells M. A. cDNA and gene sequence of Manduca sexta arylphorin, an aromatic amino acid-rich larval serum protein. Homology to arthropod hemocyanins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19052–19059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holde K. E., Miller K. I. Haemocyanins. Q Rev Biophys. 1982 Feb;15(1):1–129. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]