ABSTRACT
Enteric pathogens of the family Enterobacteriaceae colonize various niches within animals and humans in which they compete with intestinal commensals and are attacked by the host immune system. To survive these hostile environments they possess complex, multilayer regulatory networks that coordinate the control of virulence factors, host-adapted metabolic functions and stress resistance. An important part of these intricate control networks are RNA-based control systems that enable the pathogen to fine-tune its responses. Recent next-generation sequencing approaches revealed a large repertoire of conserved and species-specific riboregulators, including numerous cis- and trans-acting non-coding RNAs, sensory RNA elements (RNA thermometers, riboswitches), regulatory RNA-binding proteins and RNA degrading enzymes which regulate colonization factors, toxins, host defense processes and virulence-relevant physiological and metabolic processes. All of which are important cues for pathogens to sense and respond to fluctuating conditions during the infection. This review covers infection-relevant riboregulators of E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella and Yersinia, highlights their versatile regulatory mechanisms, complex target regulons and functions, and discusses emerging topics and future challenges to fully understand and exploit RNA-based control to combat bacterial infections.
KEYWORDS: CsrA, gene regulation, regulated RNA degradation, regulatory RNAs, riboswitches, RNA thermometers, virulence
Introduction
The large family of Enterobacteriaceae includes various harmless commensals but also many well-characterized enteric pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, Shigella flexneri, and Yersinia enterocolitica/Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. They colonize and replicate within the intestinal tract of mammals and have the ability to invade deeper tissues. Enteric pathogens of these species are frequently cycling between different environmental and animal reservoirs, and the human host. To adapt to these rapidly changing virulent, commensal and saprophytic lifestyles, they evolved numerous survival strategies that enable them (i) to adjust the expression of host-specific colonization factors and other virulence-relevant traits, (ii) to reprogram their metabolism in response to the changing temperature and availability of nutrients and ions, and (iii) to control their stress responses and overall physiology to encounter hazardous conditions experienced in- and outside their hosts. Complex regulatory networks coordinate the spatiotemporal expression of their survival strategies. Over the last decades numerous conserved and species-specific regulatory proteins have been identified in enteric pathogens that are implicated in virulence control networks. However, recent advances in high-throughput sequencing approaches now allow us to profile entire RNA landscapes with single nucleotide resolution. This has led to the discovery of numerous regulatory non-coding RNAs. Obviously, control of virulence is much more complex than ever imagined and often occurs on multiple layers of post-transcriptional control.
The discovered riboregulation control processes involve riboregulators such as cis- and trans-acting non-coding RNA elements (ncRNAs), RNA thermometers, and riboswitches, as well as regulatory RNA-binding proteins and RNA degrading or modifying enzymes. Many of which respond to fluctuating environmental conditions encountered during the course of infection. This review will focus on the mechanistic actions of endogenous RNA-based processes by these regulators, which serve as crucial components of virulence control networks in enteric pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae.
Molecular mechanisms underlying RNA-based control of virulence
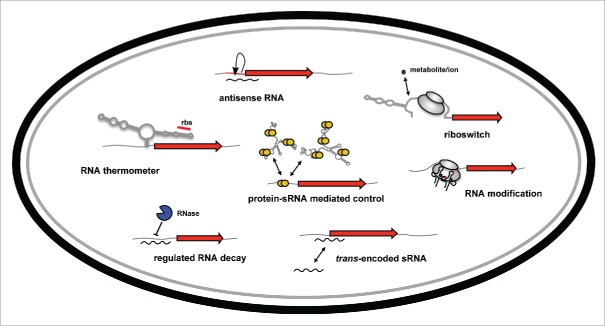
The molecular mechanisms underlying RNA-based control of virulence gene expression are very versatile (Fig. 1), but can share remarkable similarities between related species. Sensory and regulatory RNA elements operate at different levels of gene expression, ranging from the regulation of transcription and translation, control of RNA conformation, RNA stability, adjustment of replicon copy numbers, and the modulation of protein binding to RNAs/DNAs and activity.1,2
Figure 1.
Overview of RNA-based control mechanisms employed by enteric pathogens of the family Enterobacteriaceae. mRNA translation can be controlled by RNA thermometers and by riboswitches within the 5′-UTR of target mRNAs in response to temperature or metabolites. Transcription, translation and/or stability of target transcripts can be modulated by cis-encoded asRNAs or trans-encoded ncRNAs. The RNA-binding protein CsrA modulates mRNA expression by interfering with translational initiation. The CsrB and CsrC RNAs counteract its activity. RNases control processing and degradation of ncRNAs and target transcripts. RNA-modifying enzymes change the efficiency of translation.
Recent advances in next generation sequencing technologies have provided us with large repertoires of newly identified ncRNAs of different enteric pathogens.3-9 ncRNAs of Enterobacteriaceae are generally 50-400 nucleotides in lengths and are usually not translated. The vast majority of ncRNAs basepairs with one or multiple target mRNAs and influences distinct or numerous processes important for housekeeping functions, virulence regulation and the response to environmental challenges. A subset of the identified ncRNAs is encoded on the opposite strand of the regulated target mRNA (cis-encoded antisense RNAs/asRNAs) or is transcribed from a distant gene (trans-encoded ncRNA). The asRNAs are mostly encoded opposite to the un-translated regions of a gene and lead to autonomous RNA-RNA interactions that block ribosome-binding and translation. Alternatively, RNA-RNA duplex formation can affect the stability of the targeted mRNA through alterations of its secondary structure.3 The trans-encoded ncRNAs act mainly by base-pairing to ribosome-binding sites or start codons of their target mRNAs to which they usually have only limited complementarity.10 Most of the characterized trans-encoded ncRNAs interact with multiple target mRNAs with the assistence of the RNA chaperone Hfq 11 and act in concert with RNases that cleave the target mRNA and control its half-life.12,13
Other types of riboregulators are RNA thermometers,14,15 and riboswitches.16 These sensory RNA elements are found in the 5′-untranslated regions (5′-UTRs) or within intergenic regions, and control expression of the downstream gene through structural remodeling of the RNA segment. RNA thermometers typically respond to sudden thermal changes, a key signal sensed by enteric pathogens to detect host entry and activate relevant virulence programs. Currently several RNA thermometers of pathogens are known which act as thermo-responsive RNA zippers that control translation via RNA structure destabilization or alteration. They all form thermo-sensitive stem-loop structures at moderate (environmental) temperatures (‘closed’ conformation) in which the ribosome-binding site is hidden within the stem of the hairpin structure. The stem segment constitutes the thermosensing stretch of the RNA element. It typically includes internal bulges and/or non-canonical base pairs that decrease its stability and make it more susceptible to thermo-triggered zipper-like melting upon host entry. Gradual opening of the double-stranded segment of the RNA thermometer (‘open’ conformation) renders the ribosome-binding site accessible for the 30S subunit to initiate translation. This simple thermo-responsive mechanism allows a very rapid, extremely precise (range within the 1°C scale) and low/no energy-consuming adjustment of virulence factor synthesis without the need for additional factors and costly feedback loops to prevent uncontrolled hyper-induction.
In contrast to RNA thermometers, bacterial riboswitches represent sensory RNA elements that respond to varying metabolite or metal ion concentrations. Riboswitches typically regulate expression of protein-encoding mRNAs, but recently they have also been shown to control the expression of non-coding RNAs and regulate binding of proteins, e.g. the ribonuclease E (RNase E) or the transcriptional termination factor Rho to nascent RNAs.17,18 Riboswitches sense different metal ions (e.g., Mg2+, Mn2+, fluoride), metabolites (e.g., vitamin B12, S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), thiamine pyrophosphate, flavin mononucleotide) or signaling molecules (e.g. c-di-GMP). Binding of these molecules to an evolutionary conserved ligand binding segment (sensor region) leads to the formation of an alternative molecule-bound RNA conformation which influences expression of the coding sequences located downstream. The set of regulated downstream genes mainly includes biosynthesis and transport systems of equivalent or related metabolites.19 Hence, the cognate riboswitch ligand does not only act as the stimulating substance, it often represents the end product of the controlled metabolic pathway and is implicated in feed back control.
Besides riboregulators, several global, highly conserved transcription factors and RNA chaperones have been shown to participate in RNA-based control mechanisms of virulence.7,20 One important player in the coordinated control of regulatory RNA function is the RNA chaperone Hfq. The Hfq protein was originally identified in E. coli many decades ago as a host factor essential for the replication of the RNA phage Qβ and has since then been shown to be crucial for virulence of many enteric pathogens.21 Mutants of enteropathogenic Salmonella, E. coli, Yersinia and Shigella species have pleiotropic phenotypes. Lack of Hfq leads to reduced growth rates, altered utilization of nutrients and major changes of the metabolic profile, and dramatically alters expression of pathogenicity factors and virulence-relevant traits which impairs virulence.21 Hfq is ubiquitous and highly conserved among the Enterobacteriaceae where it is implicated in many ncRNA-based control processes, and the molecular mechanisms used by this central RNA manipulator to modulate gene expression are very diverse.22,23 Hfq can act as a matchmaker from ncRNA-mRNA duplexes leading to translational repression, due to steric hindrance of ribosome binding, or to translational activation through disruption of repressive secondary structures. Moreover, Hfq can protect target mRNAs from ribolysis by (i) direct binding or (ii) assistance of ncRNA binding to RNase cleavage sites within the target mRNA.11 Vice versa, Hfq can directly interact with RNases such as RNase E and the target ncRNA or mRNA to trigger formation of a degradosome-like complex that promotes RNA cleavage. Additionally, Hfq can promote 3′ – 5′ degradation of mRNAs by exoribonucleases through 3′-polyadenylation by the poly(A)polymerase.24,25
Another RNA-binding protein that is required for virulence of enteric pathogens is the CsrA protein that belongs to the post-transcriptional carbon storage regulator (Csr) sytem. Similar to Hfq, CsrA is highly conserved between different Enterobacteriaceae and is annotated in many other bacterial genomes.26,27 CsrA has originally been identified in E. coli as a regulator of glycogen biosynthesis. Work over the last 2 decades has revealed that it also plays a crucial role in the regulation of virulence genes and converges them into complex regulatory networks with numerous metabolic functions, stress responses as well as cellular and physiological processes.26,27 CsrA typically interacts with successive GGA motifs located in single-stranded RNA elements of the 5′-UTRs of its target mRNA, which usually includes the GGA motif of the ribosome-binding site. First, sequence-based computational approaches as well as systemic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) and currently also RIP-Seq (RNA immunoprecipitation high-throughput sequencing) and CLIP-Seq (crosslinking immunoprecipitation high-throughput sequencing) analyses were performed to define CsrA targets and CsrA binding sites in individual pathogens. The vast majority of identified binding sites contains GGA motifs within loops of predicted hairpin structures.28-30 CsrA binding to these sites results in the repression of ribosome association and prevents translation initiation and/or transcription elongation, and in many cases also increases the general turnover of the mRNA.27 However, a few examples exist in which CsrA binding to a target mRNA activates gene expression. In this case it has been shown that CsrA stabilizes the target mRNA by protection of the transcript against cleavage by RNases.31 Function of the CsrA regulator protein is controlled by a distinct set of ncRNAs, the so-called Csr-type RNAs.26,27 This type of RNAs shows low sequence conservation. However, all members fold into complex secondary structures with multiple RNA hairpins of which the majority contains a GGA motif within single-stranded loops with conserved base-pairing flanking regions (CAGGA(U/A/C)G).27,32,33 Pathogenic E. coli, Salmonella and Yersinia species encode at least 2 CsrA-sequestering RNAs, CsrB and CsrC,27,34, 35 which carry several of the high-affinity CsrA-binding sites. This enables them to bind multiple CsrA homodimers and to sequester/titrate them away from their specific positions on their natural mRNA targets.32
Long-time focus on transcription initiation generated a view that prokaryotic gene expression is primarily controlled at the ‘birth’ of an mRNA, mRNA processing and degradation was mostly considered to be responsible for the fast functional trimming and turnover of transcripts. Several ribonucleases (RNases) involved in mRNA turnover were identified and the classical principles how they mediate mRNA degradation in prokaryotes are known. However, recent studies showed that the level and activity of individual RNases as well as the composition of the RNA degrading machinery can vary significantly under different growth/infection conditions.36,37 Moreover, there is a burgeoning list of examples that RNase activity can be modulated by adaptor proteins, and a plethora of small non-coding RNAs have been discovered which can confer target selectivity to prokaryotic RNases.38 Furthermore, the cellular localization of the RNA-degrading complexes seems to vary under different environmental conditions, and a fascinating new observation of spatial distribution patterns of the microbial mRNA species strongly suggests that microbes organize mRNA decay in time and space.39,40 Our knowledge about the environmental signals and regulators that control mRNA decay is still in its infancy, but recent studies have undoubtedly shown that ‘regulated ribolysis’ is a crucial control mechanism for the expression of virulence factors in enteric pathogens.
