Abstract
Amphetamine and cocaine are stimulant drugs that act on central monoaminergic neurons to produce both acute psychomotor activation and long-lasting behavioral effects including addiction and psychosis. Here we report that single doses of these drugs induce rapid expression of the nuclear proto-oncogene c-fos in the forebrain and particularly in the striatum, an extrapyramidal structure implicated in addiction and in long-term drug-induced changes in motor function. The two drugs induce strikingly different patterns of c-fos expression in the striosome-matrix compartments and limbic subdivisions of the striatum, and their effects are pharmacologically distinct, although both are sensitive to dopamine receptor blockade. We propose that differential activation of immediate-early genes by psychostimulants may be an early step in drug-specific molecular cascades contributing to acute and long-lasting psychostimulant-induced changes in behavior.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bain G. T., Kornetsky C. Naloxone attenuation of the effect of cocaine on rewarding brain stimulation. Life Sci. 1987 Mar 16;40(11):1119–1125. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldino F., Jr, Chesselet M. F., Lewis M. E. High-resolution in situ hybridization histochemistry. Methods Enzymol. 1989;168:761–777. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)68057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. Second messenger dualism in neuromodulation and memory. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):294–295. doi: 10.1038/323294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besson M. J., Graybiel A. M., Nastuk M. A. [3H]SCH 23390 binding to D1 dopamine receptors in the basal ganglia of the cat and primate: delineation of striosomal compartments and pallidal and nigral subdivisions. Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):101–119. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff S., Heinrich M., Sonntag J. M., Krauss J. The D-1 dopamine receptor antagonist SCH 23390 also interacts potently with brain serotonin (5-HT2) receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 7;129(3):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90449-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. L., Squinto S. P., Harlan R. E. Morphine activation of c-fos expression in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):698–704. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. J., Saffen D. W., Baraban J. M., Worley P. F. Rapid increase of an immediate early gene messenger RNA in hippocampal neurons by synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):474–476. doi: 10.1038/340474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue J. P., Herkenham M. Neostriatal projections from individual cortical fields conform to histochemically distinct striatal compartments in the rat. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 19;365(2):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91658-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W. Pharmacology of central serotonin neurons. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:111–127. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., Baimbridge K. G., Miller J. J. The neostriatal mosaic: compartmental distribution of calcium-binding protein and parvalbumin in the basal ganglia of the rat and monkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8780–8784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R. The neostriatal mosaic: compartmentalization of corticostriatal input and striatonigral output systems. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):461–464. doi: 10.1038/311461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R. The neostriatal mosaic: striatal patch-matrix organization is related to cortical lamination. Science. 1989 Oct 20;246(4928):385–388. doi: 10.1126/science.2799392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L., Axelrod J. Storage and synthesis of norepinephrine in the reserpine-treated rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Mar;151(3):385–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelet P., Castellucci V. F., Schacher S., Kandel E. R. The long and the short of long-term memory--a molecular framework. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):419–422. doi: 10.1038/322419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. H. Regulation of neuropeptide gene expression. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:111–127. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Moratalla R. Dopamine uptake sites in the striatum are distributed differentially in striosome and matrix compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9020–9024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M. Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):244–254. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90104-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Ragsdale C. W., Jr Histochemically distinct compartments in the striatum of human, monkeys, and cat demonstrated by acetylthiocholinesterase staining. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5723–5726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves P. M., Ryan L. J., Linder J. C. Amphetamine changes neostriatal morphology. NIDA Res Monogr. 1987;78:132–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iorio L. C., Barnett A., Leitz F. H., Houser V. P., Korduba C. A. SCH 23390, a potential benzazepine antipsychotic with unique interactions on dopaminergic systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Aug;226(2):462–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanami S., Takashima M., Hirata Y., Hasegawa O., Usuda S. Synthesis and neuroleptic activity of benzamides. Cis-N-(1-benzyl-2-methylpyrrolidin-3-yl)-5-chloro-2-methoxy-4-(methylamino)benzamide and related compounds. J Med Chem. 1981 Oct;24(10):1224–1230. doi: 10.1021/jm00142a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H. K., McGinty J. F., Hong J. S. Differential modulation of striatonigral dynorphin and enkephalin by dopamine receptor subtypes. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 15;507(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90522-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Castellanos J., Graybiel A. M. Subdivisions of the dopamine-containing A8-A9-A10 complex identified by their differential mesostriatal innervation of striosomes and extrastriosomal matrix. Neuroscience. 1987 Oct;23(1):223–242. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce J. N., Sapp D. W., Marshall J. F. Human striatal dopamine receptors are organized in compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):8002–8006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.8002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemel M. L., Desban M., Glowinski J., Gauchy C. Distinct presynaptic control of dopamine release in striosomal and matrix areas of the cat caudate nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob G. F., Bloom F. E. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of drug dependence. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):715–723. doi: 10.1126/science.2903550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob G. F., Le H. T., Creese I. The D1 dopamine receptor antagonist SCH 23390 increases cocaine self-administration in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Aug 31;79(3):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer L. F., Graybiel A. M. Distinct nigrostriatal projection systems innervate striosomes and matrix in the primate striatum. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 2;498(2):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loopuijt L. D. Distribution of dopamine D-2 receptors in the rat striatal complex and its comparison with acetylcholinesterase. Brain Res Bull. 1989 May;22(5):805–817. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(89)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein P. R., Joyce J. N., Coyle J. T., Marshall J. F. Striosomal organization of cholinergic and dopaminergic uptake sites and cholinergic M1 receptors in the adult human striatum: a quantitative receptor autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1990 Feb 26;510(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90736-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., Burch R. M., Monsma F. J., Jr, Sibley D. R. Expression of striatal D1 dopamine receptors coupled to inositol phosphate production and Ca2+ mobilization in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2196–2200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello N. K., Mendelson J. H., Bree M. P., Lukas S. E. Buprenorphine suppresses cocaine self-administration by rhesus monkeys. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):859–862. doi: 10.1126/science.2772637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. C. Induction of c-fos mRNA expression in rat striatum by neuroleptic drugs. J Neurochem. 1990 Apr;54(4):1453–1455. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L., Seiger A., Fuxe K. Heterogeneity of striatal and limbic dopamine innervation: highly fluorescent islands in developing and adult rats. Brain Res. 1972 Sep 15;44(1):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90385-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzi M., Da Prada M., Valerio A., Memo M., Spano P. F., Haefely W. E. Dopamine D2 receptor stimulation inhibits inositol phosphate generating system in rat striatal slices. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 26;456(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale C. W., Jr, Graybiel A. M. A simple ordering of neocortical areas established by the compartmental organization of their striatal projections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6196–6199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz M. C., Lamb R. J., Goldberg S. R., Kuhar M. J. Cocaine receptors on dopamine transporters are related to self-administration of cocaine. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1219–1223. doi: 10.1126/science.2820058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. A., Peterson M. R., Murphy K., Robertson G. S. D1-dopamine receptor agonists selectively activate striatal c-fos independent of rotational behaviour. Brain Res. 1989 Dec 4;503(2):346–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
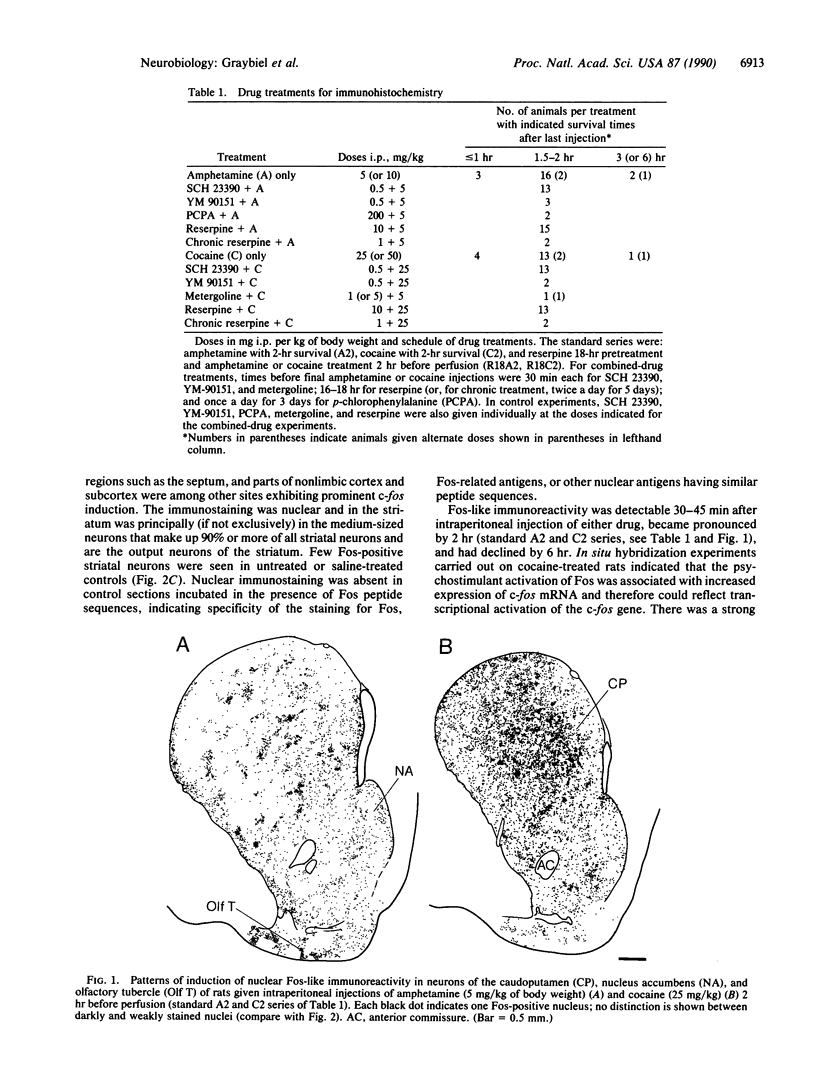
- Sagar S. M., Sharp F. R., Curran T. Expression of c-fos protein in brain: metabolic mapping at the cellular level. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1328–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.3131879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J. L., Macgregor-Leon P. F., Curran T., Morgan J. I. Dynamic alterations occur in the levels and composition of transcription factor AP-1 complexes after seizure. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J. L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morgan J. I., Curran T. Regulation of proenkephalin by Fos and Jun. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1622–1625. doi: 10.1126/science.2512642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoof J. C., Kebabian J. W. Opposing roles for D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors in efflux of cyclic AMP from rat neostriatum. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):366–368. doi: 10.1038/294366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Meldolesi J. Mechanisms of signal transduction at the dopamine D2 receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Feb;10(2):74–77. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. A. Neural mechanisms of the reinforcing action of cocaine. NIDA Res Monogr. 1984;50:15–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]