Abstract
This systematic review and cumulative analysis aimed to explore the efficacy and safety of the combination of intravesical mitomycin C (MMC) plus bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) patients. A comprehensive literature search using Pubmed, Embase, Medline, Cochrane Library, CBM, CNKI and VIP databases was performed to identify studies applying intravesical MMC plus BCG therapy on NMIBC patients up to June 2016. Summarized unadjusted odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to assess the efficacy and safety of the combination therapy. A total of 25 studies containing 2749 NMIBC patients were included in this systematic review. Compared with BCG monotherapy, the combination therapy could significantly reduce the tumor recurrence rate (OR = 0.64, 95% CI: 0.44–0.94, P = 0.02) and cancer-specific mortality (OR = 0.54, 95% CI: 0.34–0.87, P = 0.01), without more toxicities (OR = 0.58, 95% CI: 0.17–1.94, P = 0.37). The combination therapy could also lead to significant lower tumor recurrence rate than MMC monotherapy (OR = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.24–0.69, P = 0.0009). Our study indicates that the combination of MMC plus BCG instillation is an effective and safe adjuvant treatment for NMIBC patients.
Introduction
Urinary bladder cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors all over the world, occupying about 4% of the cancer. The incidence of bladder cancer was approximately 7%1, ranked fourth among male tumors. 70% of these patients suffer from superficial or non-muscle-invasive tumors2. Transurethral resection (TUR) is the current primary treatment. Subsequent intravesical adjuvant treatments including chemotherapy and immunotherapy are recommended to reduce the recurrence rate and delay the progression of the tumor3, 4.
Most widely used adjuvant agents are bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) and mitomycin C (MMC), especially for tumors with intermediate to high recurrence or progression rate5. Intravesical BCG is the most recommended treatment for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) with a relative satisfactory effect according to EAU guidelines6. However, the recurrent rate is still up to 60–70% and 30% of tumors turn out to be higher grade7. Therefore, advanced adjuvant regimens are necessary to improve the efficacy. Combination of intravesical MMC plus BCG instillation, a novel adjuvant therapy, has been researched in a variety of studies and showed a more enhanced antitumor effect8, 9. Detailed combined regimens, drug doses and therapeutic courses varied among these studies, which brought different results10–13.
No guidelines or protocols have been made yet to recommend the combination of intravesical MMC and BCG therapy for NMIBC. And as far as we have concerned, few conclusive articles or reviews focused on the efficacy and safety of various intravesical MMC plus BCG therapies on NMIBC patients. Consequently, we conducted this systematic review and cumulative analysis based on all relevant original studies and aimed to provide further instructions for adjuvant treatments of NMIBC.
Results
Eligible studies and characteristics
25 studies10–34 containing 2749 NMIBC patients were included in this systematic review (Fig. 1). Baseline characteristics of all eligible studies were shown in Table 1. Among 25 included studies, 16 were randomized controlled trials (RCTs)10–13, 15–21, 24, 28, 31, 33, 34, 4 were retrospective comparative trials14, 26, 27, 29, 1 was retrospective cohort study30 and remaining 4 were clinical series22, 23, 32, 25.
Figure 1.
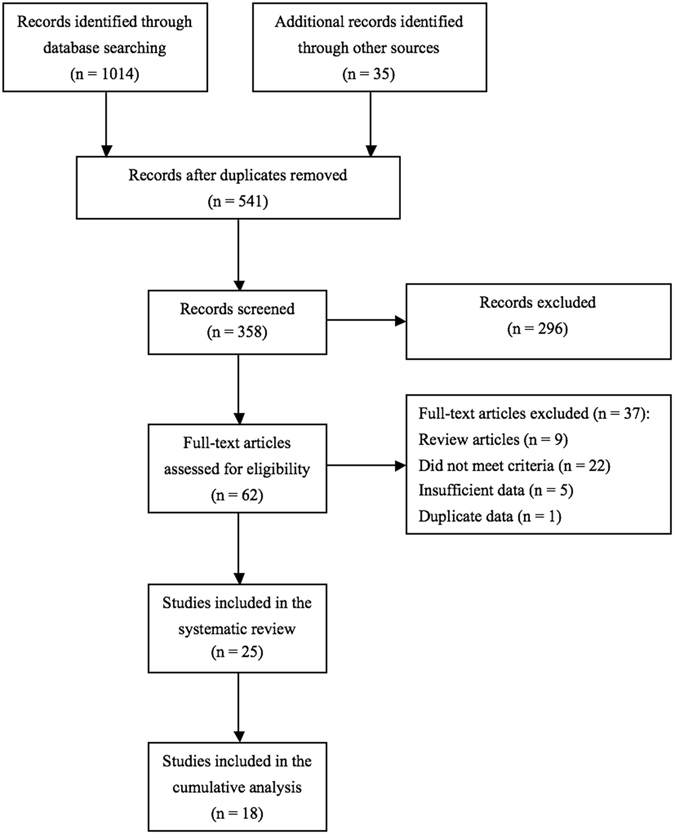
Flow diagram of the systematic review.