The aim of the following chapter is to highlight the importance of RNA-mediated regulatory mechanisms for host-pathogen interactions and other virulence-relevant processes, dictating the progress of an intestinal infection. A selection of the most important virulence processes under RNA-based control and implicated sensory and regulatory control factors are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Examples of virulence processes under RNA-based control.
| Species | RNA/RNase/RNA-modifying enzyme | Mechanism | Virulence function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | AfaR | trans-encoded ncRNA destabilizes the afaD mRNA by binding to the 5′-UTR | Regulation of expression of afimbrial adhesins of the Afa family in ExPEC | 64 |
| CsrABC | CsrA: RNA binding protein, CsrB/CsrC: trans-encoded CsrA-binding RNAs CsrA binds to the LEE4 mRNA, overexpression of CsrA represses expression of the LEE1-5 transcripts through a reduction of GrlA and Ler in EPEC CsrA binds to the 5′-UTR of the pga mRNA encoding biofilm matrix components CsrA directly binds and stabilizes the flhDC transcript | Global control of pathogenesis (colonization, immune resistance), stress responses and metabolism. Expression of type 1 fimbriae and Pef fimbriae. Control of c-di-GMP synthesis Important for pedestal formation and for membrane depolarization of epithelial cells, in EHEC, Control of biofilm formation and motility | 26,27,31,52 | |
| GadY | trans-encoded ncRNA interacts with 3′-UTR of the gadY transcript in the gadX-gadY mRNA which stimulates processing into stable gadX and gadY transcripts | Glutamate-dependent extreme acid resistance | 136 | |
| GcvB | trans-encoded ncRNA Hfq-dependent a 30 nt stretch of G/U residues of GcvB recognize extended C/A elements overlapping the ribosome binding site in some targets acts by direct antisense interaction with the csgD 5′-UTR | Repression of curli biogenesis. Regulation of ABC transporters and amino acid biosynthesis genes | 44 | |
| GlmY, GlmZ | trans-encoded ncRNAs destabilization of mRNA transcripts and facilitation of translation | Control of pathogenesis, regulation of the LEE4 and LEE5 operons, the LEE-encoded effector EspFu and the non-LEE-encoded effector NleA in EHEC, promote expression of the curli adhesin, repress tryptophan metabolism genes, and promote acid resistance | 46-48,53 | |
| McaS | trans-encoded ncRNA resembles CsrB and sequestrates CsrA, represses in collaboration with Hfq expression of the transcriptional activator gene csgD and activates the flhDC gene | Repression of curli biogenesis, Activation of flagella synthesis | 44 | |
| OmrA, OmrB | trans-encoded ncRNAs sibling ncRNA encoded in tandem, act by direct antisense interaction with the respective 5′-UTR, Hfq-dependent, highly redundant functions | Regulation of curli formation, motility and iron sequestration. Regulation of outer membrane proteins implicated in iron metabolism/uptake (CirA, FecA, FepA) and protein degradation (OmpT) | 44 | |
| sRNA103 | trans-encoded ncRNA activates expression of the transcriptional activator gene fimZ | Expression of type 1 fimbriae and the filament protein EspA of the T3SS in EHEC | 48 | |
| RyhB | trans-encoded ncRNA acts through direct base-pairing with target mRNAs, Hfq-dependent | Regulation of iron metabolism and other iron-containing proteins, production of siderophores | 121 | |
| 5′-UTR-chuA | FourU RNA thermometer | Iron uptake in EPEC | 132 | |
| GidA | tRNA-modifying enzyme | Regulation of the cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1) | 69 | |
| VacC | tRNA-guanine glycolase | Enhances expression of the Shigella T3SS effectors IpaB, IpaC and IpaD, reduces amounts of VirG important for cell-to-cell spreading of EIEC | 67 | |
| Salmonella | CsrABC | CsrA: RNA binding protein, CsrB/CsrC: CsrA-binding RNAs CsrA directly binds and stabilizes the flhDC and the fliA transcript | Regulation of expression of type 1 and Pef fimbrae, regulation of SPI-1 gene expression via translational repression of the SPI-1 regulator HilD, control of motility and biofilm formation, regulation of c-di-GMP synthesis | 49,50,54 |
| IsrJ | unknown | Regulation of invasion and SPI-1 effector translocation | 65 | |
| IsrM | trans-encoded ncRNA reduces mRNA stability by binding to the 5′-UTR of its target mRNA | Control of SPI-1 gene expression by regulation of the global SPI-1 regulator HilE and the effector SopA | 66 | |
| LesR-1 | antisense RNA interacts with the 3′-UTR of PSLT047 modulating translation rate | Control of virulence in mice | 87 | |
| RydC | trans-encoded ncRNA folds as a pseudoknot and interacts with Hfq | Control of the yejABEF operon which interferes with MHCI presentation, counteracts antimicrobial peptides and promotes survival and proliferation within the host. Control of the curli adhesin through repression of the major curli regulator CsgD; | 44 | |
| PinT/STnc440 | trans-encoded ncRNA Hfq-dependent | Repression of SPI-2 genes and SPI-1 effector genes (sopE, sopE2), manipulation of host cell pathways to promote replication, important for the transition from the extracellular to the intracellular state, influences regulators of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway (e.g. STAT3), IL-8 production, and mitochondria localization and functions. Colonization in pigs and cattle | 65,79,85 | |
| RaoN | trans-encoded ncRNA | Induced under oxidative stress and nutrient limitation, important for survival in macrophages, controls expression of the lactate dehydrogenase gene ldhA | 135 | |
| RyhB-1, RyhB-2 | trans-encoded ncRNAs Hfq-dependent | Iron homeostasis, oxidative and acidic stress, intracellular growth, redundant functions but RyhB-2 targets some motility genes (flgJ, cheY, and fliF) that are not regulated by RyhB1, and RyhB1 influences safA, acnB expression but not RyhB2 | 129,130 | |
| SgrS | trans-encoded ncRNA Hfq-dependent | Resistance against phosphosugar stress | 60,61 | |
| GidA, MnmE | tRNA-modifying enzymes | Active induction of the T3SS genes invAEG, spaPQ and prgHJ. Control of the oxidoreductase YghA and thiol peroxidase Tpx Important for cell invasion, survival in macrophages and mouse virulence | 68 | |
| PNPase | Polynucleotide phosphorylase | Influence on the expression of the AgfA fibers, the SPI-1 invasion genes, as well as the spv and SPI-2 genes important for macrophage survival, controls the ncRNAs RyhB, SgrS, CsrB and CsrC | 4,12,73,90,105 | |
| Shigella | CsrABC | CsrA: RNA binding protein, CsrB/CsrC: CsrA-binding RNAs | Regulation of attachment and invasion via control of the regulators VirF and VirB | 55 |
| RnaG | antisense RNA to icsA, expression leads to premature termination of icsA transcription | Control of host colonization by repression of the IcsA invasion protein | 62,63 | |
| RyhB | trans-encoded ncRNA acts through direct base-pairing with target mRNAs, Hfq-dependent | Regulation of invasion and cell-to-cell spreading via control of VirB synthesis, acid resistance | 123-125,127 | |
| 5′-UTR-shuA | FourU RNA thermometer | Iron uptake | 126,132 | |
| RNase R | ribonuclease | Synthesis of the T3SS effector proteins IpaB, IpaC and IpaD | 72 | |
| VacC | tRNA-guanine glycolase tRNA-modifying enzyme | Enhances expression of the Shigella T3SS effectors IpaB, IpaC and IpaD, reduces amounts of VirG important for cell-to-cell spreading | 67 | |
| Yersinia | CsrABC | CsrA: RNA binding protein, CsrB/CsrC: CsrA-binding RNAs | Contribute to attachment and invasion via regulation of global regulators of invasion factors (e.g.(e.g., InvA, PsaA/pH6 antigen), Control of biofilm formation and motility Regulation of c-di-GMP synthesis | 26,35 |
| Ysr29 | trans-encoded ncRNA | Specific to the Y. pseudotuberculosis strain IP32953, important for the virulence in a mouse model of Yersiniosis, represses synthesis of glutathione-S transferase (GST) and activates production of RpsA, OmpA and GroEL | 5,6,134 | |
| Ysr35 | trans-encoded ncRNA | Survival in a Yersiniosis mouse model | 5 | |
| Ysr141 | trans-encoded ncRNA acts through base-pairing with the yopJ 5′-UTR | Regulation of T3SS components (YopE, YscF, YopK, YopJ) and the T3SS activator LcrF | 5,117 | |
| RyhB-1, RyhB-2 | Hfq-dependent trans-encoded ncRNA | Iron homeostasis | 122,131 | |
| YopD/LcrH | YopD: RNA-binding protein,interacts with 30S particle of the ribosome LcrF: YopD chaperone YopD-LcrH protein complex binds to the 5′-UTR of target transcripts preventing translation and/or enhancing degradation | Important for T3SS, Yop effector injection, survival of phagocyte attacks | 96,97,99 | |
| LcrQ (YscM1, YscM2) | cooperates with YopD-LcrH complex | Important for T3SS, Yop effector injection, survival of phagocyte attacks | 98 | |
| 5′-UTR-lcrF | FourU RNA thermometer | Control of pathogenesis (T3SS regulation and Yop effector secretion), survival of phagocyte attacks | 94,95 | |
| SsrA (tmRNA) /SmpB | SsrA: aminoacylated SsrA RNA mimicking a tRNA or a mRNA SmpB: RNA binding protein that interacts with SsrA | Important for virulence (regulation of T3SS expression, survival of phagocyte attacks), activation of LcrF expression | 114 | |
| YbeY | single-strand specific endoribonuclease | Important for virulence (regulation of T3SS expression, survival of phagocyte attacks), regulation of LcrF expression | 110 | |
| PNPase RNase E | Ribonucleases part of the degradosome, regulated RNA degradation | Influence on the expression and activity of T3SS, Yop effector injection into host cells, survival of phagocyte attacks. Degradation of the hmsT and pgaABCD transcript, allows rapid regulation of c-di-GMP synthesis and biofilm production | 100-103 |
Riboregulation of enterobacterial virulence
RNA-based control of colonization factors
Control of adhesion
An early step in the pathogenesis of enteric pathogens is their adhesion to the intestinal epithelial layer. The ability of certain bacteria to adhere to host cells is of fundamental importance for a successful colonization since they have to compete with the intestinal microflora and resist the flushing action of the intestinal peristalsis. For this purpose bacterial pathogens usually express a set of different adhesion factors (adhesins) that mediate tight association to intestinal epithelial cells (Fig. 2). Adhesion can be mediated by pili/fimbriae or afimbrial adhesive surface proteins.41 Both types of adhesive structures can be regulated by ncRNA-mediated control mechanisms. For example, multiple ncRNAs have been identified in E. coli to control expression of curli fimbriae (Fig. 2A). They are involved in attachment of the pathogens to host cells as well as abiotic surfaces and are important for biofilm formation.42,43 Six different regulatory ncRNAs repress curli production in response to specific environmental changes by downregulation of the LuxR-type regulator CsgD. The ncRNAs McaS, RydC and GcvB block CsgD synthesis dependent on carbon limitation, nutrient uptake and amino acid supply. The ncRNAs OmrA/OmrB inhibit CsgD production under high osmolarity and RprA under membrane stress conditions.44 They all bind to specific regions within the 5′-UTR of the csgD mRNA, which was described as a hub for signal transduction of multiple ncRNAs and reduce CsgD translation initiation.45 The 2 related regulatory RNAs GlmY and GlmZ activate the translation of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthetase (GlmS), an enzyme important for cell wall biosynthesis.46,47 Recently, they have also been shown to promote expression of genes encoding the curli adhesin in enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC).48 Another EHEC-specific ncRNA (sRNA103) was identified directly downstream of the Shiga toxin-encoding stx2b gene, which regulates synthesis of the transcriptional regulator FimZ, that controls expression of type 1 fimbriae.48 Moreover, the regulatory RNAs CsrB and CsrC, which control the abundance and activity of the RNA-binding protein CsrA, seem to influence the expression of type 1 fimbriae, but also the Pef fimbriae in S. Typhimurium.49,50 Interestingly, the 5′-UTR of the type I fimbrial fimAICDGF polycistronic mRNA is highly abundant. It titrates CsrA from other transcripts (molecular sponge), including the pefA mRNA which is positively regulated by CsrA.49,50 This regulatory system promotes a hierarchical control for expression of different types of fimbriae in response to surrounding conditions dedicated to modulate cell adhesion strength and/or specificity.
