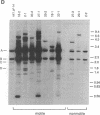
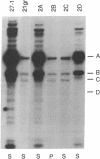
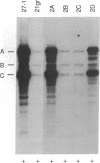
Abstract
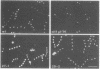
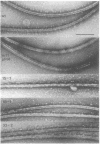
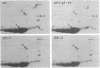
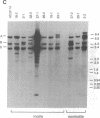
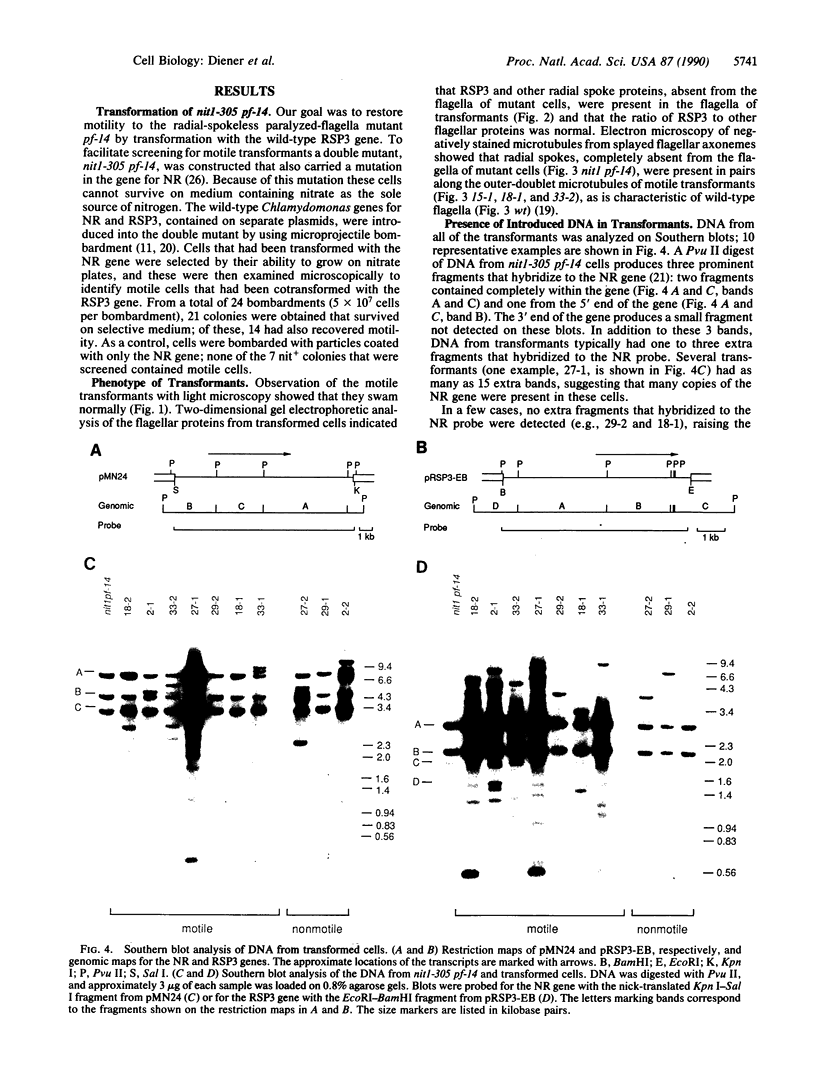
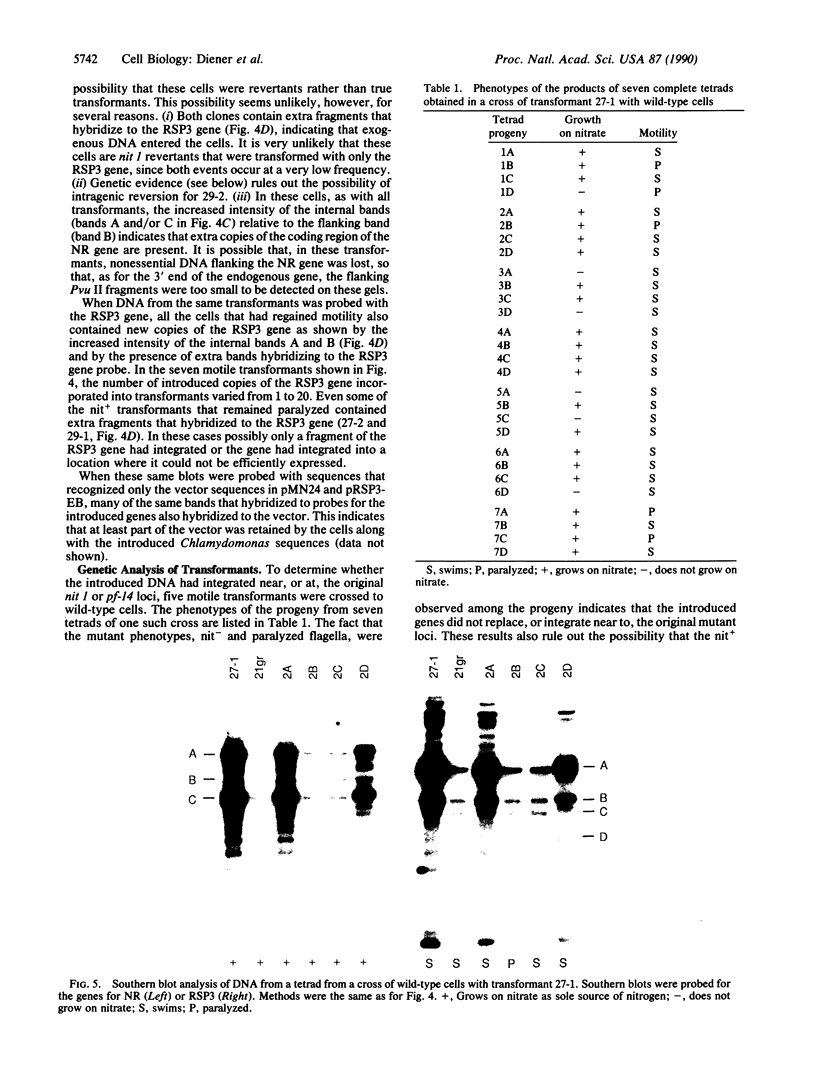
The biflagellate alga Chlamydomonas has been used extensively in the genetic and biochemical analysis of flagellar assembly and motility. We have restored motility to a paralyzed-flagella mutant of Chlamydomonas by transforming with the corresponding wild-type gene. A nitrate reductase-deficient paralyzed-flagella strain, nit1-305 pf-14, carrying mutations in the genes for nitrate reductase and radial spoke protein 3, was transformed with wild-type copies of both genes. Two-thirds of the cells that survived nitrate selection also regained motility, indicating that they had been transformed with both the nitrate reductase and radial spoke protein 3 genes. Transformants typically contained multiple copies of both genes, genetically linked to each other, but not linked to the original mutant loci. Complementation of paralyzed-flagella mutants by transformation is a powerful tool for investigating flagellar assembly and function.
Full text
PDF
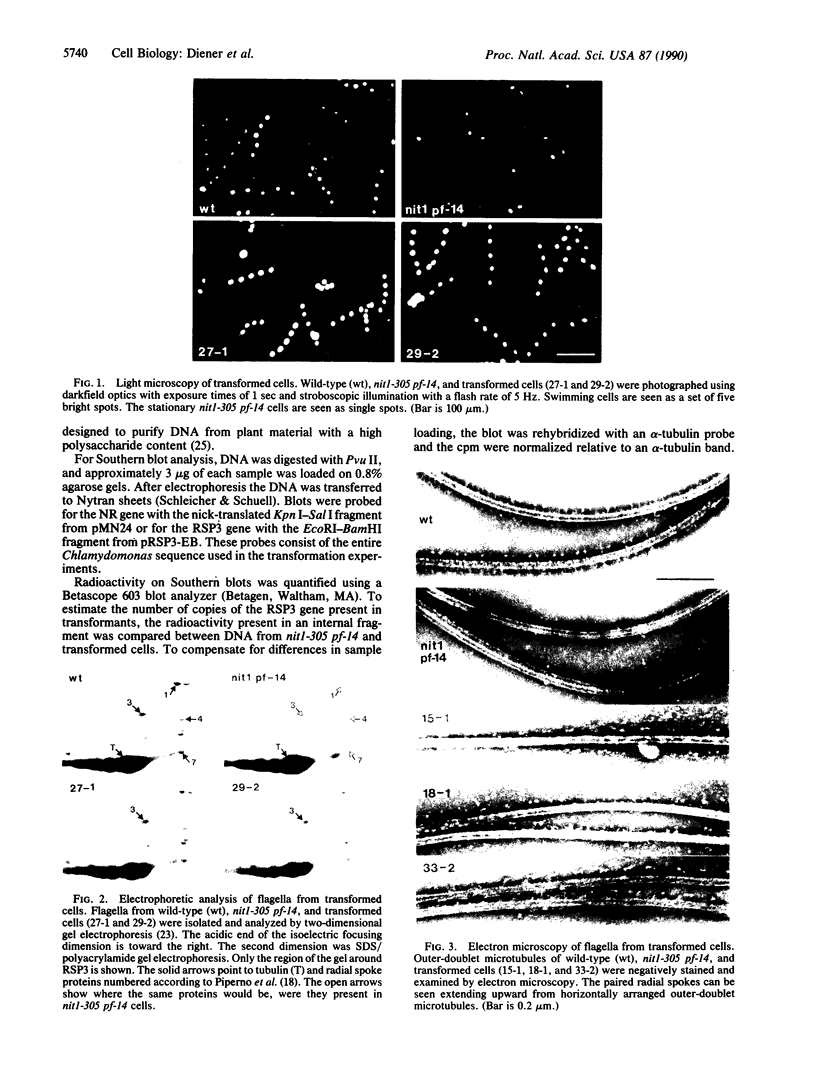

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolduc C., Lee V. D., Huang B. Beta-tubulin mutants of the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):131–135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brokaw C. J., Kamiya R. Bending patterns of Chlamydomonas flagella: IV. Mutants with defects in inner and outer dynein arms indicate differences in dynein arm function. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8(1):68–75. doi: 10.1002/cm.970080110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brokaw C. J., Luck D. J., Huang B. Analysis of the movement of Chlamydomonas flagella:" the function of the radial-spoke system is revealed by comparison of wild-type and mutant flagella. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):722–732. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debuchy R., Purton S., Rochaix J. D. The argininosuccinate lyase gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: an important tool for nuclear transformation and for correlating the genetic and molecular maps of the ARG7 locus. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2803–2809. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Flagellar elongation and shortening in Chlamydomonas. III. structures attached to the tips of flagellar microtubules and their relationship to the directionality of flagellar microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):747–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández E., Schnell R., Ranum L. P., Hussey S. C., Silflow C. D., Lefebvre P. A. Isolation and characterization of the nitrate reductase structural gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6449–6453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough U. W., StClair H. S. BALD-2: a mutation affecting the formation of doublet and triplet sets of microtubules in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):480–491. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Ramanis Z., Dutcher S. K., Luck D. J. Uniflagellar mutants of Chlamydomonas: evidence for the role of basal bodies in transmission of positional information. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):745–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90436-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik J. W., Chojnacki B. Flagellar morphology in stumpy-flagella mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Protozool. 1985 Nov;32(4):649–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R. Mutations at twelve independent loci result in absence of outer dynein arms in Chylamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2253–2258. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L. High-frequency nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1228–1232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Schnell R. A., Fernández E., Lefebvre P. A. Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas using the Chlamydomonas gene for nitrate reductase. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2589–2601. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchka M. R., Jarvik J. W. Analysis of flagellar size control using a mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a variable number of flagella. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):170–175. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Hernault S. W., Rosenbaum J. L. Chlamydomonas alpha-tubulin is posttranslationally modified in the flagella during flagellar assembly. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):258–263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield S. P., Kindle K. L. Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using a C. reinhardtii gene as the selectable marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2087–2091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVittie A. Flagellum mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Aug;71(3):525–540. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-3-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. R., Rosenbaum J. L. A motile Chlamydomonas flagellar mutant that lacks outer dynein arms. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1228–1234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Huang B., Ramanis Z., Luck D. J. Radial spokes of Chlamydomonas flagella: polypeptide composition and phosphorylation of stalk components. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):73–79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Chisholm R. L., Conner T. W., Ranum L. P. The two alpha-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi code for slightly different proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2389–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. P., Beerman N., Griffith O. M. A small-scale five-hour procedure for isolating multiple samples of CsCl-purified DNA: application to isolations from mammalian, insect, higher plant, algal, yeast, and bacterial sources. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90423-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. D., Mitchell D. R., Rosenbaum J. L. Molecular cloning and expression of flagellar radial spoke and dynein genes of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):1–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. D., Velleca M. A., Curry A. M., Rosenbaum J. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the Chlamydomonas gene coding for radial spoke protein 3: flagellar mutation pf-14 is an ochre allele. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):235–245. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B., Plummer J., Sander G. Chlamydomonas flagellar mutants lacking radial spokes and central tubules. Structure, composition, and function of specific axonemal components. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):729–747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngblom J., Schloss J. A., Silflow C. D. The two beta-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii code for identical proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2686–2696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]