Table 1.
The baseline characteristics of included studies.
| Combination regimen of MMC+BCG | Reference | Country | Ethnicity | Recruitment period | Study design | LOE | Tumor stage | No. of cases receiving MMC+BCG | Mean/median age(yr) | Mean/median follow-up time (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A single dose of perioperative MMC prior to instillation with BCG | ||||||||||
| Badalato et al.14 | USA | mixed | 2000–2010 | Retrospective comparative trial | 3 | Ta, T1, Tis | 48 | 69.6 | 33 | |
| Gülpinar et al.10 | Turkey | Europeans | 2004–2006 | RCT | 2b | Ta, T1 | 25 | 58.2 | 41.3 | |
| Ye et al.15 | China | Asian | 1997–2002 | RCT | 2b | Ta, T1 | 50 | 57 | 32 | |
| Weiss et al.29 | USA | mixed | 1977–2009 | Retrospective comparative trial | 3 | Ta, T1, Tis | 23 | — | 54 | |
| Sequential instillation with MMC and BCG | ||||||||||
| Di Stasi et al.11 | Italy | Europeans | 1994–2002 | RCT | 2b | T1, Tis | 107 | 66 | 91 | |
| Oosterlinck et al.16 | Multi-country in Europe | Europeans | 2001–2005 | RCT | 1b | Ta, T1, Tis | 41 | 68 | 56.4 | |
| He et al.17 | China | Asians | 2005–2009 | RCT | 2b | Ta, T1 | 40 | 61.2 | 21.2 | |
| Liu et al.18 | China | Asians | 2000–2003 | RCT | 2b | Ta, T1 | 59 | 55 | 35 | |
| Ma et al.19 | China | Asians | 1996–1998 | RCT | 2b | — | 29 | 52 | 37.9 | |
| Kaasinen et al.20 and Järvinen et al.21 | Finland | Europeans | 1992–1996 | RCT | 2a | Ta, T1 | 102 | 68 | 30.7 | |
| 117.6 | ||||||||||
| Svatek et al.22 | USA | mixed | — | Case series | 4 | Ta, T1, Tis | 12 | 67 | 21.4 | |
| Cai et al.23 | China | Asians | 2007–2011 | Case series | 4 | Ta, T1 | 30 | 60.3 | 20.4 | |
| Gan et al.30 | UK | Europeans | 2009–2013 | Retrospective cohort study | 3 | Ta, T1, Tis | 104 | 68 | 24 | |
| Witjes et al.31 | Netherlands | Europeans | 1991–1993 | RCT | 2a | Ta, T1, Tis | 90 | — | 32 | |
| Van der Meijden et al.32 | Netherlands | Europeans | 1990–1992 | Case series | 4 | Ta, T1 | 35 | 70 | 19.8 | |
| Alternating instillation with MMC and BCG | ||||||||||
| Rintala et al.33 and Järvinen et al.12 | Finland | Europeans | 1987–1992 | RCT | 2a | Ta, T1, Tis | 28 | 66 | 33 | |
| 86.4 | ||||||||||
| Kaasinen et al.24 | Finland, Norway and Sweden | Europeans | 1992–1997 | RCT | 2a | Ta, T1, Tis | 159 | 71 | 56.3 | |
| Zhang et al.25 and Sun et al.26 | China | Asians | 1998–2006 | Retrospective comparative trial | 3 | Ta, T1 | 32 | 62.5 | 28 | |
| Bao et al.27 | China | Asians | 1999–2006 | Retrospective comparative trial | 3 | Ta, T1, Tis | 20 | 70 | 24 | |
| Rintala et al.34 | Finland | Europeans | 1987–1992 | RCT | 2a | Ta, T1 | 95 | 68.5 | 34 | |
| Mixed instillation with MMC plus BCG | ||||||||||
| Solsona et al.13 | Spain | Europeans | 1993–1994 | RCT | 1b | Ta, T1, Tis | 211 | 65 | 85.2 | |
| Fang et al.28 | China | Asians | 1999–2000 | RCT | 2a | Ta, T1 | 21 | 67.5 | 23.4 | |
BCG = bacillus Calmette-Guerin; LOE = level of evidence; MMC = mitomycin C; RCT = randomized controlled trial.