Figure 2.
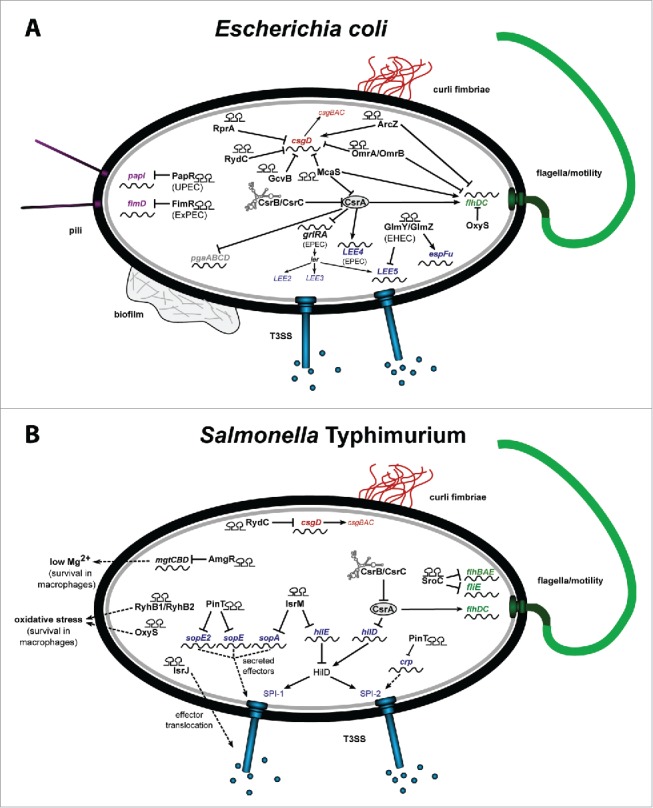
RNA-based control mechanism of E. coli and Salmonella. (A) Riboregulators controlling the colonization factors of pathogenic E. coli important for efficient cell adhesion and invasion. (B) Riboregulators coordinating the expression of Salmonella pathogenicity factors, responsible for cell entry, intracellular persistence and proliferation. The riboregulators are given in black and the target genes in green for flagella biosynthesis, in red for curli formation, in purple for pili production, and in blue for T3SS genes encoded on the pathogenicity islands LEE of EHEC/EPEC (A) or SPI-1 and SPI-2 of Salmonella (B).
Regulation of pedestal formation
Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) and EHEC strains, which cause attaching and effacing (A/E) lesions characterized by disruption of the intestinal microvilli, form special actin-filled membranous protrusions. These structures termed ‘pedestals’ emanate beneath the cell-attached bacteria and are important for pathogenicity. All genes required for pedestal formation are encoded in five 5 polycistronic operons in the pathogenicity island LEE (locus for enterocyte effacement).51 In a recent study, the Csr system was shown to regulate pedestal formation.52 Purified CsrA protein was found to bind to the LEE4-mRNA leader encoding the translocator exporter SepL, and the secreted translocators EspA, EspB and EspD of the type III secretion system (T3SS) machinery that promotes injection of effector molecules to initiate pedestal formation by the host cell. CsrA-binding to the leader segment enhances the steady-state transcript and protein levels. In contrast to single-copy expression, multi-copy expression of CsrA globally repressed expression of the LEE locus (operons LEE1-5), most likely through a reduction of GrlA protein levels. Low GrlA amounts reduce Ler protein levels, which in turn results in a down-regulation of all LEE-encoded operons.52 Moreover, the GlmZ/Y ncRNAs play a role in EHEC pathogenicity as they affect pedestal formation. Both ncRNAs control LEE4 and LEE5 transcripts and the secreted effector EspFu.53
Control of invasion
Following the colonization of the intestinal epithelial tract, the majority of the enteric pathogens penetrates and transmigrates through the intestinal epithelium to colonize subepithelial tissues. This invasion process is generally associated with the synthesis of outer membrane proteins, termed invasins that promote active invasion into epithelial cells. Several ncRNAs have recently emerged as key regulators of these invasion proteins in S. flexneri, Y. pseudotuberculosis and S. Typhimurium. Striking examples are the homologous ncRNAs CsrB and CsrC in Shigella, Salmonella and Yersinia, which positively regulate the expression of the primary invasion genes in all 3 pathogens. In Salmonella, CsrB and CsrC together with CsrA control the translation of the transcriptional activator HilD.54 HilD promotes expression of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1) encoded invasion genes through the master regulator HilA 27,54 (Fig. 2B).
In Yersinia, the CsrABC system controls the expression of the primary cell invasion factor InvA and the afimbrial adhesin PsaA through a regulatory cascade implicating the LysR-type regulator RovM and the virulence master regulator RovA.26,35 Moreover, the CsrABC system was also shown to contribute to the attachment and invasion of S. flexneri into cultured cells and to cell-to-cell spreading.55 Although much less is known about the molecular mechanism, it has been demonstrated that similar to Yersinia and Salmonella influence on invasion was due to decreased expression of the S. flexneri virulence factor regulators VirF and VirB, resulting in decreased production of the Shigella invasion plasmid antigens (Ipa).55,56 In summary, the conserved Csr system is generally located upstream of the species-specific regulator cascades controlling expression of the invasion genes.
Besides the global post-transcriptional control system CsrABC, also other more specific conserved regulatory RNAs can influence the host cell invasion process of Enterobacteriaceae. One example is the ncRNA SgrS, which controls a metabolic stress response (phosphosugar stress resistance) that occurs upon accumulation of certain glycolytic intermediates, e.g., glucose-6-P.57,58 Upregulation of SgrS leads to translation repression and destabilization of several transcripts of metabolic genes and sugar transport, e.g. the ptsG and manXYZ mRNAs.59 Besides all metabolic targets, in S. Typhimurium SgrS is also recruited to the sopD mRNA, encoding an important T3SS effector of SPI-1 that contributes to host cell invasion.60,61 This allows Salmonella to adjust expression of its invasion factors according to the metabolic status of the pathogen. Notably, SgrS is highly selective and does not recognize the duplicated sibling mRNA sopD2 found in some Salmonella isolates. The sopD2 messenger only differs in a single nucleotide within the SgrS binding region.60
In addition, the following species-specific regulatory RNAs control host cell uptake of the enteric pathogens. An antisense RNA called RnaG was discovered to control expression of the icsA/virG mRNA, encoding the IcsA/VirG invasin of S. flexneri. This protein is crucial for cell internalization and cell-to-cell spreading as it induces host actin polymerization, which propels the pathogen from one cell into another.62,63 The RnaG ncRNA can directly bind to the icsA transcript via kissing complexes. This alters the mRNA structure and promotes premature transcriptional termination. Moreover, close convergent location of the rnaG and icsA promoter results in a reduced transcription of the icsA gene through promoter interference, until the activator VirF is produced to enhance icsA transcription.62,63 RnaG is most likely synthesized during the initial stages of the infection when Shigella first reaches sub-epithelial tissues to prevent premature production of IcsA, which may lead to unwanted immune responses.
Furthermore, an Hfq-dependent trans-acting regulatory RNA AfaR (SQ109) of pathogenic E. coli was lately characterized which regulates expression of afimbrial adhesins of the Afa family.64 AfaR interacts with the 5′-UTR of the afaD invasin mRNA. This initiates RNase E-mediated degradation of the transcript, leading to downregulation of AfaD-VIII invasin production in pathogenic E. coli.64 A computational screen and experimental verification identified several unique ncRNA genes encoded within genetic islands in S. Typhimurium.65 Of those a 74 nt ncRNA IsrJ was shown to be activated by the major regulator HilA of the SPI-1 virulence genes and to be required for host cell invasion and effector translocation.65 Another trans-acting ncRNA, IsrM, is implicated in expression of the SPI-1-encoded virulence genes. Salmonella deficient for isrM is impaired in its ability to invade and replicate in human cells and to colonize ileum and spleen of infected mice.66 IsrM targets the 5′-UTR of the mRNA of the SPI-1 effector SopA and the mRNA of HilE, a global regulator of bacterial evasion genes. This demonstrates that the pathogenicity island-encoded ncRNAs seem to function as a distinct class of specific virulence regulators that significantly contribute to pathogenicity.
It is worth mentioning that tRNA-modifying enzymes have been found to play a potential role in the expression of colonization factors of S. enterica and S. flexneri. One example is the VacC protein of S. flexneri, which is homologous to a tRNA-guanine transglycosylase of E. coli. A vacC mutant of Shigella and entero-invasive E. coli (EIEC) is characterized by lower levels of the T3SS proteins IpaB, IpaC and IpaD that are essential for Shigella and EIEC invasion into host cells, and by reduced amounts of VirG, a protein important for cell-to-cell spreading.67 A more detailed analysis indicated that this phenotype is caused by a downregulation of the major virulence regulator VirF.
A more comprehensive investigation was performed with the interacting tRNA modifying enzymes GidA and MnmE. Knock-out mutations in the equivalent genes were shown to significantly reduce the colonization of S. Typhimurium in liver and spleen. This effect can be explained in part by the fact that several colonization genes, including the T3SS genes invAEG, spaPQ and prgHJ important for host cell invasion, were down regulated in the attenuated mutants. However, the overall contribution of both tRNA modifying enzymes to host tissue colonization is certainly greater as they also control expression of several proteins promoting the survival of Salmonella under the stressful conditions experienced within host macrophages, i.e. the oxidoreductase YghA, and the thiol peroxidase Tpx.68 In this context it is further notable that a study by Yu et al.69 reported that the tRNA modifying enzyme GidA inhibits translation of the cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF-1). CNF-1 is an important toxin in meningitis-causing E. coli K1, uropathogenic E. coli strains but also enteric E. coli isolates.70,71 It is likely that tRNA modifying enzymes help the pathogen to fine-tune the synthesis of highly energy-consuming virulence factors under stressful conditions.
Another RNA-based mechanism by which bacteria can alter gene expression to promote host colonization is the regulation of RNA stability. In fact, the ribonuclease R (RNase R) of S. flexneri has been reported to be required for the synthesis of the effector proteins IpaB, IpaC and IpaD.72 In S. Typhimurium the polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) affects the levels of a subset of virulence mRNAs, in particular those encoding the AgfA fibers and the invasion genes of SPI-1.73 However, the precise molecular mechanisms how the RNases target these virulence genes remain to be elucidated.
