Abstract
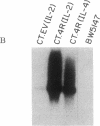
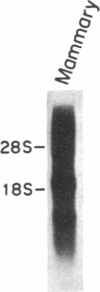
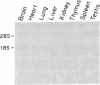
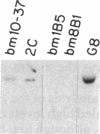
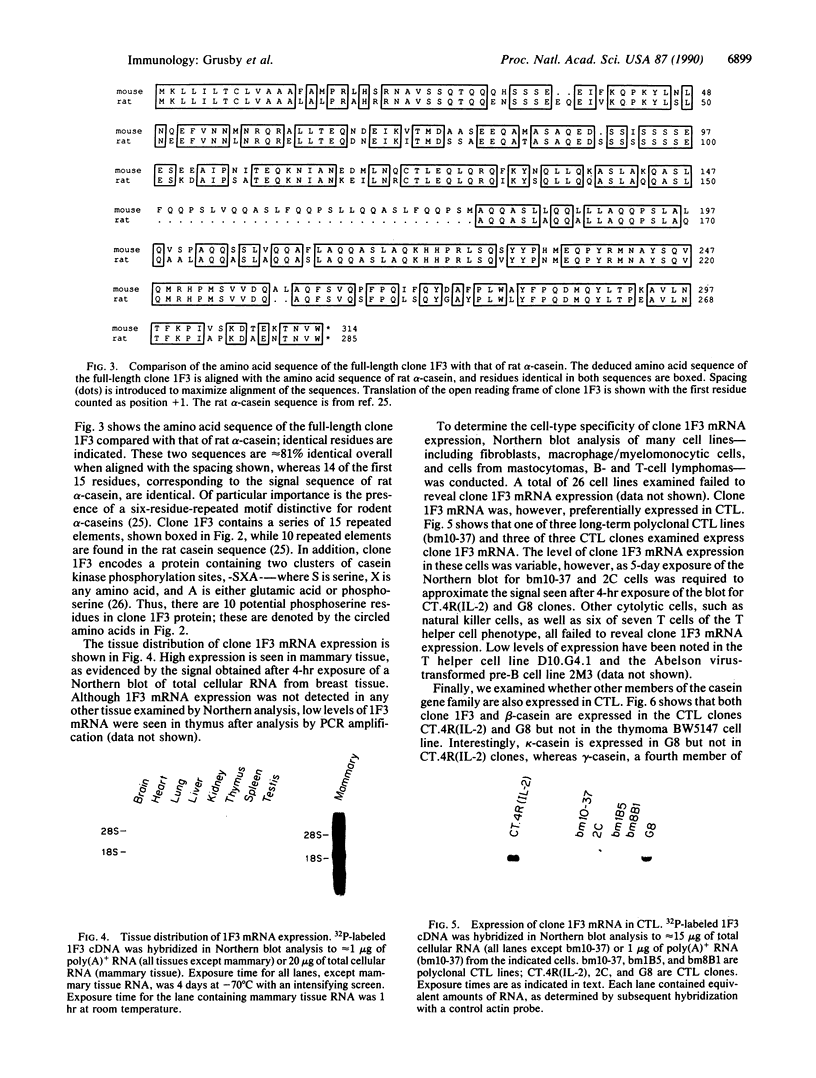
A cDNA that expresses a mRNA restricted to cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and mammary tissue has been isolated and characterized. The deduced amino acid sequence from this cDNA shows extensive homology with the previously reported amino acid sequence for rat alpha-casein. Indeed, the presence of a six-residue-repeated motif that is specific for rodent alpha-caseins strongly supports the identification of this cDNA as mouse alpha-casein. Northern (RNA) blot analysis of many hematopoietic cell types revealed that this gene is restricted to CTL, being expressed in four of six CTL lines examined. Furthermore, CTL that express this gene were also found to express other members of the casein gene family, such as beta- and kappa-casein. These results suggest that caseins may be important in CTL function, and their potential role in CTL-mediated lysis is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet J. F., Dosseto M., Denizot F., Mattei M. G., Clark W. R., Haqqi T. M., Ferrier P., Nabholz M., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Luciani M. F. The inducible cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated gene transcript CTLA-1 sequence and gene localization to mouse chromosome 14. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):268–271. doi: 10.1038/322268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Eisen H. N. Effects of N alpha-tosyl-L-lysyl-chloromethylketone on the activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1028–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershenfeld H. K., Weissman I. L. Cloning of a cDNA for a T cell-specific serine protease from a cytotoxic T lymphocyte. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):854–858. doi: 10.1126/science.2422755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grusby M. J., Nabavi N., Wong H., Dick R. F., Bluestone J. A., Schotz M. C., Glimcher L. H. Cloning of an interleukin-4 inducible gene from cytotoxic T lymphocytes and its identification as a lipase. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90596-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Rosen J. M., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F. H. Localization of the casein gene family to a single mouse chromosome. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):199–204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L. G., Sippel A. E. Characterization and cloning of the mRNAs specific for the lactating mouse mammary gland. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jun 15;125(1):131–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L. G., Steudle A., Sippel A. E. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA coding for mouse epsilon casein. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;126(3):569–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. A., Rosen J. M. Sequence of rat alpha- and gamma-casein mRNAs: evolutionary comparison of the calcium-dependent rat casein multigene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8079–8098. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu-Li J., Ohara J., Watson C., Tsang W., Paul W. E. Derivation of a T cell line that is highly responsive to IL-4 and IL-2 (CT.4R) and of an IL-2 hyporesponsive mutant of that line (CT.4S). J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):800–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudig D., Redelman D., Minning L. L. The requirement for proteinase activity for human lymphocyte-mediated natural cytotoxicity (NK): evidence that the proteinase is serine dependent and has aromatic amino acid specificity of cleavage. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2647–2654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D., Rey C., Haefliger J. A., Qiao B. Y., Groscurth P., Tschopp J. Identification and sequencing of cDNA clones encoding the granule-associated serine proteases granzymes D, E, and F of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4814–4818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D., Rey C., Masson D., Stanley K. K., Herz J., Plaetinck G., Tschopp J. cDNA cloning of granzyme C, a granule-associated serine protease of cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):318–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Kestler D., Lee E., Wakulchik M., Young J. D. Isolation and sequence analysis of serine protease cDNAs from mouse cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1839–1854. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Leib Z., Servadio C. The mechanism of human NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Mode of action of surface-associated proteases in the early stages of the lytic reaction. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1470–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. F., Atiee S. H., Rosen J. M. Differential regulation of rat beta-casein-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase fusion gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):560–565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Growth-related changes in specific mRNAs of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Steffen M., King F., Young J. D. Identification, isolation, and characterization of a novel cytotoxin in murine cytolytic lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobe C. G., Finlay B. B., Paranchych W., Paetkau V. H., Bleackley R. C. Novel serine proteases encoded by two cytotoxic T lymphocyte-specific genes. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):858–861. doi: 10.1126/science.3518058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier J. C. Phosphorylation of caseins, present evidence for an amino acid triplet code posttranslationally recognized by specific kinases. Biochimie. 1981 Jan;63(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. J., Henkart M. P., Reynolds C. W., Henkart P. A. Purification and properties of cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat LGL tumors. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3197–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R. Granule-mediated cytolysis of target cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;140:1–9. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-73911-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Konigsberg P. J. Cytolytic T cell granules. Isolation, structural, biochemical, and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):695–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redelman D., Hudig D. The mechanism of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. I. Killing by murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes requires cell surface thiols and activated proteases. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):870–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Hoschützky H., Fruth U., Simon H. G., Kramer M. D. Purification and characterization of a T cell specific serine proteinase (TSP-1) from cloned cytolytic T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3267–3274. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04638.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Simon H. G., Fruth U., Epplen J., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Kramer M. D. Cloned cytolytic T-effector cells and their malignant variants produce an extracellular matrix degrading trypsin-like serine proteinase. Immunology. 1987 Feb;60(2):219–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. D., Dave J. R., Nakhasi H. L. Molecular cloning of mouse mammary gland kappa-casein: comparison with rat kappa-casein and rat and human gamma-fibrinogen. DNA. 1985 Aug;4(4):263–271. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapani J. A., Klein J. L., White P. C., Dupont B. Molecular cloning of an inducible serine esterase gene from human cytotoxic lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Banerjee M. R., Oka T. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding mouse beta casein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8224–8224. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Leong L. G., Liu C. C., Damiano A., Wall D. A., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and characterization of a serine esterase from cytolytic T cell granules. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Liu C. C., Persechini P. M., Cohn Z. A. Perforin-dependent and -independent pathways of cytotoxicity mediated by lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1988 Mar;103:161–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]