In all studies, 1810–19, 24, 26–29, 31, 33, 34 were included in our cumulative analysis, comparing the efficacy of combined MMC plus BCG therapy with MMC or BCG monotherapy on NMIBC patients. Among them, MMC + BCG versus BCG alone was conducted in 10 studies10, 11, 13, 14, 16–18, 24, 27, 29, MMC + BCG versus MMC alone was referred in 7 studies12, 15, 19, 28, 31, 33, 34 and the rest 126 compared MMC + BCG with either MMC or BCG.
Quality assessments of included studies
Level of evidence (LOE) was accessed for all 25 included studies and results were listed in Table 1. Among 16 RCTs, 9 were in low risk of bias12, 13, 16, 20, 21, 24, 28, 33, 34, 6 were in moderate risk of bias10, 15, 17–19, 31 and the remaining one was in high risk of bias11 according to the quality assessment (Fig. 2). However, the risk of detection and attrition biases were low in all of them. Additionally, 7 RCTs were in relative high quality12, 13, 16, 20, 21, 33, 34.
Figure 2.

Assessment of bias risk for included RCTs. (A) Methodological quality graph: authors’ judgments about each methodological quality item presented as percentages across all included studies; (B) Methodological quality summary: authors’ judgments about each methodological quality item for each included study, “+” low risk of bias; “?” unclear risk of bias; “−” high risk of bias).
Instillation regimens and prognoses of intravesical MMC plus BCG
1361 NMIBC patients from 25 eligible studies received intravesical MMC plus BCG instillation as an adjuvant therapy besides surgery (Table 2). Combination regimens in these studies could be divided into four subtypes: single dose of perioperative MMC prior to BCG (combination regimen 1) was applied in 4 studies10, 14, 15, 29; sequential instillations with MMC and BCG (combination regimen 2) were used in 12 studies11, 16–23, 30–32; 7 studies12, 24–27, 33, 34 adopted alternating instillations with MMC and BCG (combination regimen 3); and last 2 studies13, 28 preferred mixed instillations with MMC plus BCG (combination regimen 4). Table 3 showed prognoses of patients receiving combination therapies in all included studies according to different instillation regimen and follow-up time.
Table 2.
Detailed outcomes of patients receiving combination therapy.
| Combination regimen of MMC + BCG | Reference | No. of case receiving MMC + BCG | Mean/median age(yr) | Mean/median follow-up time (mo) | During follow-up time | 5-year recurrence-free survival rate | No. severe side-effects (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. recurrence (%) | No. disease-free case (%) | No. progression (%) | No. death from any causes (%) | No. death from bladder cancer (%) | |||||||
| A single dose of perioperative MMC prior to instillation with BCG | |||||||||||
| Badalato et al.14 | 48 | 69.6 | 33 | 21 (43.8) | 27 (56.2) | — | — | — | 56.3% | — | |
| Gülpinar et al.10 | 25 | 58.2 | 41.3 | 9 (36) | 16 (64) | 1 (4) | — | — | — | 0 | |
| Ye et al.15 | 50 | 57 | 32 | 3 (6) | — | 0 | — | 0 | — | 0 | |
| Weiss et al.29 | 23 | — | 54 | 10 (43.5) | 10 (43.5) | — | 3 (13) | — | 48.4% | — | |
| Sequential instillation with MMC and BCG | |||||||||||
| Di Stasi et al.11 | 107 | 66 | 91 | 45 (42.1) | 62 (57.9) | 10 (9.3) | 23 (21.5) | 6 (5.6) | — | 3 (2.8) | |
| Oosterlinck et al.16 | 41 | 68 | 56.4 | 23 (56.1) | 25 (61) | 3 (7.3) | 7 (17.1) | 0 | 51.4% | 5 (12.2) | |
| He et al.17 | 40 | 61.2 | 21.2 | 5 (12.5) | — | — | — | 0 | — | 0 | |
| Liu et al.18 | 59 | 55 | 35 | 9 (15.3) | — | 3 (5.1) | — | 0 | — | 0 | |