RNA-mediated suppression of host stresses and immune responses
Regulatory ncRNAs and RNases with impact on intracellular survival and replication of Salmonella
Salmonella strains that passed the intestinal epithelial layer are engulfed and taken up by phagocytic cells of the innate immune system such as macrophages.74,75 S. Typhimurium evades macrophage killing by secreting effector proteins encoded on Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI-2), that generate a special protective membrane-bound compartment, the Salmonella-containing vacuole (SCV). In the SCV Salmonella replicates and is able to form persister cells.76 Use of computational and experimental approaches, including recent RNA-Seq analyses, led to the identification of numerous ncRNAs (> 200) which are expressed or even activated during the infection of murine and human cells.65,77-79 Those ncRNAs might contribute to the regulation of pathogenicity factors during infection, but so far very little is known about their role in virulence. Among the ncRNAs which are strongly up-regulated within macrophages and/or human epithelial cell are the iron-regulated ncRNAs RyhB1/RfrA and RyhB2/RfrB/IsrE (also found to be upregulated in Salmonella Typhi within macrophages),80 as well as the stress-induced ncRNAs OxyS, OmrA, OmrB, MicA, MicF, MicL/RyeF and RybB. Expression changes of these conserved ncRNAs seem to reflect iron-limitation, reactive oxygen species and multiple other stressors experienced within the hostile vacuolar compartment of host cells (see also below). In addition, several other less-characterized ncRNAs were up-regulated in macrophages (STnc440/PinT, STnc470 and STnc3750) and/or human epithelial cells (STnc440/PinT, MgrR, IsrH), whereas others were downregulated (DapZ, STnc270/InvR) corresponding to the induction of the SPI-2 and repression of the SPI-1 encoded genes.65,78,79,81,82 The highest induced 80 nt ncRNA PinT is encoded on a Salmonella-specific horizontally acquired locus. It was found to be controlled by the SPI-2 activating 2-component system PhoP/PhoQ which is crucial for intracellular survival and replication of Salmonella.83 79,84 Most strikingly, this ncRNA was also previously identified as a potential virulence factor of Salmonella in a genome-wide in vivo mutagenesis screen (called TraDIS) in pigs and cattle.85 A dual RNA-Seq time-course of Salmonella-infected cells from humans and pigs, subsequent validation, and pulse-induced expression of PinT demonstrated that this ncRNA represses transcription of the SPI-2 genes very early after host cell invasion. Repression seems to occur upstream of the SPI-2 master regulator SsrB independent of PhoP/PhoQ and HilD, and seems to involve the metabolic global regulator CRP as signal transmitter for PinT-mediated activation of SPI-2.79,86 Interestingly, in addition to a premature activation of SPI-2, the transcripts of the secreted SPI-1 effectors SopE and SopE2 were significantly de-repressed in Salmonella pinT mutants within macrophages. This strongly suggests that PinT plays a crucial role in the transition from extracellular to intracellular life-style after host cell invasion. The elegant dual RNA-Seq approach by Westermann et al. further revealed that PinT-mediated influence on SPI-1 and SPI-2 genes resulted in a differential regulation of key regulators of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and chemokine secretion (e.g., SOC3, STAT3, IL-8).79 Another example of a regulatory RNA that is implicated in the control of intracellular Salmonella is the antisense RNA LesR-1. The lesR-1 gene is encoded on the pSLT virulence plasmid and is preferentially expressed in non-growing dormant bacteria residing within fibroblasts. Direct interaction of the 3′-end of the asRNA to the PSLT047 transcript results in a significant reduction of the PSLT047 protein level, and a deletion of lesR-1 impaired virulence in a mouse infection model.87 Another recently discovered RNA-based mechanism of S. Typhimurium impacts the expression of SPI-2 and the plasmid-encoded spv genes needed for intracellular survival and propagation inside the macrophages of liver and spleen.88,89 The mutational inactivation of the PNPase gene (pnp) resulted in an up-regulation of SPI-2 and the spv genes and this altered the pathogenesis of the infection. Salmonella pnp mutants established more frequently persistent infections in Balb/c mice compared to the wild-type which caused mainly acute systemic infections.73 The exact mechanism is still unknown, but elimination of the spvR regulator gene inhibited expression of the spv gene cluster and affected growth also in the absence of pnp, indicating that PNPase acts upstream or at the level of SpvR.90
Post-transcriptional control mechanisms of Yersinia T3SS/Yop-mediated defense against immune cells
Also pathogenic yersiniae are confronted with phagocytic immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages and dendritic cells after entry of the sub-epithelial, gut-associated lymphatic tissues. In order to resist phagocytosis by professional phagocytes and induce apoptosis of the host immune cells they express a virulence plasmid-encoded Ysc-Yop T3SS to inject multiple effector molecules, the Yops.91,92 During infection it is a prerequisite for Yersinia to tightly control the expression of the secretion system, as it requires a large energetic effort of the bacteria to fuel the production of the components of this injectisome and promote effector translocation. Several RNA-based control mechanisms have already been characterized which are part of a complex, multi-layered regulatory network that controls the expression and synthesis of the Yersinia T3SS.93 Many years ago Hoe et al. 94 published a report in which they predicted post-transcriptional regulation of the major transcriptional activator (LcrF/VirF) of T3SS/Yop expression. New results by Böhme et al. 95 further showed that translation of the lcrF mRNA is controlled through a FourU RNA thermometer, a thermo-responsive secondary structure formed of 2 stem-loops within the intergenic region of the yscW-lcrF transcript. The first stem-loop enhances the stability of the second hairpin which includes a stretch of 4 uridines (FourU) base-paired with the AGGA sequence of the lcrF ribosome binding site.95 Structure-probing and toe-printing analysis further demonstrated thermo-induced melting and partial opening of the second stem-loop which allows ribosome binding at 37°C, but not at moderate temperatures. The importance of the RNA thermometer for the control of Yersinia virulence was proven with mutant variants of the lcrF RNA thermometer that prevent melting of the thermometer at host temperature. Mice infected with this closed thermometer variant survived the infection without any disease symptoms.95
Another intriguing observation is that a complex of the translocon protein YopD and its secretion chaperone LcrH controls the translation of a cohort of ysc/yop mRNAs. The YopD-LcrH complex was found to bind mRNAs in the 5′-UTRs and promotes translation repression most likely by blockage of the ribosome binding site or/and by enhancing the degradation of the ysc/yop transcripts.96,97 Translational repression is eliminated when intracellular YopD levels decrease as a result of activated secretion. AU-rich regions including multiple AUAAA sequence motifs in the proximity of the ribosome binding site appear to support YopD-LcrH complex binding, but this alone does not seem to be sufficient to confer YopD-LcrH mediated translational repression.97,98 Furthermore, LcrQ (YscM1 and YscM2 in Y. enterocolitica) was shown to participate in the post-transcriptional control of the ysc/yop genes. The molecular mechanism is unclear, but it has been proposed that it may associate with the YopD-LcrH complex to repress ysc/yop translation.98 A recent study further showed that YopD also associates with 30S ribosomal particles in an LcrH-dependent fashion.99 This suggests that transient interaction of the YopD-LcrH-LcrQ/YscM complex on the ysc/yop mRNA with the 30S particle might affect translational initiation by perturbing the formation of the 30S complex before the 50S particle binds to assemble the ribosome.
Another study analyzing the post-transcriptional regulation of T3SS showed that Y. pseudotuberculosis expressing a dominant negative variant of RNase E (a rne knock-outknockout is lethal) or a PNPase mutant secreted only a reduced amount of the YopE effector protein.100-102 Counter-intuitively, a Δpnp Yersinia mutant possessed increased levels of all 3 T3SS-encoding and several yop transcripts, demonstrating that the PNPase affects the expression and activity of the T3SS by distinct mechanisms.101 This is in clear contrast to the situation in Salmonella in which increased T3SS expression levels matched with a corresponding increase in the T3SS-mediated increase of bacterial invasion 73 (see above). RNase E and PNPase both associate with the RNA helicase RhlB and the glycolytic enzyme enolase (Eno) to form the RNA degradosome, a large multi-protein complex or hyper-structure controlling RNA degradation in Yersinia and other enteric pathogens.103,104 Most interestingly, blockage of T3S could be restored in the pnp mutant strain by expressing the S1 domain of PNPase and RNase E.101 The S1 domain is characterized by a distinctive β-barrel core, which binds to nucleic acids, carbohydrates or is involved in protein-protein interactions. Use of different truncated S1 domains further demonstrated that especially residues 50-65, forming the conserved oligonucleotide binding cleft, play an important role in controlling Yop secretion, but are not involved in the alteration of T3SS/Yop expression levels.101 This finding indicated that the S1 domain of PNPase or RNase E might bind an mRNA or ncRNA that modulates T3SS-mediated Yop secretion.
Why PNPase influences T3SS/Yop expression in the opposite manner is less clear.101 It is assumed that the yersiniae prepare and/or readjust the T3SS/Yop expression profiles through the removal of unnecessary T3SS transcripts prior or after the attack of immune cells to minimize the energetic burden.103 The molecular mechanism by which PNPase controls T3SS/Yop expression is also unknown. However, PNPase was shown to control several regulatory RNAs including RyhB and SgrS, known to be important to control virulence-relevant metabolic traits in Salmonella.4,105 It is thus tempting to speculate that the degradosome could also protect ncRNAs of Yersinia implicated in the expression of the T3SS machinery. In fact, the RNA chaperone Hfq is required for the expression of many Yersinia RNAs,5,7,106 and regulates expression of PNPase.107 Hfq was found to play a critical role in Yersinia virulence (i.e. phagocytosis resistance, intracellular survival, growth within mice organs) by participating in the regulation of the expression of T3SS effector proteins.108,109 The abundance of all tested Yop effector proteins was decreased in the absence of Hfq, although the yop transcript levels remained unchanged. This together indicates that Hfq- and PNPase/RNaseE-dependent ncRNAs participate directly or indirectly through interactions with a T3S/Yop regulator in the control of Yop effectors. In fact, a recent study of our group further showed that several antisense RNAs are expressed from the virulence plasmid opposite of important T3SS genes, including ypkA, yopD, lcrV, and yscC.7 All these T3SS-associated proteins were upregulated in a Δpnp mutant of Y. pseudotuberculosis, suggesting that PNPase negatively regulates the expression of the T3SS machinery, e.g. through the asRNAs. In addition to RNase E and PNPase, another ribonuclease, YbeY, was shown to repress ysc/yop expression in Y. enterocolitica through a down-regulation of VirF/LcrF levels and manipulates many other virulence-related features.110 How this RNase influences expression of the virulence determinants is unclear. It is likely that it implicates a more general gene control process as this RNase is usually implicated in the processing of the 16S rRNA and ribosome biogenesis as well as in the late-stage 70S ribosome quality control.111,112 It generally recognizes defective 30S ribosomal particles and functions together with RNase R or PNPase to remove non-functional 70S ribosomes. YbeY acts as a single-strand-specific endoribonuclease that is able to degrade rRNA and mRNA and has an impact on ncRNAs.111,113
Intriguingly, also the unique bacterial translational control system, composed of the small stable RNA A (SsrA/tmRNA/10Sa/sR022/Yp-sR31) and the small RNA-binding protein B (SmpB), affects expression of the ysc/yop genes.114 This system rescues stalled ribosomes from incomplete transcripts, a process called trans-translation, to maintain the bacterial translational machinery in a fully operational state.115 The SmpB protein interacts with the amino-acylated SsrA RNA mimicking a tRNA and mRNA, and this complex enters the empty site of a stalled ribosome.116 A trans-peptidation reaction then links the unfinished peptide chain to SsrA, and SsrA replaces the aberrant mRNA. This promotes translation of an additional 11 amino acid residue tag until the apparatus reaches a built-in stop codon marking the polypeptide for degradation by bacterial proteases.115 A detailed study addressing the function of the SsrA-SmpB tagging and ribosome rescue system in Y. pseudotuberculosis demonstrated that loss of both genes renders the bacteria sensitive to sublethal antibiotic concentrations, less efficient in their cytotoxicity toward macrophages, and avirulent in the oral mouse infection model.114 This phenotype was consistent with the observation that expression of the key regulator of the ysc/yop gene LcrF was significantly reduced in a ssrA-smpB deficient mutant and could not be activated under secretion-inducing conditions.114
Although the precise molecular mechanisms and the interplay of the different post-transcriptional regulatory steps in the complex multi-layered network of T3SS/Yop expression and synthesis are far from understood, they clearly demonstrate that this pathogen resides in an energy-balanced stand-by position that prepares the pathogen for translocation of effectors immediately upon host cell contact. The regulatory circuits allow only low-level transcription, but no translation of the lcrF and ysc/yop mRNAs in the absence of host cell contact. However, under secretion conditions, tight coupling between the transcription, translation, RNA degradation and secretion machineries enables the pathogen to immediately upregulate synthesis and export of the virulence determinants.
