Abstract
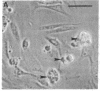
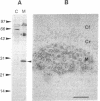
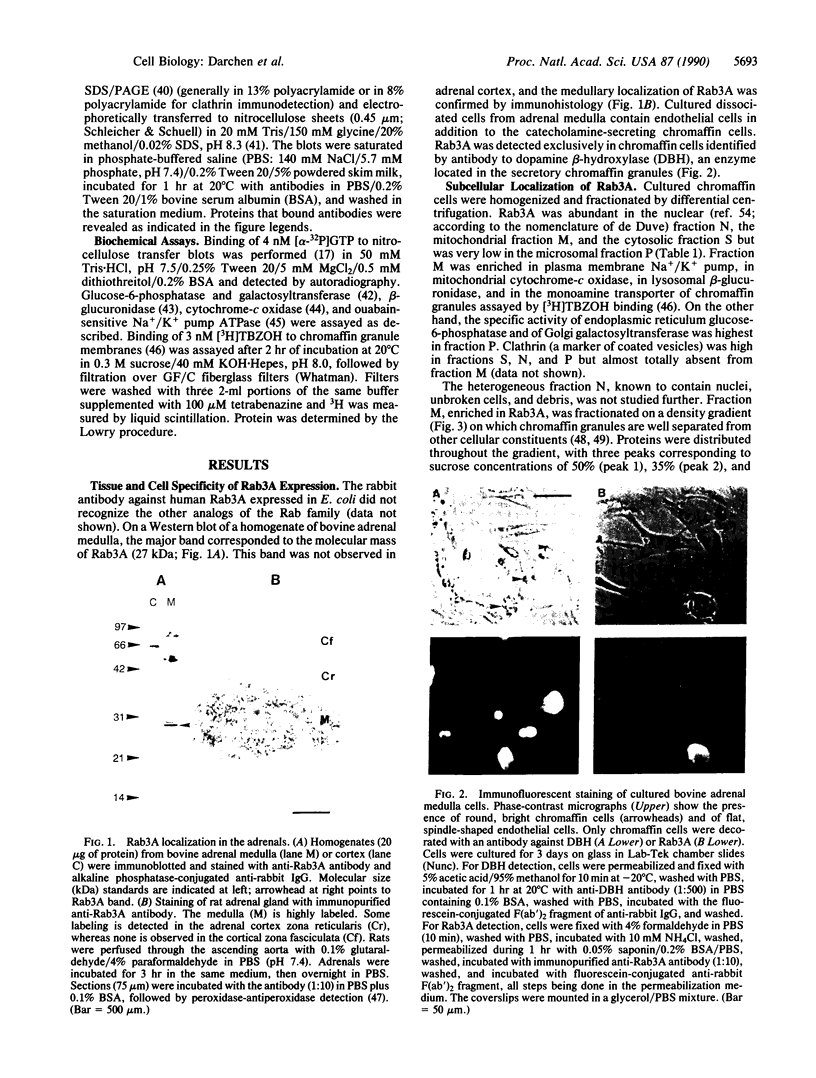
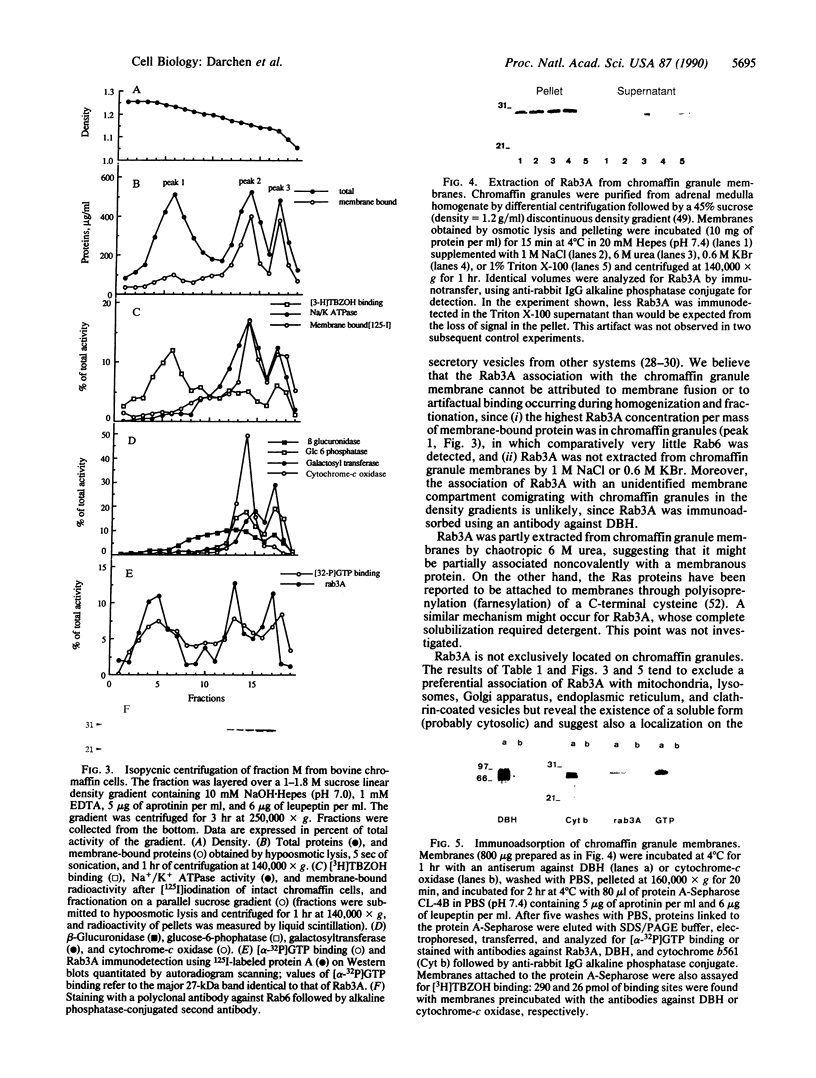
The Rab3A protein belongs to a large family of small GTP-binding proteins that are present in eukaryotic cells and that share amino acid identities with the Ras proteins (products of the ras protooncogenes). Rab3A, which is specifically located in nervous and endocrine tissues, is suspected to play a key role in secretion. Its localization was investigated in bovine adrenal gland by using a polyclonal antibody. Rab3A was detected in adrenal medulla but not in adrenal cortex. In cultured adrenal medulla cells. Rab3A was specifically expressed in the catecholamine-secreting chromaffin cells. Subcellular fractionation suggested that Rab3A is about 30% cytosolic and that particulate Rab3A is associated with the membrane of chromaffin granules (the catecholamine storage organelles) and with a second compartment likely to be the plasma membrane. The Rab3A localization on chromaffin granule membranes was confirmed by immunoadsorption with an antibody against dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Rab3A was not extracted from this membrane by NaCl or KBr but was partially extracted by urea and totally solubilized by Triton X-100, suggesting either an interaction with an intrinsic protein or a membrane association through fatty acid acylation. This study suggests that Rab3A, which may also be located on other secretory vesicles containing noncharacterized small GTP-binding proteins, is involved in their biogenesis or in the regulated secretion process.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar-Costesec A., Beaufay H., Wibo M., Thinès-Sempoux D., Feytmans E., Robbi M., Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. II. Preparation and composition of the microsomal fraction. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):201–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apps D. K., Pryde J. G., Sutton R. Characterization of detergent-solubilized adenosine triphosphatase of chromaffin granule membranes. Neuroscience. 1983 Jul;9(3):687–700. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayala J., Olofsson B., Touchot N., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A., Prochiantz A. Developmental and regional expression of three new members of the ras-gene family in the mouse brain. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Apr;22(4):384–389. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLASCHKO H., HAGEN J. M., HAGEN P. Mitochondrial enzymes and chromaffin granules. J Physiol. 1957 Dec 3;139(2):316–322. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader M. F., Sontag J. M., Thiersé D., Aunis D. A reassessment of guanine nucleotide effects on catecholamine secretion from permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16426–16434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaufay H., Amar-Costesec A., Feytmans E., Thinès-Sempoux D., Wibo M., Robbi M., Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. I. Biochemical methods. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):188–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaufay H., Amar-Costesec A., Thinès-Sempoux D., Wibo M., Robbi M., Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. 3. Subfractionation of the microsomal fraction by isopycnic and differential centrifugation in density gradients. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):213–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A. Low molecular mass GTP-binding proteins of adrenal chromaffin cells are present on the secretory granule. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein E., Macara I. G. The ras-like protein p25rab3A is partially cytosolic and is expressed only in neural tissue. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4807–4811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Tavitian A. The ral gene: a new ras related gene isolated by the use of a synthetic probe. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2203–2208. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Howell T. W., Gomperts B. D. Two G-proteins act in series to control stimulus-secretion coupling in mast cells: use of neomycin to distinguish between G-proteins controlling polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2745–2750. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet J. P., Fournier S., Parulekar M., Trifaró J. M. Detection of low molecular mass GTP-binding proteins in chromaffin granules and other subcellular fractions of chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 10;247(1):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Fajdiga P. B., Howe N. B., Livett B. G. Functional and morphological characterization of isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jan;76(1):12–30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. A GTP-binding protein required for secretion rapidly associates with secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):753–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A., Saraste J. Small GTP-binding protein associated with Golgi cisternae. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):553–556. doi: 10.1038/345553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder R., Bönisch H. Large-scale preparation of plasma membrane vesicles from PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells and their use in noradrenaline transport studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 8;775(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata M., Matsui Y., Kondo J., Hishida T., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. A novel small molecular weight GTP-binding protein with the same putative effector domain as the ras proteins in bovine brain membranes. Purification, determination of primary structure, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18965–18971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Yamashita T., Kawata M., Yamamoto K., Ikeda K., Tanimoto T., Takai Y. Purification and characterization of a novel GTP-binding protein with a molecular weight of 24,000 from bovine brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2897–2904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., von Grafenstein H., Athayde C. M. Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent exocytosis. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Lacal J. C., Reep B. R., Molina y Vedia L. A ras-related protein is phosphorylated and translocated by agonists that increase cAMP levels in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3131–3134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R. A novel ras-related gene family. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maly K., Uberall F., Loferer H., Doppler W., Oberhuber H., Groner B., Grunicke H. H. Ha-ras activates the Na+/H+ antiporter by a protein kinase C-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11839–11842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Kikuchi A., Kondo J., Hishida T., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of a GTP-binding protein family with molecular weights of 25,000 from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11071–11074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Glick B. S., Malhotra V., Weidman P. J., Serafini T., Gleason M. L., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Involvement of GTP-binding "G" proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi A., Kim S., Ueda T., Takai Y. Tissue distribution of smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, studied by use of a specific monoclonal antibody. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1438–1445. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90835-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson B., Chardin P., Touchot N., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A. Expression of the ras-related ralA, rho12 and rab genes in adult mouse tissues. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Neher E. The patch-clamp technique in the study of secretion. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Apr;12(4):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Müller M., De Duve C. Lysosomes of the arterial wall. I. Isolation and subcellular fractionation of cells from normal rabbit aorta. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1117–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizon V., Chardin P., Lerosey I., Olofsson B., Tavitian A. Human cDNAs rap1 and rap2 homologous to the Drosophila gene Dras3 encode proteins closely related to ras in the 'effector' region. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polakis P. G., Snyderman R., Evans T. Characterization of G25K, a GTP-binding protein containing a novel putative nucleotide binding domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91615-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Kikuchi A., Matsui Y., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Tissue-specific expression of a novel GTP-binding protein (smg p25A) mRNA and its increase by nerve growth factor and cyclic AMP in rat pheochromocytoma PC-12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 31;158(2):377–385. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherman D., Jaudon P., Henry J. P. Characterization of the monoamine carrier of chromaffin granule membrane by binding of [2-3H]dihydrotetrabenazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):584–588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N., Mulholland J., Botstein D. The yeast GTP-binding YPT1 protein and a mammalian counterpart are associated with the secretion machinery. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90433-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell J. L., Kahn R. A. Sequences of the bovine and yeast ADP-ribosylation factor and comparison to other GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. A simple method for the isolation of adrenal chromaffin granules on a large scale. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):480–482. doi: 10.1042/bj1030480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamanoi F. Yeast RAS genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 3;948(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(88)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8210–8214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N. C., Goud B., Kabcenell A. K., Novick P. J. Mutational analysis of SEC4 suggests a cyclical mechanism for the regulation of vesicular traffic. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1685–1693. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Kim S., Kikuchi A., Takai Y. Multiple small molecular weight GTP-binding proteins in bovine brain cytosol. Purification and characterization of a 24KDa protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahraoui A., Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. The human Rab genes encode a family of GTP-binding proteins related to yeast YPT1 and SEC4 products involved in secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12394–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]