| Ma et al.19 | 29 | 52 | 37.9 | 3 (10.3) | — | — | — | — | — | 0 | |
| Kaasinen et al.20 and Järvinen et al.21 | 102 | 68 | 30.7 | 14 (13.7) | 73 (71.6) | 3 (2.9) | 4 (3.9) | 0 | 67% | 2 (2) | |
| 117.6 | 44 (43.1) | 32 (31.4) | 6 (5.9) | 56 (54.9) | 3 (2.9) | — | |||||
| Svatek et al.22 | 12 | 67 | 21.4 | 1 (8.3) | 11 (91.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | — | 0 | |
| Cai et al.23 | 30 | 60.3 | 20.4 | 4 (13.3) | 26 (86.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | — | 0 | |
| Gan et al.30 | 104 | 68 | 24 | 31 (29.8) | 66 (63.5) | 5 (4.8) | 1 (1) | 0 | — | 1 (1) | |
| Witjes et al.31 | 90 | — | 32 | 35 (38.9) | 47 (52.2) | 5 (5.6) | 21 (23.3) | 5 (5.6) | 52.2% | 16 (17.8) | |
| Van der Meijden et al.32 | 35 | 70 | 19.8 | 8 (22.9) | — | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 0 | — | 2 (5.7) | |
| Alternating instillation with MMC and BCG | |||||||||||
| Rintala et al.33 and Järvinen et al.12 | 28 | 66 | 33 | 6 (21.4) | 14 (50) | 2 (7.1) | 0 | 0 | — | 0 | |
| 86.4 | 19 (67.9) | — | 8 (28.6) | 20 (71.4) | 8 (28.6) | 34% | — | ||||
| Kaasinen et al.24 | 159 | 71 | 56.3 | 71 (44.7) | 72 (45.3) | 34 (21.4) | — | 13 (8.2) | 40.7% | 10 (6.3) | |
| Zhang et al.25 and Sun et al.26 | 32 | 62.5 | 28 | 2 (6.3) | 30 (93.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | — | 0 | |
| Bao et al.27 | 20 | 70 | 24 | 0 | — | 0 | — | 0 | — | 0 | |
| Rintala et al.34 | 95 | 68.5 | 34 | 57 (60) | 38 (40) | 3 (3.2) | 2 (2.1) | 0 | — | 6 (6.3) | |
| Mixed instillation with MMC plus BCG | |||||||||||
| Solsona et al.13 | 211 | 65 | 85.2 | 44 (20.9) | — | 26 (12.3) | 51 (24.2) | 10 (4.7) | — | 20 (9.5) | |
| Fang et al.28 | 21 | 67.5 | 23.4 | 1 (4.8) | — | — | — | 0 | — | 0 | |
BCG = bacillus Calmette-Guerin; MMC = mitomycin C.
Table 3.
Patients’ prognoses with different combination regimen and follow-up time.
| Combination regimen | Follow-up time | No. of included study | No. recurrence/total (%) | No. disease-free case/total (%) | No. progression/total (%) | No. death from any causes/total (%) | No. death from bladder cancer/total (%) | No. severe side-effects/total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combination regimen 1 | Medium-term (2–5 yrs) | 4 | 43/146 (29.5) | 53/96 (55.2) | 1/75 (1.3) | 3/23 (13) | 0/50 | 0/75 |
| Combination regimen 2 | Short-term (≤2 yrs) | 5 | 49/221 (22.2) | 103/146 (70.5) | 6/181 (3.3) | 1/181 (0.6) | 0/221 | 3/221 (1.4) |
| Medium-term (2–5 yrs) | 5 | 84/321 (26.2) | 145/233 (62.2) | 14/292 (4.8) | 32/233 (13.7) | 5/292 (1.7) | 23/321 (7.2) | |
| Long-term (≥5 yrs) | 2 | 89/209 (42.6) | 94/209 (45) | 16/209 (7.7) | 79/209 (37.8) | 9/209 (4.3) | 5/209 (2.4) | |
| Combination regimen 3 | Short-term (≤2 yrs) | 1 | 0/20 | — | 0/20 | — | 0/20 | 0/20 |
| Medium-term (2–5 yrs) | 5 | 136/314 (43.3) | 154/314 (49) | 39/314 (12.4) | 2/155 (1.3) | 13/314 (4.1) | 16/314 (5.1) | |
| Long-term (≥5 yrs) | 1 | 19/28 (67.9) | — | 8/28 (28.6) | 20/28 (71.4) | 8/28 (28.6) | — | |
| Combination regimen 4 | Short-term (≤2 yrs) | 1 | 1/21 (4.8) | — | — | — | 0/21 | 0/21 |
| Long-term (≥5 yrs) | 1 | 44/211 (20.9) | — | 26/211 (12.3) | 51/211 (24.2) | 10/211 (4.7) | 20/211 (9.5) |
Combination regimen 1: a single dose of perioperative MMC prior to BCG; Combination regimen 2: sequential instillation with MMC and BCG; Combination regimen 3: alternating instillation with MMC and BCG; Combination regimen 4: mixed instillation with MMC plus BCG.
MMC plus BCG instillation versus BCG alone
11 studies compared the efficacy of MMC plus BCG with BCG alone instillation (Supplementary Table 1).