In contrast to the previous described riboregulators, the ncRNAs Ysr35 and Ysr141 are Yersinia-specific ncRNAs, which have also been found to contribute to virulence. Very little is known about Ysr35, but significant compromised survival of a Ysr35 mutant in a Yersiniosis mouse model indicates that this ncRNA is important for Yersinia adaptation to its host.5 Ysr141 is an unstable ncRNA, which is encoded on the Yersinia virulence plasmid on the opposite strand within the intergenic region of yopH and a putative transposase.5,117 Expression of Ysr141 stimulates the production of multiple T3SS/Yop proteins (e.g. YopE, YscF, YopK) as well as their main activator LcrF, and seems to control yopJ mRNA translation through basepairing with its 5′-UTR.117
RNA-based control of virulence-associated traits
Control of host-adapted metabolism and ion homeostasis through small RNAs and riboswitches
Over the last decades many regulatory RNAs and riboswitches have been discovered as important regulators affecting myriad aspects of bacterial stress responses, ion homeostasis, metabolism, motility and other physiological properties, which also influence bacterial virulence. In particular riboregulators that are conserved among the well-characterized Enterobacteriaceae and implicated in the control of primary and secondary metabolic pathways have been characterized in more detail. The identified RNA-controlled mechanisms and their action at the interface of bacterial metabolism and virulence control have been recently summarized in several comprehensive review articles 4,118-120 and are thus not in the focus of this article.
Ion homeostasis
One of the most important and best-characterized small ncRNA is RyhB found in all enteric E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia species. The RyhB ncRNAs are activated following iron scarcity and are negatively regulated by the ferric uptake regulator Fur.121,122 The RyhB ncRNAs regulate iron homeostasis by (i) inhibiting the translation of transcripts encoding non-essential iron-containing proteins under iron starvation conditions in order to liberate iron for essential iron-dependent cellular functions and by (ii) upregulation of the synthesis of iron-chelating molecules (siderophores) to scavenge iron under iron-limiting conditions as experienced during infection.121 RyhB is highly similar between E. coli and Shigella and impacts conserved, but also species-specific virulence genes.123-125 One of which is the virulence regulator VirB controlling the expression of the IcsP protease, which limits the production of the actin polymerizing IcsA protein.125,126 Upon cell entry, iron levels become limiting and relieve Fur-mediated repression of RyhB transcription, which in turn increase host actin polymerization and cell-to-cell spreading through activation of the VirB-IcsP-IcsA cascade,124 and promotes acid resistance by a so far unknown mechanism.127
Interestingly, both Salmonella and Yersinia possess 2 RyhB homologs, RyhB1 and RyhB2, recently termed sibling ncRNAs, which are slightly differentially regulated in response to iron and nutrient starvation.65,122,128 Both ncRNAs have additional redundant functions such as protecting the pathogen against oxidative and acidic stress,129,130 and they are both highly induced and important for the intracellular growth of Salmonella 65,77-80 (see also above/below). However, it appears that sequence differences at the 5′-end of the ncRNAs could account for some differences in the regulatory targets of the RyhB RNAs. For instance, Kim et al. have shown that RyhB2 of Salmonella targets some motility genes (flgJ, cheY, and fliF) that are not regulated by RyhB1 and vice versa, RyhB1 influences safA and acnB expression, but not RyhB2.129 In Yersinia, the region that mediates target gene recognition is highly conserved between both RyhB ncRNAs, indicating regulatory redundancy, but only RyhB1 is stabilized by Hfq and is slightly more sensitive to alterations of degradosome factors.122,131 Differences in the 5′-end of the RNAs may result in these differences in stability. Both ncRNAs are strongly expressed in the infected tissues, but a ryhB1/ryhB2 double mutant has no major influence on the colonization and dissemination of the pathogen, indicating that other systems with redundant function(s) can compensate for the loss of the ncRNAs.122
Another riboregulator implicated in iron homeostasis is the FourU RNA thermometer located within the 5′-UTR of the Shigella heme uptake system shuA and in the orthologous gene chuA in pathogenic E. coli.132 Transcription of the heme transporter is subject to iron-dependent repression by the Fur protein and translation is under control of the thermo-responsive RNA thermometer, ensuring that ShuA synthesis only occurs when Shigella encounters heme as a potential iron source in the human body.132
Stress response
Multiple ncRNAs have been identified which are implicated in general and specific stress responses. Several of them are expressed in all well-characterized enteric pathogens of the family Enterobacteriaceae, i.e. OxyS, 6S RNA, FnrS, ArcZ, MicF, OmrA, OmrB, RybB, RprA, DrsA, SgrS, SraL, RyhB, (RyhB1, RyhB2). Their physiological role has recently been summarized in a review by Michaux et al. 133 They confer resistance against acid, oxidative and osmotic stress, cell envelope perturbations and nutrient starvation/stress, which are experienced by the pathogen during the different stages of the infection (i.e., oxidative and nutrient stress within phagosomal compartments in host cells, and acid and osmotic stress in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract). Many of these conserved ‘core’ ncRNAs are implicated in the primary metabolism, ion/nutrient sensing and transport, and participate in the fine regulation of cellular processes important to adapt to environmental changes. However, some of them were also found to control species-specific virulence factors (e.g. GlmY/Z, SgrS, ArcZ), which are explained in more detail in the individual virulence chapters.
Other identified ncRNAs involved in the regulation of stress responses are species- or even strain-specific. The ncRNA Ysr29 is specific to Y. pseudotuberculosis strain IP32953 and was found to contribute significantly to mortality in a mouse model for Yersiniosis.5,6 Ysr29 was shown to repress the synthesis of glutathione-S transferase (GST) and activates production of RpsA, OmpA and GroEL.5,6 As GST allows protection against the damage of oxidative stress, it has been suggested that this ncRNA, which is mostly induced at moderate temperatures, could be involved in the response to reactive oxygen species produced by insect vectors, e.g. flies and fleas upon infection.134 In addition, the Salmonella-specific 200 nt long ncRNA (RaoN) encoded on SPI-11 between the cspH and envE locus was recently shown to be highly induced under oxidative stress conditions and nutrient limitation. Loss of the raoN gene resulted in high susceptibility against both of these stresses and reduced the survival of the pathogen in macrophages. RaoN controls the expression of the lactate dehydrogenase gene ldhA, and it is assumed that it promotes stress resistances at least to some extent through the generation of NAD+ from NADH when converting pyruvate to lactate.135 A multi-component glutamate-dependent acid resistance system (GadABC) is responsible for the extreme acid tolerance of enteric E. coli and Shigella. This system converts glutamate into γ-aminobutyric acid and exports the product in exchange of extracellular glutamate to consume intracellular H+. Its expression is tightly regulated by the transcriptional activators GadE, GadX and GadW, and the regulatory RNA GadY encoded within the intergenic region of gadX and gadW.136 The GadY ncRNA is induced upon nutrient starvation and acid stress through the alternative sigma factor σS and interacts with the 3′-UTR of the gadX transcript. This interaction stimulates processing of the gadX gene after the stop codon resulting in more stable gadX and gadW transcripts.136
Concluding remarks
The rapidly increasing amount of transcriptomic data obtained from next-generation sequencing approaches and tiling microarrays combined with sophisticated bioinformatics tools provided us with a vast number of transcribed but non-translated sensory and regulatory RNA elements implicated in the fine-tuning of physiological and cellular processes important for pathogenesis. The diversity of their physiological role, the complexity and accuracy of their molecular function as well as their central role in the coordinated regulatory network of virulence-relevant processes illustrates their regulatory potential and relevance. The huge amount of riboregulators presented in this review not only demonstrates that RNA-based control mechanisms represent a crucial additional level of regulation, as they allow a less-energy consuming and faster control of gene expression, it also shows that it enables the bacteria to fine-tune and coordinate their responses to environmental changes in a more rapid and sensitive fashion. The majority of conserved ncRNAs of Enterobacteriaceae contribute to the regulation of metabolism and stress responses, but these ‘core’ ncRNAs were also hijacked to regulate mRNAs of horizontally acquired virulence factor through Hfq and base-pairing or other conserved global RNA-binding regulators, e.g. CsrA. In addition, many species- or even strain-specific ncRNAs have evolved which modulate more specific virulence processes of the pathogen to promote optimal adaptation to its host niches. The combined set forms an impressive number of versatile, programmable and highly efficient RNA-based regulators. As outlined in the review by Papenfort & Vanderpool,137 no special characteristics seem to define an ncRNA as an inhibitor or activator. Action of an ncRNA seems to depend on the target and how the ncRNA interferes with its structure or recruited proteins that influence its stability or translation. The characterization of the molecular details of the individual control mechanisms will be key to understand the full potential of riboregulators.
Perspectives and future challenges
Considering the tremendous amount of sensory and regulatory RNAs identified in the different pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae, very little is known about their physiological relevance and molecular action. Only a very small number of ncRNAs has been functionally characterized and the direct and indirect targets of most regulatory RNA elements have yet not or only partially been identified. The analysis of their physiological role, including the characterization of the molecular interactions with their individual targets constitutes one of the great challenges that we are currently facing in our attempt to understand bacterial pathogenesis and virulence control.
In addition, there are many intriguing questions and unaddressed issues associated with the ncRNA elements:
Recently, several regulatory and sensory RNAs were shown to encode small peptides (e.g. SgrS, mgtA leader), which participate in the sensory or regulatory process of the encoding ncRNA or 5′-UTR.60,138 A screening of the bacterial ncRNAomes indicates that there are many more potential dual function ncRNAs. Up to date, their potential has been mostly disregarded because of the difficulty in the detection of small oligopeptides. A combination of next generation sequencing-based transcriptomics and novel proteomic tools optimized for small peptides will help to identify and characterize their biological activities and regulatory potential.
More sensitive RNA-Seq technologies now allow us to simultaneously profile the transcriptome of the pathogen and the infected host cells.78,79 This gives us a catalogue of putative virulence-relevant riboregulators, but which of them are relevant for pathogenesis is still an open question. Based on the observed redundancy of their function more powerful tools are needed that allow high-throughput evaluation and exploration of their role during infection. Transposon-insertion sequencing (TraDIS) 85,139 or adaptation of the CRISPR-Cas technology for high-throughput use could be applied to construct single and multiple ncRNA-deficient mutants of pathogens and dissect the influence of sensory and regulatory RNAs on the overall fitness and pathogenicity. Another possibility to gain a systems-level view of ncRNA activity is to globally follow the dynamics of their structure, stability and translational dynamics of RNAs. Moreover, many enteric pathogens, including Yersinia and Salmonella form phenotypically distinct subpopulations in host niches 140-142 which demands new highly sensitive single-cell dual RNA-Seq protocols to characterize the different expression programs in individual bacterial cells during infection.
Although some prototypical control mechanisms of ncRNAs have emerged, it became also obvious that ncRNAs use numerous ways to influence gene expression. A future task will be to find global approaches that will allow us to comprehensively trace the regulatory networks and the target regulons of specific ncRNAs, identify proteins (e.g., RNA chaperones, degradation adaptors) involved in their regulatory activity and/or RNA degradation functions associated with their action. Another unsolved question is: What is the advantage of having sibling ncRNAs with redundant functions? It is possible that they differ in their regulatory outcome - target regulons and/or the strength of target regulation, which implies a slightly better fitness.
