Abstract
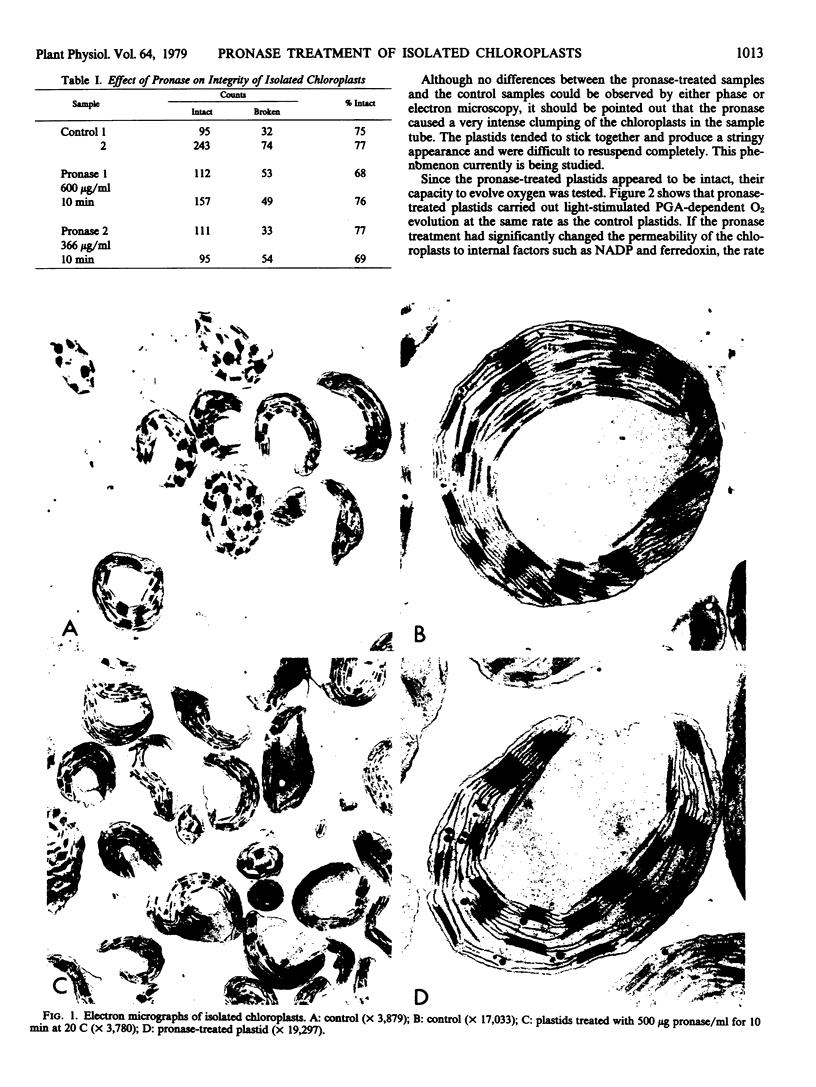
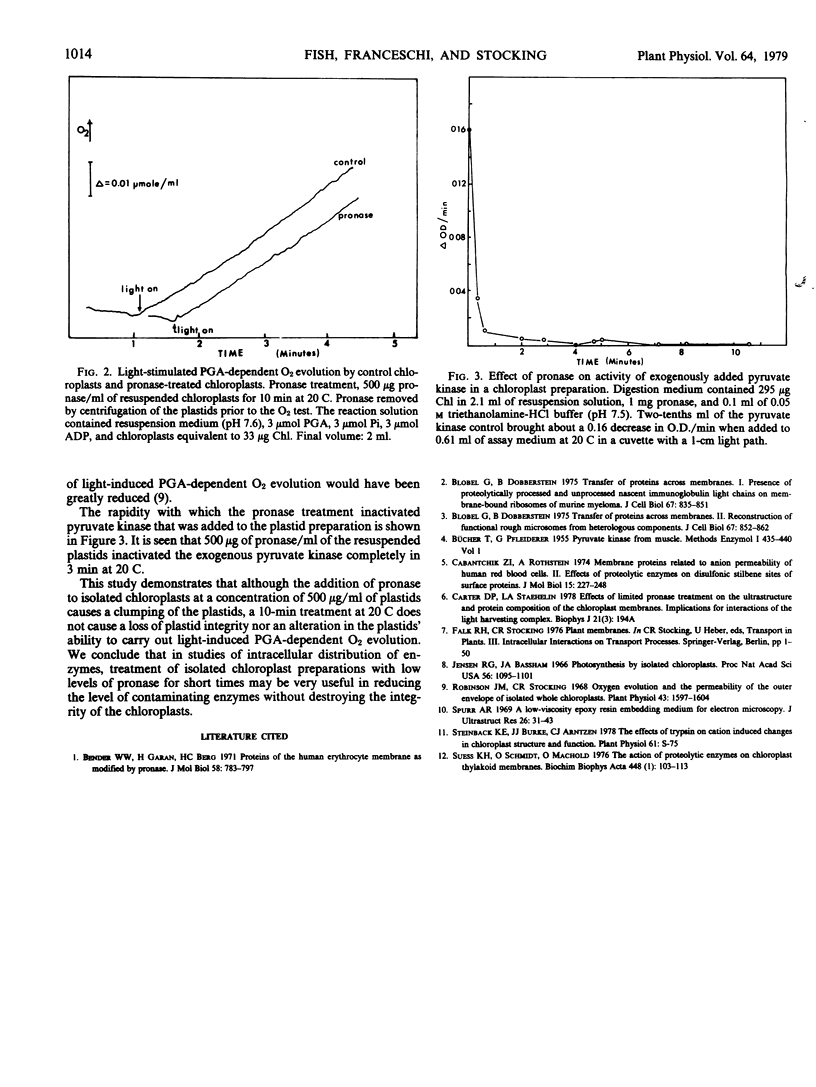
Subjecting isolated spinach chloroplasts to mild proteolysis (10-minute incubation at 20 C in 500 micrograms per milliliter pronase) caused chloroplast clumping but did not affect their integrity as measured by their ability to carry out light stimulated, glycerate-3-P-dependent O2 evolution. Transmission electron microscopy revealed no detectable differences between the control and treated plastids. Mild proteolysis inactivated exogenously added pyruvate kinase and should be a useful technique in certain enzyme distribution studies.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender W. W., Garan H., Berg H. C. Proteins of the human erythrocyte membrane as modified by pronase. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):783–797. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. II. Reconstitution of functional rough microsomes from heterologous components. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):852–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. Membrane proteins related to anion permeability of human red blood cells. II. Effects of proteolytic enzymes on disulfonic stilbene sites of surface proteins. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(3):227–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01870089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. G., Bassham J. A. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. M., Stocking C. R. Oxygen evolution and the permeability of the outer envelope of isolated whole chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1968 Oct;43(10):1597–1604. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.10.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Süss K. H., Schmidt O., Machold O. The action of proteolytic enzymes on chloroplast thylakoid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 21;448(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]