Recurrence
Tumor recurrence rate was compared between intravesical MMC plus BCG instillation and BCG alone treatment among NMIBC patients in all 11 studies. Slight heterogeneity was observed (I 2 = 57%, P = 0.009), and the recurrence rate in patients receiving MMC + BCG was significantly lower than BCG alone [odds ratio (OR) = 0.64, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.44–0.94, P = 0.02) (Fig. 3). In subgroup analyses, patients in following subgroups also benefited more from MMC + BCG instillations significantly than BCG alone: retrospective comparative trials, combination regimen 2, combination regimen 4, short-term and long-term follow-ups, Asians populations, therapeutic courses ≤1yr and >2 yrs, and instillation numbers ≥24 (Supplementary Table 2). No publication bias was detected through both inverted funnel plot and Egger’s test (t = −1.65, P = 0.138).
Figure 3.
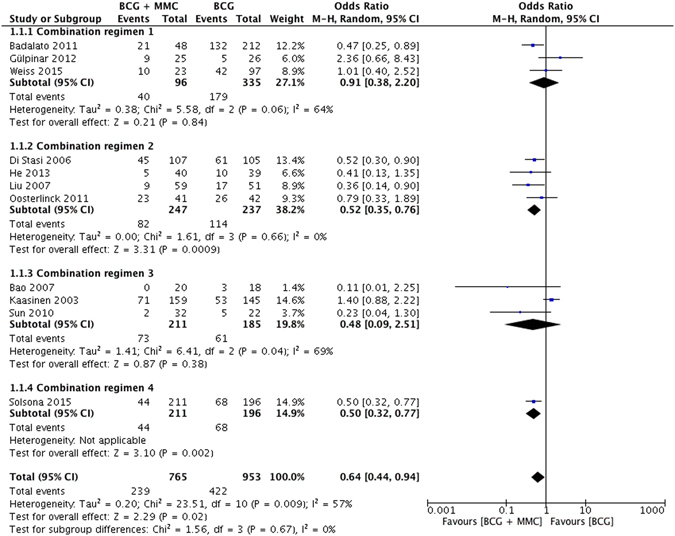
Forest plot of tumor recurrence rate comparing combination therapy with BCG monotherapy.
In 3 studies, we reported multivariable adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) to prevent tumor recurrence of combined MMC and BCG instillation compared with BCG alone. No significant difference was found between two groups (HR = 0.86, 95% CI: 0.50–1.49, P = 0.59) with moderate heterogeneity (I 2 = 80%, P = 0.007).
Disease-free survival
Number of disease-free patients during follow-up time was mentioned in 6 studies, and slight heterogeneity was found (I 2 = 67%, P = 0.01). Although no significant difference was observed between MMC + BCG and BCG groups (OR = 1.16, 95% CI: 0.70–1.92, P = 0.56), patients receiving combination regimen 2 shared a significant higher disease-free survival rate than BCG alone (OR = 1.76, 95% CI: 1.11–2.79, P = 0.02) without heterogeneity (I 2 = 0%, P = 0.57) (Supplementary Fig. 1). No publication bias was detected through the inverted funnel plot.
Progression
7 studies compared rate of tumor progression between MMC + BCG and BCG alone groups. No significant difference occurred (OR = 0.65, 95% CI: 0.33–1.29, P = 0.22) with slight heterogeneity (I 2 = 63%, P = 0.01). However, subgroup analyses indicated that the application of combination regimen 2 could significantly reduce the risk of progression for NMIBC patients compared with BCG alone (OR = 0.32, 95% CI: 0.18–0.60, P = 0.0004) bearing no heterogeneity among these relevant studies (I 2 = 0%, P = 0.38) (Fig. 4). The inverted funnel plot did not demonstrate any indication of publication bias.
Figure 4.

Forest plot of tumor progression rate comparing combination therapy with BCG monotherapy.
Cancer-specific mortality
During the follow-up time, patients who died from bladder cancer were reported in 5 studies. Significant lower cancer-specific mortality was discovered in MMC + BCG compared with BCG group (OR = 0.54, 95% CI: 0.34–0.87, P = 0.01) sharing no heterogeneity (I 2 = 41%, P = 0.15) (Supplementary Fig. 2). Furthermore, significant advantage was only tested in combination regimen 2 (OR = 0.24, 95% CI: 0.10–0.59, P = 0.002) after subgroup analyses were conducted. The inverted funnel plot showed no publication bias.
Severe side-effects
Toxicities of intravesical MMC + BCG versus BCG alone therapies were assessed in 5 studies with moderate heterogeneity (I 2 = 80%, P = 0.0004). Combination of intravesical MMC + BCG instillation did not seem to bring fewer toxicities than BCG alone (OR = 0.58, 95% CI: 0.17–1.94, P = 0.37) (Supplementary Fig. 3). Nevertheless, subgroup analyses indicated that combination regimen 3 could significantly decrease the toxicity of combination therapy compared with BCG monotherapy (OR = 0.18, 95% CI: 0.09–0.38, P < 0.00001). No publication bias was detected through the inverted funnel plot.