The function of sensory and regulatory RNA elements depends on the formation of a particular secondary and tertiary structure. New approaches in which structure-specific chemical cleavage is combined with RNA-Seq have been developed which allow detailed RNA probing and structural profiling in vivo.143 These methods not only enable us to identify RNA thermometers and RNA riboswitches on the system-level, they will also allow us to follow the dynamic of these processes in the context of an infection and compare RNA structuromes from different clinical isolates to identify functionally important differences in RNA structures (riboSNitches).
Recently, a bacterial RNA has been shown to use a cis-acting signal to change its localization within the bacterial cell in response to environmental changes.39,40 Development of fluorescent labels for direct tracking of RNA in vivo will give novel insights into the spatial organization of (s)RNAs (e.g. association of an ncRNA to hyper-structures such as translational and degradation machineries) and dynamic changes of ncRNA transport in the context of an infection (e.g., during secretion of effectors upon host cell contact).
RNA modifications are known to manipulate the stability and interaction of RNAs with interacting proteins. Transcriptional profiling employing different RNA-Seq-based technologies now enables us to identify intrinsic modified nucleotides and investigate their regulatory potential.
Another tempting question is how we could exploit ncRNAs or associated RNA-based control systems for therapeutic applications to disrupt host-pathogen interaction. One possibility is the discovery of small molecule inhibitors or design of tailor-made compounds for a particular ncRNA or riboswitch.144,145 In fact, an effective riboswitch inhibitor (ribocil) and an aptamer-based riboswitch blocker have recently been identified.144,146 A pitfall in this approach is that many trans-encoded ncRNAs are non-essential or have partially redundant function and are per se not very well suited as drug targets. Consequently, central riboregulators such as CsrA or global transcriptional or post-transcriptional regulators such as Crp or Hfq which influence many RNA-mediated control systems seem to be much more promising targets for the design of novel diagnostics and therapeutic measures.
Disclosure of potential confllicts of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Martin Fenner for discussion and Claudia Munzel for critical reading of the manuscript.
Funding
German Research Foundation provided funding to Petra Dersch under the grant number DE616/4 and DE616/5 for the analysis of sensory and regulatory RNAs and host-adapted metabolism of Yersinia. Petra Dersch is further supported by the German Center for Infection Research under grant number DZIF-TTU 06.801.
References
- 1.Waters LS, Storz G. Regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Cell 2009; 136:615-28; PMID:19239884; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gottesman S, Storz G. Bacterial small RNA regulators: versatile roles and rapidly evolving variations. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011; 3:pii: a003798; PMID:20980440; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1101/cshperspect.a003798 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Caldelari I, Chao Y, Romby P, Vogel J. RNA-mediated regulation in pathogenic bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2013; 3:a010298; PMID:24003243; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1101/cshperspect.a010298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Papenfort K, Vogel J. Small RNA functions in carbon metabolism and virulence of enteric pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2014; 4:91; PMID:25077072; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Koo JT, Alleyne TM, Schiano CA, Jafari N, Lathem WW. Global discovery of small RNAs in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis identifies Yersinia-specific small, noncoding RNAs required for virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011; 108:E709-17; PMID:21876162; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1073/pnas.1101655108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Koo JT, Lathem WW. Global discovery of small noncoding RNAs in pathogenic Yersinia species. Adv Exp Med Biol 2012; 954:305-14; PMID:22782777; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1007/978-1-4614-3561-7_38 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nuss AM, Heroven AK, Waldmann B, Reinkensmeier J, Jarek M, Beckstette M, Dersch P. Transcriptomic profiling of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis reveals reprogramming of the Crp regulon by temperature and uncovers Crp as a master regulator of small RNAs. PLoS Genet 2015; 11:e1005087; PMID:25816203; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Landstorfer R, Simon S, Schober S, Keim D, Scherer S, Neuhaus K. Comparison of strand-specific transcriptomes of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 EDL933 (EHEC) under eleven different environmental conditions including radish sprouts and cattle feces. BMC Genomics 2014; 15:353; PMID:24885796; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1186/1471-2164-15-353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Raghavan R, Groisman EA, Ochman H. Genome-wide detection of novel regulatory RNAs in E. coli. Genome Res 2011; 21:1487-97; PMID:21665928; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1101/gr.119370.110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Storz G, Vogel J, Wassarman KM. Regulation by small RNAs in bacteria: expanding frontiers. Mol Cell 2011; 43:880-91; PMID:21925377; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vogel J, Luisi BF. Hfq and its constellation of RNA. Nat Rev Microbiol 2011; 9:578-89; PMID:21760622; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrmicro2615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Viegas SC, Pfeiffer V, Sittka A, Silva IJ, Vogel J, Arraiano CM. Characterization of the role of ribonucleases in Salmonella small RNA decay. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35:7651-64; PMID:17982174; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gkm916 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Saramago M, Barria C, Dos Santos RF, Silva IJ, Pobre V, Domingues S, Andrade JM, Viegas SC, Arraiano CM. The role of RNases in the regulation of small RNAs. Curr Opin Microbiol 2014; 18:105-15; PMID:24704578; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.mib.2014.02.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kortmann J, Narberhaus F. Bacterial RNA thermometers: molecular zippers and switches. Nat Rev Microbiol 2012; 10:255-65; PMID:22421878; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrmicro2730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Steinmann R, Dersch P. Thermosensing to adjust bacterial virulence in a fluctuating environment. Future Microbiol 2013; 8:85-105; PMID:23252495; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.2217/fmb.12.129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Serganov A, Nudler E. A decade of riboswitches. Cell 2013; 152:17-24; PMID:23332744; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mellin JR, Cossart P. Unexpected versatility in bacterial riboswitches. Trends Genet 2015; 31:150-6; PMID:25708284; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.tig.2015.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Peselis A, Serganov A. Themes and variations in riboswitch structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014; 1839:908-18; PMID:24583553; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Henkin TM. Riboswitch RNAs: using RNA to sense cellular metabolism. Genes Dev 2008; 22:3383-90; PMID:19141470; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1101/gad.1747308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Papenfort K, Vogel J. Regulatory RNA in bacterial pathogens. Cell Host Microbe 2010; 8:116-27; PMID:20638647; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.chom.2010.06.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chao Y, Vogel J. The role of Hfq in bacterial pathogens. Curr Opin Microbiol 2010; 13:24-33; PMID:20080057; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sobrero P, Valverde C. The bacterial protein Hfq: much more than a mere RNA-binding factor. Crit Rev Microbiol 2012; 38:276-99; PMID:22435753; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3109/1040841X.2012.664540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wagner EG. Cycling of RNAs on Hfq. RNA Biol 2013; 10:619-26; PMID:23466677; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.4161/rna.24044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Morita T, Maki K, Aiba H. RNase E-based ribonucleoprotein complexes: mechanical basis of mRNA destabilization mediated by bacterial noncoding RNAs. Genes Dev 2005; 19:2176-86; PMID:16166379; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1101/gad.1330405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hajnsdorf E, Regnier P. Host factor Hfq of Escherichia coli stimulates elongation of poly(A) tails by poly(A) polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000; 97:1501-5; PMID:10677490; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1073/pnas.040549897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Heroven AK, Bohme K, Dersch P. The Csr/Rsm system of Yersinia and related pathogens: A post-transcriptional strategy for managing virulence. RNA Biol 2012; 9:379-91; PMID:22336760; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.4161/rna.19333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vakulskas CA, Potts AH, Babitzke P, Ahmer BM, Romeo T. Regulation of Bacterial Virulence by Csr (Rsm) Systems. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2015; 79:193-224; PMID:25833324; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/MMBR.00052-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dubey AK, Baker CS, Romeo T, Babitzke P. RNA sequence and secondary structure participate in high-affinity CsrA-RNA interaction. Rna 2005; 11:1579-87; PMID:16131593; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1261/rna.2990205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kulkarni PR, Jia T, Kuehne SA, Kerkering TM, Morris ER, Searle MS, Heeb S, Rao J, Kulkarni RV. A sequence-based approach for prediction of CsrA/RsmA targets in bacteria with experimental validation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42:6811-25; PMID:24782516; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gku309 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Holmqvist E, Wright PR, Li L, Bischler T, Barquist L, Reinhardt R, Backofen R, Vogel J. Global RNA recognition patterns of post-transcriptional regulators Hfq and CsrA revealed by UV crosslinking in vivo. EMBO J 2016; 35:991-1011; PMID:27044921; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.15252/embj.201593360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yakhnin AV, Baker CS, Vakulskas CA, Yakhnin H, Berezin I, Romeo T, Babitzke P. CsrA activates flhDC expression by protecting flhDC mRNA from RNase E-mediated cleavage. Mol Microbiol 2013; 87:851-66; PMID:23305111; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/mmi.12136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Babitzke P, Romeo T. CsrB sRNA family: sequestration of RNA-binding regulatory proteins. Curr Opin Microbiol 2007; 10:156-63; PMID:17383221; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.mib.2007.03.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Liu MY, Gui G, Wei B, Preston JF 3rd, Oakford L, Yuksel U, Giedroc DP, Romeo T. The RNA molecule CsrB binds to the global regulatory protein CsrA and antagonizes its activity in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 1997; 272:17502-10; PMID:9211896; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1074/jbc.272.28.17502 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kulkarni PR, Cui X, Williams JW, Stevens AM, Kulkarni RV. Prediction of CsrA-regulating small RNAs in bacteria and their experimental verification in Vibrio fischeri. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34:3361-9; PMID:16822857; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gkl439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Heroven A, Bohme K, Rohde M, Dersch P. A Csr-type regulatory system, including small non-coding RNAs, regulates the global virulence regulator RovA of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis through RovM. Mol Microbiol 2008; 68:1179-95; PMID:18430141; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06218.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Garneau NL, Wilusz J, Wilusz CJ. The highways and byways of mRNA decay. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8:113-26; PMID:17245413; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrm2104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Silva IJ, Saramago M, Dressaire C, Domingues S, Viegas SC, Arraiano CM. Importance and key events of prokaryotic RNA decay: the ultimate fate of an RNA molecule. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2011; 2:818-36; PMID:21976285; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1002/wrna.94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lalaouna D, Simoneau-Roy M, Lafontaine D, Masse E. Regulatory RNAs and target mRNA decay in prokaryotes. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013; 1829:742-7; PMID:23500183; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.02.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Buskila AA, Kannaiah S, Amster-Choder O. RNA localization in bacteria. RNA Biol 2014; 11:1051-60; PMID:25482897; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.4161/rna.36135 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nevo-Dinur K, Govindarajan S, Amster-Choder O. Subcellular localization of RNA and proteins in prokaryotes. Trends Genet 2012; 28:314-22; PMID:22521614; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.tig.2012.03.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pizarro-Cerda J, Cossart P. Bacterial adhesion and entry into host cells. Cell 2006; 124:715-27; PMID:16497583; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pawar DM, Rossman ML, Chen J. Role of curli fimbriae in mediating the cells of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli to attach to abiotic surfaces. J Appl Microbiol 2005; 99:418-25; PMID:16033475; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02499.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Barnhart MM, Chapman MR. Curli biogenesis and function. Annu Rev Microbiol 2006; 60:131-47; PMID:16704339; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev.micro.60.080805.142106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bordeau V, Felden B. Curli synthesis and biofilm formation in enteric bacteria are controlled by a dynamic small RNA module made up of a pseudoknot assisted by an RNA chaperone. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42:4682-96; PMID:24489123; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gku098 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Boehm A, Vogel J. The csgD mRNA as a hub for signal integration via multiple small RNAs. Mol Microbiol 2012; 84:1-5; PMID:22414234; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08033.