Abstract
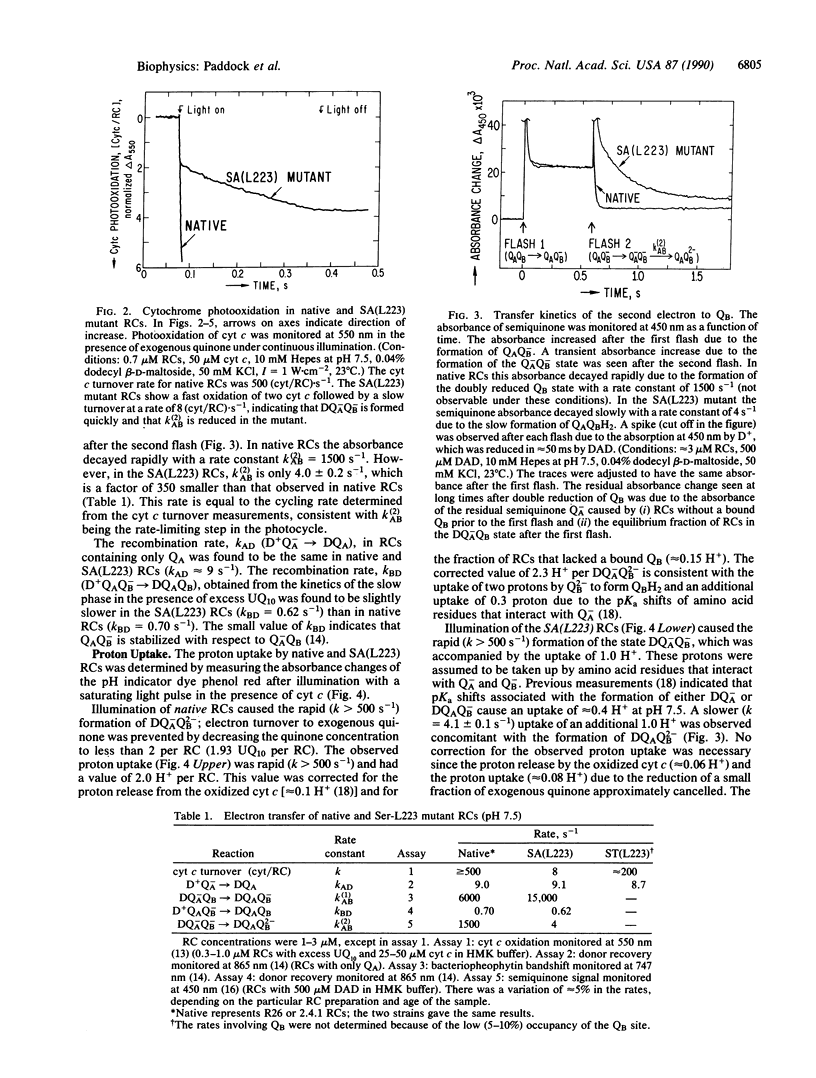
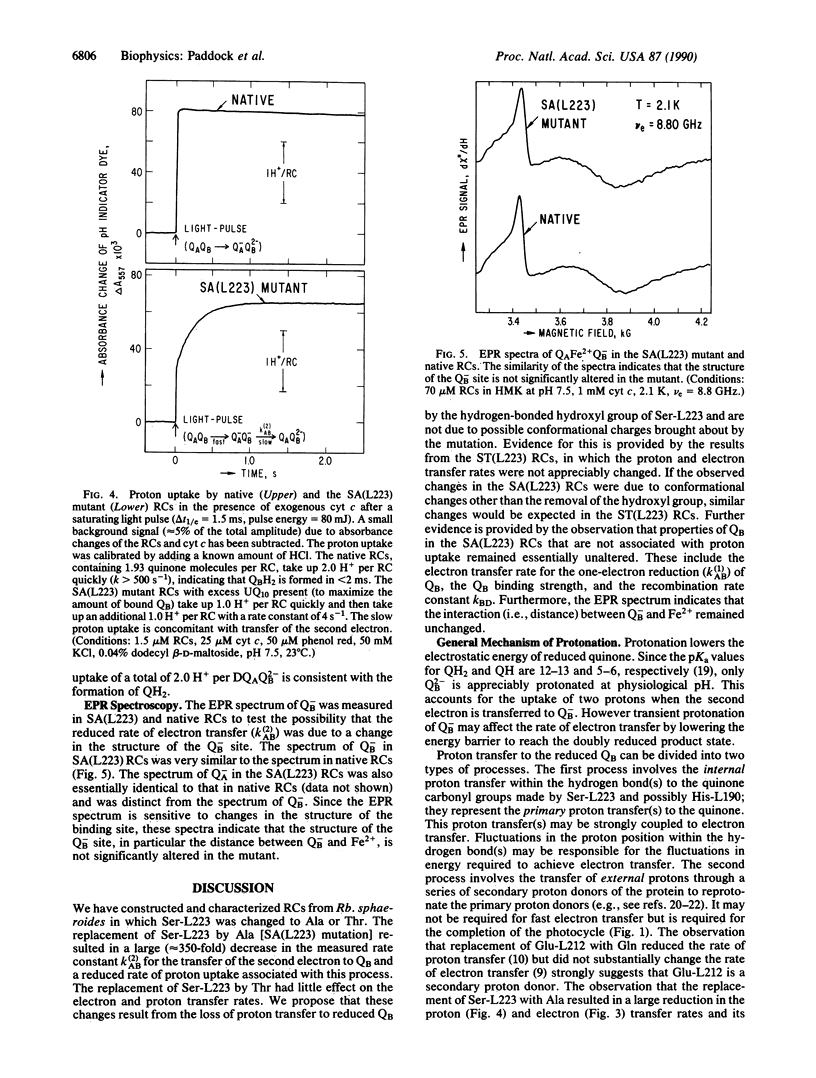
The pathway of proton transfer in the reaction center (RC) from Rhodobacter sphaeroides was investigated by site-directed mutagenesis. Ser-L223, a putative proton donor that forms a hydrogen bond with the secondary quinone acceptor QB, was replaced with Ala and Thr. RCs with Ala-L223 displayed reduced electron transfer and proton uptake rates in the reaction QA-QB- + 2H+----QAQBH2. The rate constant for this reaction, k(2)AB, was found to be reduced approximately 350-fold to 4.0 +/- 0.2 s-1. Proton uptake measurements using a pH indicator dye showed a rapid uptake of 1 H+ per RC followed by a slower uptake of 1 H+ per RC at a rate of 4.1 +/- 0.1 s-1; native RCs showed a rapid uptake of 2H+ per RC. Evidence is provided that these changes were not due to gross structural changes in the binding site of QB. RCs with Thr-L223 showed little reduction in the rates of electron and proton transfer. These results indicate that proton transfer from the hydroxyl group of Ser-L223 or Thr-L223 is required for fast electron and proton transfer associated with the formation of the dihydroquinone QH2. In contrast, previous work showed that replacing Glu-L212, another putative proton donor to QB, with Gln slowed proton uptake from solution without significantly altering electron transfer. We propose a model that involves two distinct proton transfer steps. The first step occurs prior to transfer of the second electron to QB and involves proton transfer from Ser-L223. The second step occurs after this electron transfer through a pathway involving Glu-L212.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. P., Feher G., Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: protein-cofactor (quinones and Fe2+) interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8487–8491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. F., Calvo R., Fredkin D. R., Isaacson R. A., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. The electronic structure of Fe2+ in reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. III. EPR measurements of the reduced acceptor complex. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):947–973. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84241-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinfeld D., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Electron transfer in reaction centers of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. I. Determination of the charge recombination pathway of D+QAQ(-)B and free energy and kinetic relations between Q(-)AQB and QAQ(-)B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 27;766(1):126–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(84)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Tristram-Nagle S. Hydrogen bonded chain mechanisms for proton conduction and proton pumping. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01870590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddock M. L., Rongey S. H., Feher G., Okamura M. Y. Pathway of proton transfer in bacterial reaction centers: replacement of glutamic acid 212 in the L subunit by glutamine inhibits quinone (secondary acceptor) turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6602–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulten Z., Schulten K. Proton conduction through proteins: an overview of theoretical principles and applications. Methods Enzymol. 1986;127:419–438. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)27033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinning I., Koepke J., Schiller B., Michel H. First glance on the three-dimensional structure of the photosynthetic reaction center from a herbicide-resistant Rhodopseudomonas viridis mutant. Z Naturforsch C. 1990 May;45(5):455–458. doi: 10.1515/znc-1990-0525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