MMC+BCG instillation versus MMC alone
8 studies concentrated on the efficacy of intravesical MMC + BCG instillation versus MMC alone on NMIBC patients (Supplementary Table 3). Recurrence rate was compared in all 8 studies, and our results indicated that combined intravesical therapy was significantly more effective to decrease tumor recurrence than MMC alone (OR = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.24–0.69, P = 0.0009) with slight heterogeneity (I 2 = 47%, P = 0.07) (Fig. 5). In addition, 5 studies compared the tumor progression rate between MMC + BCG and MMC alone groups with no significant difference (OR = 0.83, 95% CI: 0.43–1.59, P = 0.57) (Supplementary Fig. 4). No heterogeneity existed either (I 2 = 0%, P = 0.88). Comparison of toxicities between two groups was also conducted in 5 studies and no significant difference was observed (OR = 1.18, 95% CI: 0.63–2.19, P = 0.61) (Supplementary Fig. 5). Cancer-specific mortality was only reported in 2 studies, and no significant difference was discovered.
Figure 5.
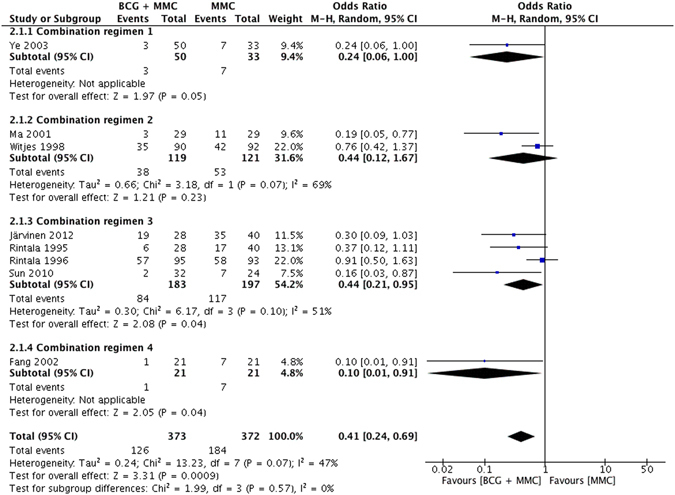
Forest plot of tumor recurrence rate comparing combination therapy with MMC monotherapy.
Discussion
This systematic review aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combined intravesical MMC plus BCG instillation as a novel adjuvant therapy for NMIBC. Our analyses concluded that, compared with BCG or MMC monotherapy, the combination therapy could reduce the recurrence rate of NMIBC significantly without causing more toxicities. As a result, all evidences we have achieved till now support that combined intravesical MMC plus BCG instillation may be a better choice for NMIBC patients.
Previous studies have shown that the adherence to bladder wall of BCG is an important step for immunotherapy35, 36. Chemical disruption of the bladder urothelium induced by MMC could enable BCG to attach more efficiently to bladder wall and then improve the immune response and antitumor activity37. Furthermore, MMC instillation could also promote BCG uptake and activate related immune effector cells38–40. Therefore, an enhanced antitumor effect could be achieved by combined intravesical MMC and BCG instillation.
So far, several studies8–13 have investigated the antitumor effect of combined intravesical MMC plus BCG instillation. Lan et al.41 recently conducted a meta-analysis including only RCTs, having compared the efficacy of combined BCG and MMC therapy with each monotherapy on NMIBC patients. Results from 8 RCTs in their study showed a significant decreased recurrence rate in patients receiving combination therapy compared with monotherapy. However, since a lot of comparative and cohort studies were not included, their conclusions appeared to be rigorous to some extent. Some animal experiments also drew a similar conclusion with us22, 42. Matsushima et al.42 found MMC plus BCG treatment could inhibit tumor growth and cellular proliferation, and prolong the survival period compared to the BCG-alone therapy through an orthotopic bladder cancer model. Moreover, Svatek et al.22 identified macrophages were polarized toward a beneficial M1 phenotype after MMC plus BCG instillation in a murine model of bladder cancer, which indicated the antitumor effect of combination instillation could be improved by increased number of beneficial cells.
In this systematic review, we recognized that different combination regimens were carried out in these studies, which might have caused varied effects. Table 3 showed that combination regimen 4 could reduce recurrence but lead to more severe side-effects than others. While considering delaying tumor progression and reducing cancer-specific mortality in long-term follow-up, combination regimen 2 might be a better choice. Several courses of MMC before sequential BCG instillation could not only improve the antitumor function, but also promote the activation and production of immune effector cells38–40. Nevertheless, since these findings were not obtained by statistical comparisons and cumulative analyses of different combination regimens, they should only represent our own opinions and could not be regarded as evidential results.
