Abstract
Based upon prior demonstrations that human microvascular endothelial cells (ECs) could serve as natural killer (NK) cell targets, we established NK cell lines and clones by repeated stimulation of highly purified CD16-positive, CD3/T-cell receptor (Ti)-negative cells with allogeneic ECs. After 3 weeks in culture these lymphoid cells, which neither expressed surface CD3/Ti molecules nor rearranged Ti beta- or gamma-chain genes and which lysed K562 human erythroleukemia cells, displayed specific cytotoxicity for the stimulating ECs. Furthermore, freshly isolated NK cells bound and then removed from each of several allogeneic EC lines displayed selective cytotoxicity for the adsorbing EC line. These results provide evidence for alloantigen-specific recognition of microvascular ECs by NK cells that appears to be determined, at least in part, at the level of adherence. We discuss the implications of these findings with respect to the rejection of vascularized organ allografts.
Full text
PDF
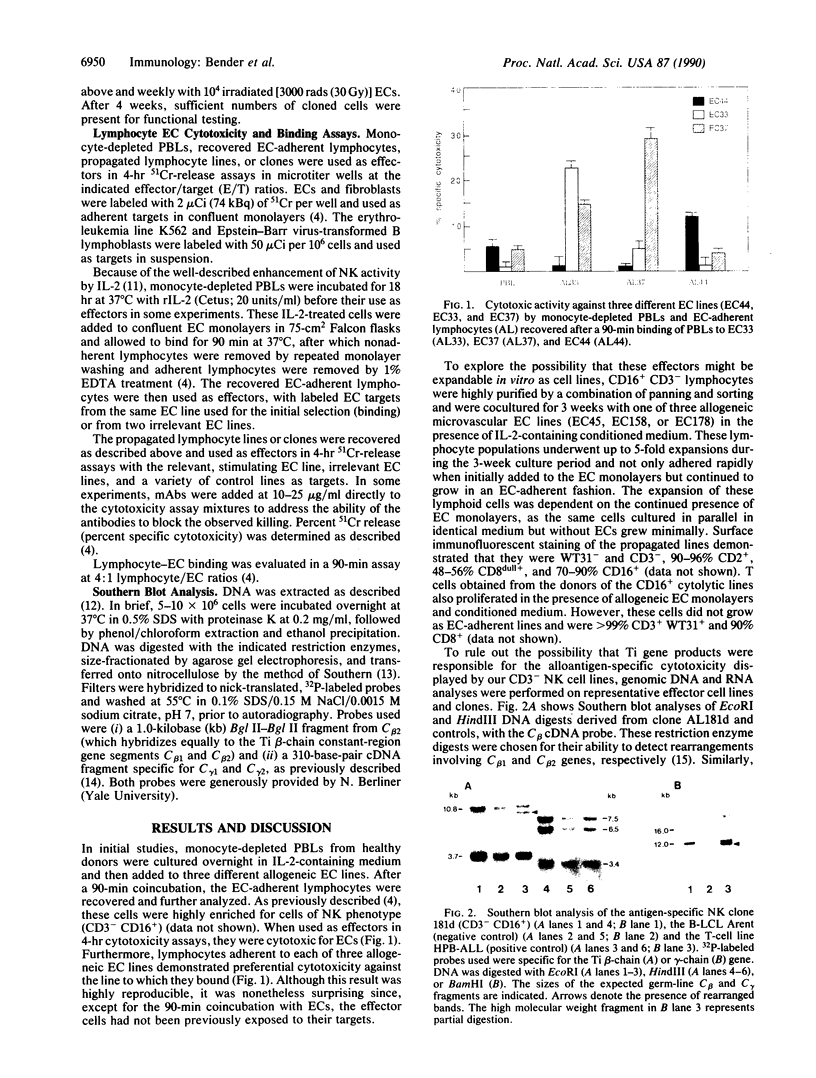
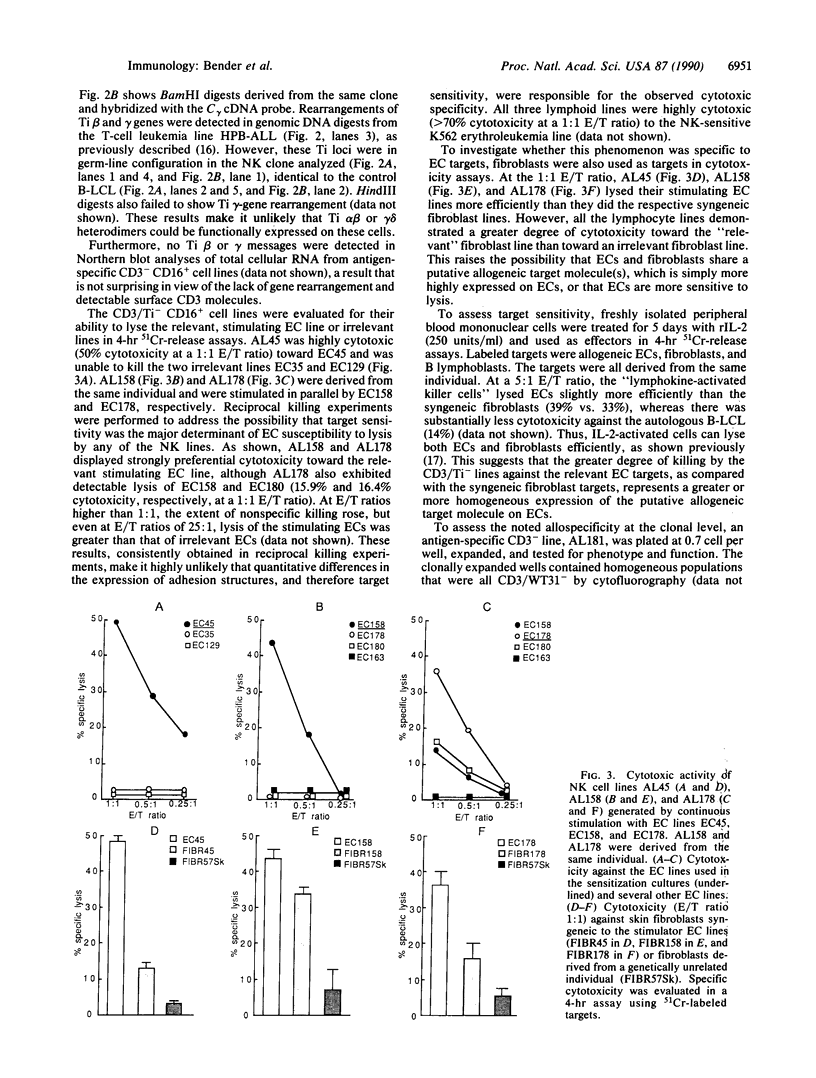
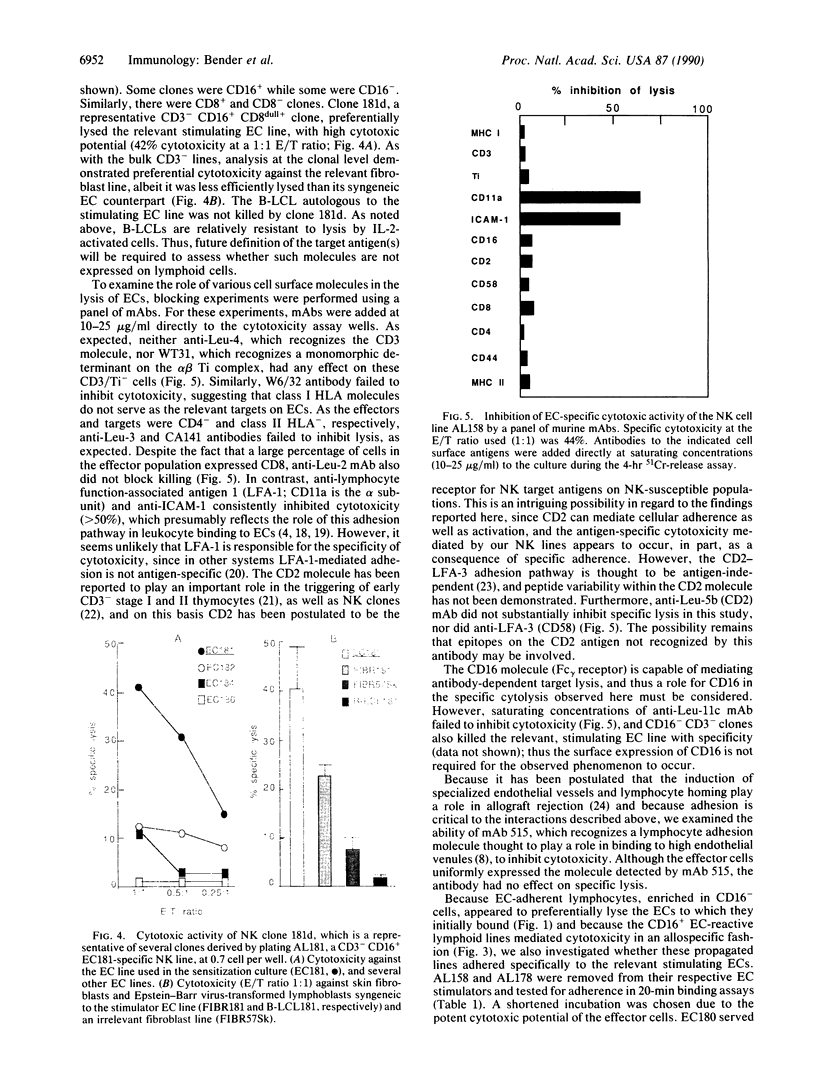

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S. D., Turek P. J., Foung S. K., Engleman E. G. Human monoclonal anti-T cell antibody from a patient with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J. R., Pardi R., Karasek M. A., Engleman E. G. Phenotypic and functional characterization of lymphocytes that bind human microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. Evidence for preferential binding of natural killer cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1679–1688. doi: 10.1172/JCI113007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J. R., Pardi R., Kosek J., Engleman E. G. Evidence that cytotoxic lymphocytes alter and traverse allogeneic endothelial cell monolayers. Transplantation. 1989 Jun;47(6):1047–1053. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198906000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
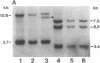
- Berliner N., Duby A. D., Linch D. C., Murre C., Quertermous T., Knott L. J., Azin T., Newland A. C., Lewis D. L., Galvin M. C. T cell receptor gene rearrangements define a monoclonal T cell proliferation in patients with T cell lymphocytosis and cytopenia. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):914–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Mendrick D. L., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Identification of an inducible endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9238–9242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. K., Jutila M. A., Sedmak D. D., Beattie M. S., Orosz C. G. Lymphocyte entry into inflammatory tissues in vivo. Qualitative differences of high endothelial venule-like vessels in sponge matrix allografts vs isografts. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4219–4224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolhuis R. L., van de Griend R. J. Phytohemagglutinin-induced proliferation and cytolytic activity in T3+ but not in T3- cloned T lymphocytes requires the involvement of the T3 antigen for signal transmission. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jun;93(1):46–57. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordignon C., Daley J. P., Nakamura I. Hematopoietic histoincompatibility reactions by NK cells in vitro: model for genetic resistance to marrow grafts. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1398–1401. doi: 10.1126/science.3906897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUDKOWICZ G., STIMPFLING J. H. DEFICIENT GROWTH OF C57BL MARROW CELLS TRANSPLANTED IN F1 HYBRID MICE. ASSOCIATION WITH THE HISTOCOMPATIBILITY-2 LOCUS. Immunology. 1964 May;7:291–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone E., Viale O., Pende D., Malnati M., Biassoni R., Melioli G., Moretta A., Long E. O., Moretta L. Specific lysis of allogeneic cells after activation of CD3- lymphocytes in mixed lymphocyte culture. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2403–2408. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudkowicz G., Nakamura I. Genetics of the murine hemopoietic-histocompatibility system: an overview. Transplant Proc. 1983 Dec;15(4):2058–2063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle N. K., Doyle L. V., Bender J. R., Bradley E. C. Interleukin 2-activated human lymphocytes exhibit enhanced adhesion to normal vascular endothelial cells and cause their lysis. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1779–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Murre C., Quertermous T., Boss J. M., Leiden J. M., Seidman J. G., Strominger J. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of complementary DNA encoding an aberrantly rearranged human T-cell gamma chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2619–2623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Bensussan A., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Activation of human thymocytes via the 50KD T11 sheep erythrocyte binding protein induces the expression of interleukin 2 receptors on both T3+ and T3- populations. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):330–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskard D., Cavender D., Beatty P., Springer T., Ziff M. T lymphocyte adhesion to endothelial cells: mechanisms demonstrated by anti-LFA-1 monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2901–2906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. J., Koren H. S. Depletion of NK by cellular immunoadsorption. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1127–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kansas G. S., Wood G. S., Dailey M. O. A family of cell-surface glycoproteins defined by a putative anti-endothelial cell receptor antibody in man. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3050–3057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Benike C. J., Phillips J. H., Engleman E. G. Recombinant interleukin 2 enhanced natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity in human lymphocyte subpopulations expressing the Leu 7 and Leu 11 antigens. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):794–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz M., Jorkasky D., Kornbluth J. Increase in natural killer activity in cyclosporine-treated renal allograft recipients during rejection. Hum Immunol. 1987 Jun;19(2):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marboe C. C., Knowles D. M., 2nd, Chess L., Reemtsma K., Fenoglio J. J., Jr The immunologic and ultrastructural characterization of the cellular infiltrate in acute cardiac allograft rejection: prevalence of cells with the natural killer (NK) phenotype. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Apr;27(1):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohagheghpour N., Damle N. K., Moonka D. K., Terrell C. P., Engleman E. G. A human alloreactive inducer T cell clone that selectively activates antigen-specific suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Waldmann R. A., Morton C. C., Bongiovanni K. F., Waldmann T. A., Shows T. B., Seidman J. G. Human gamma-chain genes are rearranged in leukaemic T cells and map to the short arm of chromosome 7. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):549–552. doi: 10.1038/316549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemlander A., Soots A., Häyry P. In situ effector pathways of allograft destruction. 1. Generation of the "cellular" effector response in the graft and the graft recipient. Cell Immunol. 1984 Dec;89(2):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardi R., Bender J. R., Engleman E. G. Lymphocyte subsets differentially induce class II human leukocyte antigens on allogeneic microvascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2585–2592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. H., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Selective depletion of human natural killer cells on monolayers of target cells. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2322–2327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Ahrlund-Richter L., Jondal M. Target-effector interaction in the human and murine natural killer system: specificity and xenogeneic reactivity of the solubilized natural killer-target structure complex and its loss in a somatic cell hybrid. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):471–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., Hercend T., Fox D. A., Bensussan A., Bartley G., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L., Ritz J. The role of interleukin 2 and T11 E rosette antigen in activation and proliferation of human NK clones. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):672–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Luce G. E., Quinones R., Gress R. E., Springer T. A., Sanders M. E. Two antigen-independent adhesion pathways used by human cytotoxic T-cell clones. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):262–264. doi: 10.1038/323262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
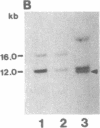
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., van Schooten W., Keizer H., van Seventer G., van de Rijn M., Terhorst C., de Vries J. E. Alloantigen recognition is preceded by nonspecific adhesion of cytotoxic T cells and target cells. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):403–405. doi: 10.1126/science.3485822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Perussia B. Human natural killer cells: biologic and pathologic aspects. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):489–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]