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Urban JH, Vogel J. Two seemingly homologous noncoding RNAs act hierarchically to activate glmS mRNA translation. PLoS Biol 2008; 6:e64; PMID:18351803; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060064 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gopel Y, Luttmann D, Heroven AK, Reichenbach B, Dersch P, Gorke B. Common and divergent features in transcriptional control of the homologous small RNAs GlmY and GlmZ in Enterobacteriaceae. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39:1294-309; PMID:20965974; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gkq986 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gruber CC, Sperandio V. Global analysis of posttranscriptional regulation by GlmY and GlmZ in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Infect Immun 2015; 83:1286-95; PMID:25605763; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/IAI.02918-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Teplitski M, Al-Agely A, Ahmer BM. Contribution of the SirA regulon to biofilm formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microbiology 2006; 152:3411-24; PMID:17074910; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1099/mic.0.29118-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sterzenbach T, Nguyen KT, Nuccio SP, Winter MG, Vakulskas CA, Clegg S, Romeo T, Bäumler AJ. A novel CsrA titration mechanism regulates fimbrial gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium. EMBO J 2013; 32:2872-83; PMID:24056837; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/emboj.2013.206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.McDaniel TK, Kaper JB. A cloned pathogenicity island from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli confers the attaching and effacing phenotype on E. coli K-12. Mol Microbiol 1997; 23:399-407; PMID:9044273; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.2311591.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bhatt S, Edwards AN, Nguyen HT, Merlin D, Romeo T, Kalman D. The RNA binding protein CsrA is a pleiotropic regulator of the locus of enterocyte effacement pathogenicity island of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 2009; 77:3552-68; PMID:19581394; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/IAI.00418-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gruber CC, Sperandio V. Posttranscriptional control of microbe-induced rearrangement of host cell actin. MBio 2014; 5:e01025-13; PMID:24425733; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/mBio.01025-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Martinez LC, Yakhnin H, Camacho MI, Georgellis D, Babitzke P, Puente JL, Bustamante VH. Integration of a complex regulatory cascade involving the SirA/BarA and Csr global regulatory systems that controls expression of the Salmonella SPI-1 and SPI-2 virulence regulons through HilD. Mol Microbiol 2011; 80:1637-56; PMID:21518393; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07674.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Gore AL, Payne SM. CsrA and Cra influence Shigella flexneri pathogenesis. Infect Immun 2010; 78:4674-82; PMID:20713625; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/IAI.00589-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Adler B, Sasakawa C, Tobe T, Makino S, Komatsu K, Yoshikawa M. A dual transcriptional activation system for the 230 kb plasmid genes coding for virulence-associated antigens of Shigella flexneri. Mol Microbiol 1989; 3:627-35; PMID:2474742; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00210.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Vanderpool CK. Physiological consequences of small RNA-mediated regulation of glucose-phosphate stress. Curr Opin Microbiol 2007; 10:146-51; PMID:17383224; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.mib.2007.03.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Bobrovskyy M, Vanderpool CK. The small RNA SgrS: roles in metabolism and pathogenesis of enteric bacteria. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2014; 4:61; PMID:24847473; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bobrovskyy M, Vanderpool CK. Diverse mechanisms of post-transcriptional repression by the small RNA regulator of glucose-phosphate stress. Mol Microbiol 2016; 99:254-73; PMID:26411266; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/mmi.13230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Papenfort K, Podkaminski D, Hinton JC, Vogel J. The ancestral SgrS RNA discriminates horizontally acquired Salmonella mRNAs through a single G-U wobble pair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012; 109:E757-64; PMID:22383560; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1073/pnas.1119414109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Papenfort K, Sun Y, Miyakoshi M, Vanderpool CK, Vogel J. Small RNA-mediated activation of sugar phosphatase mRNA regulates glucose homeostasis. Cell 2013; 153:426-37; PMID:23582330; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Giangrossi M, Prosseda G, Tran CN, Brandi A, Colonna B, Falconi M. A novel antisense RNA regulates at transcriptional level the virulence gene icsA of Shigella flexneri. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38:3362-75; PMID:20129941; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gkq025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tran CN, Giangrossi M, Prosseda G, Brandi A, Di Martino ML, Colonna B, Falconi M. A multifactor regulatory circuit involving H-NS, VirF and an antisense RNA modulates transcription of the virulence gene icsA of Shigella flexneri. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39:8122-34; PMID:21724612; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gkr521 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Pichon C, du Merle L, Lequeutre I, Le Bouguenec C. The AfaR small RNA controls expression of the AfaD-VIII invasin in pathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41:5469-82; PMID:23563153; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gkt208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Padalon-Brauch G, Hershberg R, Elgrably-Weiss M, Baruch K, Rosenshine I, Margalit H, Altuvia S. Small RNAs encoded within genetic islands of Salmonella typhimurium show host-induced expression and role in virulence. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36:1913-27; PMID:18267966; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/nar/gkn050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gong H, Vu GP, Bai Y, Chan E, Wu R, Yang E, Liu F, Lu S. A Salmonella small non-coding RNA facilitates bacterial invasion and intracellular replication by modulating the expression of virulence factors. PLoS Pathog 2011; 7:e1002120; PMID:21949647; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Durand JM, Okada N, Tobe T, Watarai M, Fukuda I, Suzuki T, Nakata N, Komatsu K, Yoshikawa M, Sasakawa C. vacC, a virulence-associated chromosomal locus of Shigella flexneri, is homologous to tgt, a gene encoding tRNA-guanine transglycosylase (Tgt) of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 1994; 176:4627-34; PMID:8045893 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Shippy DC, Fadl AA. tRNA modification enzymes GidA and MnmE: potential role in virulence of bacterial pathogens. Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15:18267-80; PMID:25310651; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3390/ijms151018267 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yu H, Kim KS. mRNA context dependent regulation of cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 translation by GidA, a tRNA modification enzyme in Escherichia coli. Gene 2012; 491:116-22; PMID:22020226; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.gene.2011.10.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Knust Z, Blumenthal B, Aktories K, Schmidt G. Cleavage of Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 is required for full biologic activity. Infect Immun 2009; 77:1835-41; PMID:19237521; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/IAI.01145-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lemonnier M, Landraud L, Lemichez E. Rho GTPase-activating bacterial toxins: from bacterial virulence regulation to eukaryotic cell biology. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2007; 31:515-34; PMID:17680807; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00078.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Cheng ZF, Zuo Y, Li Z, Rudd KE, Deutscher MP. The vacB gene required for virulence in Shigella flexneri and Escherichia coli encodes the exoribonuclease RNase R. J Biol Chem 1998; 273:14077-80; PMID:9603904; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1074/jbc.273.23.14077 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Clements MO, Eriksson S, Thompson A, Lucchini S, Hinton JC, Normark S, Rhen M. Polynucleotide phosphorylase is a global regulator of virulence and persistency in Salmonella enterica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002; 99:8784-9; PMID:12072563; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1073/pnas.132047099 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Jones BD, Ghori N, Falkow S. Salmonella typhimurium initiates murine infection by penetrating and destroying the specialized epithelial M cells of the Peyer's patches. J Exp Med 1994; 180:15-23; PMID:8006579; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1084/jem.180.1.15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Vazquez-Torres A, Jones-Carson J, Baumler AJ, Falkow S, Valdivia R, Brown W, Le M, Berggren R, Parks WT, Fang FC. Extraintestinal dissemination of Salmonella by CD18-expressing phagocytes [In Process Citation]. Nature 1999; 401:804-8; PMID:10548107; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/44593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Helaine S, Cheverton AM, Watson KG, Faure LM, Matthews SA, Holden DW. Internalization of Salmonella by macrophages induces formation of nonreplicating persisters. Science 2014; 343:204-8; PMID:24408438; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1244705 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ortega A, Gonzalo-Asensio J, Garcia-Del Portillo F. Dynamics of Salmonella small RNA expression in non-growing bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells. RNA Biol 2012; 9:469-88; PMID:22336761; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.4161/rna.19317 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Srikumar S, Kroger C, Hebrard M, Colgan A, Owen SV, Sivasankaran SK, Cameron AD, Hokamp K, Hinton JC. RNA-seq brings new insights to the intra-macrophage transcriptome of Salmonella Typhimurium. PLoS Pathog 2015; 11:e1005262; PMID:26561851; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Westermann AJ, Forstner KU, Amman F, Barquist L, Chao Y, Schulte LN, Müller L, Reinhardt R, Stadler PF, Vogel J. Dual RNA-seq unveils noncoding RNA functions in host-pathogen interactions. Nature 2016; 529:496-501; PMID:26789254; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nature16547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Leclerc JM, Dozois CM, Daigle F. Role of the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi Fur regulator and small RNAs RfrA and RfrB in iron homeostasis and interaction with host cells. Microbiology 2013; 159:591-602; PMID:23306672; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1099/mic.0.064329-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Pfeiffer V, Sittka A, Tomer R, Tedin K, Brinkmann V, Vogel J. A small non-coding RNA of the invasion gene island (SPI-1) represses outer membrane protein synthesis from the Salmonella core genome. Mol Microbiol 2007; 66:1174-91; PMID:17971080; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05991.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Chao Y, Papenfort K, Reinhardt R, Sharma CM, Vogel J. An atlas of Hfq-bound transcripts reveals 3′ UTRs as a genomic reservoir of regulatory small RNAs. EMBO J 2012; 31:4005-19; PMID:22922465; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/emboj.2012.229 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Prost LR, Miller SI. The Salmonellae PhoQ sensor: mechanisms of detection of phagosome signals. Cellular Microbiology 2008; 10:576-82; PMID:18182085; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01111.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Groisman EA. The pleiotropic two-component regulatory system PhoP-PhoQ. Journal of Bacteriology 2001; 183:1835-42; PMID:11222580; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/JB.183.6.1835-1842.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Chaudhuri RR, Morgan E, Peters SE, Pleasance SJ, Hudson DL, Davies HM, Wang J, van Diemen PM, Buckley AM, Bowen AJ, et al.. Comprehensive assignment of roles for Salmonella typhimurium genes in intestinal colonization of food-producing animals. PLoS Genet 2013; 9:e1003456; PMID:23637626; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003456 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Chen ZW, Hsuan SL, Liao JW, Chen TH, Wu CM, Lee WC, Lin CC, Liao CM, Yeh KS, Winton JR, et al.. Mutations in the Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis cAMP-receptor protein gene lead to functional defects in the SPI-1 Type III secretion system. Vet Res 2010; 41:5; PMID:19775595; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1051/vetres/2009053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Gonzalo-Asensio J, Ortega AD, Rico-Perez G, Pucciarelli MG, Garcia-Del Portillo F. A novel antisense RNA from the Salmonella virulence plasmid pSLT expressed by non-growing bacteria inside eukaryotic cells. PLoS One 2013; 8:e77939; PMID:24205037; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pone.0077939 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Gulig PA, Danbara H, Guiney DG, Lax AJ, Norel F, Rhen M. Molecular analysis of spv virulence genes of the Salmonella virulence plasmids. Mol Microbiol 1993; 7:825-30; PMID:8483415; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01172.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Libby SJ, Lesnick M, Hasegawa P, Weidenhammer E, Guiney DG. The Salmonella virulence plasmid spv genes are required for cytopathology in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Cell Microbiol 2000; 2:49-58; PMID:11207562; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2000.00030.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Ygberg SE, Clements MO, Rytkonen A, Thompson A, Holden DW, Hinton JC, Rhen M. Polynucleotide phosphorylase negatively controls spv virulence gene expression in Salmonella enterica. Infect Immun 2006; 74:1243-54; PMID:16428774; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/IAI.74.2.1243-1254.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Cornelis GR, Wolf-Watz H. The Yersinia Yop virulon: a bacterial system for subverting eukaryotic cells. Mol Microbiol 1997; 23:861-7; PMID:9076724; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.2731623.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Shao F. Biochemical functions of Yersinia type III effectors. Curr Opin Microbiol 2008; 11:21-9; PMID:18299249; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.mib.2008.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Schiano CA, Lathem WW. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in Yersinia species. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2012; 2:129; PMID:23162797; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Hoe NP, Goguen JD. Temperature sensing in Yersinia pestis: translation of the LcrF activator protein is thermally regulated. J Bacteriol 1993; 175:7901-9; PMID:7504666 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Böhme K, Steinmann R, Kortmann J, Seekircher S, Heroven AK, Berger E, Pisano F, Thiermann T, Wolf-Watz H, Narberhaus F, et al.. Concerted actions of a thermo-labile regulator and a unique intergenic RNA thermosensor control Yersinia virulence. PLoS Pathog 2012; 8:e1002518; PMID:22359501; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Anderson DM, Ramamurthi KS, Tam C, Schneewind O. YopD and LcrH regulate expression of Yersinia enterocolitica YopQ by a posttranscriptional mechanism and bind to yopQ RNA. J Bacteriol 2002; 184:1287-95; PMID:11844757; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/JB.184.5.1287-1295.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Chen Y, Anderson DM. Expression hierarchy in the Yersinia type III secretion system established through YopD recognition of RNA. Mol Microbiol 2011; 80:966-80; PMID:21481017; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07623.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Cambronne ED, Schneewind O. Yersinia enterocolitica type III secretion: yscM1 and yscM2 regulate yop gene expression by a posttranscriptional mechanism that targets the 5′ untranslated region of yop mRNA. J Bacteriol 2002; 184:5880-93; PMID:12374821; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/JB.184.21.5880-5893.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Kopaskie KS, Ligtenberg KG, Schneewind O. Translational regulation of Yersinia enterocolitica mRNA encoding a type III secretion substrate. J Biol Chem 2013; 288:35478-88; PMID:24158443; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1074/jbc.M113.504811 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Rosenzweig JA, Weltman G, Plano GV, Schesser K. Modulation of Yersinia type three secretion system by the S1 domain of polynucleotide phosphorylase. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:156-63; PMID:15509583; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1074/jbc.M405662200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Rosenzweig JA, Chromy B, Echeverry A, Yang J, Adkins B, Plano GV, McCutchen-Maloney S, Schesser K. Polynucleotide phosphorylase independently controls virulence factor expression levels and export in Yersinia spp. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2007; 270:255-64; PMID:17391372; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00689.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Yang J, Jain C, Schesser K. RNase E regulates the Yersinia type 3 secretion systemros. J Bacteriol 2008; 190:3774-8; PMID:18359811; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/JB.00147-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Rosenzweig JA, Chopra AK. The exoribonuclease polynucleotide phosphorylase influences the virulence and stress responses of yersiniae and many other pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2013; 3:81; PMID:24312901; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00081 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Norris V, Menu-Bouaouiche L, Becu JM, Legendre R, Norman R, Rosenzweig JA. Hyperstructure interactions influence the virulence of the type 3 secretion system in yersiniae and other bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2012; 96:23-36; PMID:22949045; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1007/s00253-012-4325-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.De Lay N, Gottesman S. Role of polynucleotide phosphorylase in sRNA function in Escherichia coli. RNA 2011; 17:1172-89; PMID:21527671; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1261/rna.2531211 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Beauregard A, Smith EA, Petrone BL, Singh N, Karch C, McDonough KA, Wade JT. Identification and characterization of small RNAs in Yersinia pestis. RNA Biol 2013; 10:397-405; PMID:23324607; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.4161/rna.23590 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Mohanty BK, Maples VF, Kushner SR. The Sm-like protein Hfq regulates polyadenylation dependent mRNA decay in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 2004; 54:905-20; PMID:15522076; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04337.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Schiano CA, Bellows LE, Lathem WW. The small RNA chaperone Hfq is required for the virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun 2010; 78:2034-44; PMID:20231416; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/IAI.01046-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Geng J, Song Y, Yang L, Feng Y, Qiu Y, Li G, Guo J, Bi Y, Qu Y, Wang W, et al.. Involvement of the post-transcriptional regulator of Hfq in Yersinia pestis virulence. PLoS One 2009; 4:e6213; PMID:19593436; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pone.0006213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Leskinen K, Varjosalo M, Skurnik M. Absence of YbeY RNase compromises the growth and enhances the virulence plasmid gene expression of Yersinia enterocolitica O:3. Microbiology 2015; 161:285-99; PMID:25416689; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1099/mic.0.083097-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Jacob AI, Kohrer C, Davies BW, RajBhandary UL, Walker GC. Conserved bacterial RNase YbeY plays key roles in 70S ribosome quality control and 16S rRNA maturation. Mol Cell 2013; 49:427-38; PMID:23273979; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Grinwald M, Ron EZ. The Escherichia coli translation-associated heat shock protein YbeY is involved in rRNA transcription antitermination. PLoS One 2013; 8:e62297; PMID:23638028; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pone.0062297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Pandey SP, Winkler JA, Li H, Camacho DM, Collins JJ, Walker GC. Central role for RNase YbeY in Hfq-dependent and Hfq-independent small-RNA regulation in bacteria. BMC Genomics 2014; 15:121; PMID:24511998; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1186/1471-2164-15-121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Okan NA, Bliska JB, Karzai AW. A Role for the SmpB-SsrA system in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog 2006; 2:e6; PMID:16450010; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Karzai AW, Roche ED, Sauer RT. The SsrA-SmpB system for protein tagging, directed degradation and ribosome rescue. Nat Struct Biol 2000; 7:449-55; PMID:10881189; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/75843 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Neubauer C, Gillet R, Kelley AC, Ramakrishnan V. Decoding in the absence of a codon by tmRNA and SmpB in the ribosome. Science 2012; 335:1366-9; PMID:22422985; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1217039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Schiano CA, Koo JT, Schipma MJ, Caulfield AJ, Jafari N, Lathem WW. Genome-wide analysis of small RNAs expressed by Yersinia pestis identifies a regulator of the Yop-Ysc type III secretion system. J Bacteriol 2014; 196:1659-70; PMID:24532772; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/JB.01456-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Oliva G, Sahr T, Buchrieser C. Small RNAs, 5′ UTR elements and RNA-binding proteins in intracellular bacteria: impact on metabolism and virulence. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2015; 39:331-49; PMID:26009640; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/femsre/fuv022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Bobrovskyy M, Vanderpool CK, Richards GR. Small RNAs Regulate Primary and Secondary Metabolism in Gram-negative Bacteria. Microbiol Spectr 2015; 3; PMID:26185078; http:/dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/microbiolspec.MBP-0009-2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Mika F, Hengge R. Small Regulatory RNAs in the Control of Motility and Biofilm Formation in E. coli and Salmonella. Int J Mol Sci 2013; 14:4560-79; PMID:23443158; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3390/ijms14034560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Masse E, Gottesman S. A small RNA regulates the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002; 99:4620-5; PMID:11917098; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1073/pnas.032066599 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Deng Z, Meng X, Su S, Liu Z, Ji X, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Wang X, Yang R, Han Y. Two sRNA RyhB homologs from Yersinia pestis biovar microtus expressed in vivo have differential Hfq-dependent stability. Res Microbiol 2012; 163:413-8; PMID:22659336; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.resmic.2012.05.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Murphy ER, Payne SM. RyhB, an iron-responsive small RNA molecule, regulates Shigella dysenteriae virulence. Infect Immun 2007; 75:3470-7; PMID:17438026; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/IAI.00112-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Africa LA, Murphy ER, Egan NR, Wigley AF, Wing HJ. The iron-responsive Fur/RyhB regulatory cascade modulates the Shigella outer membrane protease IcsP. Infect Immun 2011; 79:4543-9; PMID:21859852; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/IAI.05340-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Broach WH, Egan N, Wing HJ, Payne SM, Murphy ER. VirF-independent regulation of Shigella virB transcription is mediated by the small RNA RyhB. PLoS One 2012; 7:e38592; PMID:22701677; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pone.0038592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Fris ME, Murphy ER. Riboregulators: Fine-Tuning Virulence in Shigella. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2016; 6:2; PMID:26858941; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Oglesby AG, Murphy ER, Iyer VR, Payne SM. Fur regulates acid resistance in Shigella flexneri via RyhB and ydeP. Mol Microbiol 2005; 58:1354-67; PMID:16313621; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04920.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Caswell CC, Oglesby-Sherrouse AG, Murphy ER. Sibling rivalry: related bacterial small RNAs and their redundant and non-redundant roles. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2014; 4:151; PMID:25389522; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00151 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Kim JN, Kwon YM. Identification of target transcripts regulated by small RNA RyhB homologs in Salmonella: RyhB-2 regulates motility phenotype. Microbiol Res 2013; 168:621-9; PMID:23831078; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.micres.2013.06.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Calderon PF, Morales EH, Acuna LG, Fuentes DN, Gil F, Porwollik S, McClelland M, Saavedra CP, Calderón IL. The small RNA RyhB homologs from Salmonella typhimurium participate in the response to S-nitrosoglutathione-induced stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014; 450:641-5; PMID:24937451; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.06.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Deng Z, Liu Z, Bi Y, Wang X, Zhou D, Yang R, Han Y. Rapid degradation of Hfq-free RyhB in Yersinia pestis by PNPase independent of putative ribonucleolytic complexes. Biomed Res Int 2014; 2014:798918; PMID:24818153; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1155/2014/798918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Kouse AB, Righetti F, Kortmann J, Narberhaus F, Murphy ER. RNA-mediated thermoregulation of iron-acquisition genes in Shigella dysenteriae and pathogenic Escherichia coli. PLoS One 2013; 8:e63781; PMID:23704938; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pone.0063781 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Michaux C, Verneuil N, Hartke A, Giard JC. Physiological roles of small RNA molecules. Microbiology 2014; 160:1007-19; PMID:24694375; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1099/mic.0.076208-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Martinez-Chavarria LC, Vadyvaloo V. Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection: a regulatory RNA perspective. Front Microbiol 2015; 6:956; PMID:26441890; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Lee YH, Kim S, Helmann JD, Kim BH, Park YK. RaoN, a small RNA encoded within Salmonella pathogenicity island-11, confers resistance to macrophage-induced stress. Microbiology 2013; 159:1366-78; PMID:23657681; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1099/mic.0.066688-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Tramonti A, De Canio M, De Biase D. GadX/GadW-dependent regulation of the Escherichia coli acid fitness island: transcriptional control at the gadY-gadW divergent promoters and identification of four novel 42 bp GadX/GadW-specific binding sites. Mol Microbiol 2008; 70:965-82; PMID:18808381; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06458.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Papenfort K, Vanderpool CK. Target activation by regulatory RNAs in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2015; 39:362-78; PMID:25934124; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/femsre/fuv016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Park SY, Cromie MJ, Lee EJ, Groisman EA. A bacterial mRNA leader that employs different mechanisms to sense disparate intracellular signals. Cell 2010; 142:737-48; PMID:20813261; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.van Opijnen T, Camilli A. Transposon insertion sequencing: a new tool for systems-level analysis of microorganisms. Nat Rev Microbiol 2013; 11:435-42; PMID:23712350; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrmicro3033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Diard M, Garcia V, Maier L, Remus-Emsermann MN, Regoes RR, Ackermann M, Hardt WD. Stabilization of cooperative virulence by the expression of an avirulent phenotype. Nature 2013; 494:353-6; PMID:23426324; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nature11913 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Claudi B, Sprote P, Chirkova A, Personnic N, Zankl J, Schurmann N, Schmidt A, Bumann D. Phenotypic variation of Salmonella in host tissues delays eradication by antimicrobial chemotherapy. Cell 2014; 158:722-33; PMID:25126781; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.avis KM, Mohammadi S, Isberg RR. Community behavior and spatial regulation within a bacterial microcolony in deep tissue sites serves to protect against host attack. Cell Host Microbe 2015; 17:21-31; PMID:25500192; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.chom.2014.11.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Burgess DJ. RNA. Detailed probing of RNA structure in vivo. Nat Rev Genet 2015; 16:255; PMID:25854184; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrg3939 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Lee CH, Han SR, Lee SW. Therapeutic applications of aptamer-based riboswitches. Nucleic Acid Ther 2016; 26:44-51; PMID:26539634; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1089/nat.2015.0570 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Blount KF, Breaker RR. Riboswitches as antibacterial drug targets. Nat Biotechnol 2006; 24:1558-64; PMID:17160062; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nbt1268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Howe JA, Wang H, Fischmann TO, Balibar CJ, Xiao L, Galgoci AM, Malinverni JC, Mayhood T, Villafania A, Nahvi A, et al.. Selective small-molecule inhibition of an RNA structural element. Nature 2015; 526:672-7; PMID:26416753; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nature15542 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]