Solsona et al.13 conducted a RCT demonstrating that combined MMC plus BCG therapy was more toxic than BCG alone with severe side-effects rate of 9.5%. However, our analysis indicated that taking all clinical trials into consideration, combination therapy did not cause more toxicities than BCG or MMC monotherapy. Therefore, combination of MMC plus BCG treatment seems to be safe, while more clinical studies are still needed for further evaluation.
Several potential limitations should be addressed about this analysis. First, included studies lasted a time span as long as 21 years, during which the living environment and quality of life might change. Second, data of some studies was incomplete even by contacting authors. Third, most high-quality trials were conducted in Europeans and Asians, which might restrict the application of our results on other populations. At last, insufficient numbers of related studies might bring some potential bias to our results.
Conclusion
Our study concluded that combination of MMC plus BCG intravesical instillation was an effective and safe adjuvant treatment for NMIBC patients after TUR. This therapy could significantly reduce the tumor recurrence rate and would not bring more toxicities than BCG or MMC monotherapy. However, further high-quality clinical trials are still needed to verify conclusions of our study.
Materials and Methods
Search strategy
A systematic literature search using Pubmed, Embase, Medline, Cochrane Library, CBM, CNKI and VIP databases was performed to identify studies exploring the efficacy of intravesical MMC plus BCG therapy for NMIBC patients up to June 2016. Search terms were “‘mitomycin C’ or ‘MMC’” and “‘bacillus Calmette-Guerin’ or ‘BCG’” in combination with “‘non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer’ or ‘NMIBC’ or ‘superficial bladder cancer’ or ‘orthotopic bladder cancer’ or ‘bladder carcinoma in situ’”. The study language was restricted to English and Chinese. Reference lists of relevant studies were also checked.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies applying intravesical MMC plus BCG therapy on NMIBC patients and providing detailed information were included in this systematic review, and data comparing the efficacy of combination therapy with MMC or BCG monotherapy was pooled in cumulative analysis. Accordingly, we excluded studies involving congress abstracts, conference proceedings, editorials, reviews, animal experiments and repeated publications. Two authors (T.D. and B.L.) independently assessed relevant records, evaluated the quality of included studies and extracted studies’ data. Discrepancies were resolved via open discussion.
Study quality assessment and data extraction
GRADE approach was used to assess the LOE of all eligible studies43. Furthermore, the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias Tool was applied to evaluate the quality of RCTs44. Data was attentively extracted including research methodology, participants’ information, tumor stage, surgical procedure, therapeutic regimens of MMC plus BCG (instillation schedule, dose and retaining time), course of treatment, and disease-related outcomes (recurrence, progression, disease-free survival, disease-free interval, cancer-specific survival, overall survival and severe side-effect). In comparative studies, HRs and 95% CIs were also extracted to predict the recurrence-free survival between combined MMC plus BCG and MMC or BCG alone.
Statistics analysis
In the cumulative analysis, summarized unadjusted ORs and 95% CIs were calculated to assess the efficacy of combined MMC and BCG instillation compared with MMC or BCG alone. Available multivariable adjusted HRs were also pooled as references. Subgroup analyses were conducted according to type of combination regimen, study design, patient ethnicity, number of instillation, therapeutic course, and follow-up time. Statistical heterogeneity among included studies was tested through chi-square test45. If no heterogeneity existed with p value > 0.10, the fixed-effect model was used. Otherwise, the random-effect model was applied. A two-sided p value < 0.05 was considered significant for all results in cumulative analysis. Publication bias was assessed by inverted funnel plot and Egger’s test46. All statistical analyses were conducted by RevMan (version 5.3; Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK) and STATA (version 13.0; StataCorp, College Station, Texas, USA) software.
Electronic supplementary material
Author Contributions
All authors contributed significantly to this work. G.Z. and T.D. designed this study; T.D., B.L. and X.D. performed the research study, collected and analyzed the data; T.D., B.L. and X.D. wrote the manuscript; T.Z. and C.C. resolved discrepancies and provide significant advices for this research. All authors reviewed, edited and approved the manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Tuo Deng, Bing Liu and Xiaolu Duan contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at doi:10.1038/s41598-017-03421-5
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Jemal A, et al. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. doi: 10.3322/caac.20006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lum BL, Torti FM. Adjuvant intravesicular pharmacotherapy for superficial bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991;83:682–694. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.10.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rosenberg JE, Carroll PR, Small EJ. Update on chemotherapy for advanced bladder cancer. J Urol. 2005;174:14–20. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000162039.38023.5f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hsieh JT, Dinney CP, Chung LW. The potential role of gene therapy in the treatment of bladder cancer. Urol Clin North Am. 2000;27:103–113. doi: 10.1016/S0094-0143(05)70238-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Malmstrom PU, et al. An individual patient data meta-analysis of the long-term outcome of randomised studies comparing intravesical mitomycin C versus bacillus Calmette-Guerin for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2009;56:247–256. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.04.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Babjuk M, et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2013. Eur Urol. 2013;64:639–53. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ratliff TL, Ritchey JK, Yuan JJ, Andriole GL, Catalona WJ. T-cell subsets required for intravesical BCG immunotherapy for bladder cancer. J Urol. 1993;150:1018–1023. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35678-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Oliveira P, Palmeira C, Colaço A, De la Cruz P. LF, Lopes C. Cell Proliferation and DNA Content in Rat Urothelial Lesions after Repeat Intravesical Instillations of Mitomycin C and Bacillus Calmette-Guerin. Urol Int. 2008;80:90–97. doi: 10.1159/000111737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Matsushima M, et al. Enhanced antitumor effect of combination intravesical mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy in an orthotopic bladder cancer model. Oncology letter. 2011;2:13–19. doi: 10.3892/ol.2010.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gülpinar Ö, Halilioglu AH, Gökçe MI, Göğüş Ç, Baltaci S. The value of perioperative mitomycin C instillation in improving subsequent bacillus calmette-guerin instillation efficacy in intermediate and high-risk patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a prospective randomized study. Int Braz J Urol. 2012;38:474–479. doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382012000400006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Di Stasi SM, et al. Sequential BCG and electromotive mitomycin versus BCG alone for high-risk superficial bladder cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:43–51. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70472-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Järvinen R, Kaasinen E, Rintala E, Group TF. Long-term results of maintenance treatment of mitomycin C or alternating mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin instillation therapy of patients with carcinoma in situ of the bladder: a subgroup analysis of the prospective FinnBladder 2 study with a 17-year follow-up. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2012;46:411–417. doi: 10.3109/00365599.2012.694906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Solsona E, et al. Sequential Combination of Mitomycin C Plus Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) Is More Effective but More Toxic Than BCG Alone in Patients with Non-Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer in Intermediate- and High-risk Patients: Final Outcome of CUETO 93009, a Randomized Prospective Trial. Eur Urol. 2015;67:508–516. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.09.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Badalato GM, Hruby G, Razmjoo M, McKiernan JM. Maximizing intravesical therapy options: is there an advantage to the administration of perioperative mitomycin C prior to an induction course of BCG? Can J Urol. 2011;18:5890–5895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ye LH, Chen YL, Tao SX, Qian SX. Effect of mitomycin C instilled immediately after TUR added with low dose BCG maintenance therapy to prevent recurrence of superficial bladder cancer. Chin J Rehabil Theory Practice. 2003;9:730–731. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Oosterlinck W, et al. Sequential intravesical chemoimmunotherapy with mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin and with bacillus Calmette-Guerin alone in patients with carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder: results of an EORTC genito-urinary group randomized phase 2 trial (30993) Eur Urol. 2011;59:438–446. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.11.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.He AR, Song HF, Wan QF, Du JB. Clinical observation on Bacillus Calmette-Guerin combined with mitomycin C in prevention of post-operative recurrence of superficial transitional cell carcinoma in bladder. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 2013;12:948–949. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liu SM, Liu YL. Intravesical instillation of mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin for the prevention of post-operative recurrence of superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Chinese Medicine of Factory and Mine. 2007;20:205–206. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ma SL, Li SX, Zhong QG. Sequential intravesical mitomycin plus bacillus Calmette-Guerin for preventing recurrence of superficial bladder cancer. Chinese Journal of Misdiagnostics. 2001;1:60. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kaasinen E, et al. Weekly mitomycin C followed by monthly bacillus Calmette-Guerin or alternating monthly interferon-alpha2B and bacillus Calmette-Guerin for prophylaxis of recurrent papillary superficial bladder carcinoma. J Urol. 2000;164:47–52. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67446-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Järvinen R, et al. Long-term Outcome of Patients with Frequently Recurrent Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Carcinoma Treated with One Perioperative Plus Four Weekly Instillations of Mitomycin C Followed by Monthly Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) or Alternating BCG and Interferon-alpha2b Instillations: Prospective Randomised FinnBladder-4 Study. Eur Urol. 2015;68:611–617. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Svatek RS, et al. Sequential intravesical mitomycin plus Bacillus Calmette-Guerin for non-muscle-invasive urothelial bladder carcinoma: translational and phase I clinical trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:303–311. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cai GX. Clinical observation on intravesical mitomycin C plus bacillus Calmette-Guerin instillation for superficial bladder cancer. China Health Industry. 2012;27:92. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kaasinen E, et al. Alternating mitomycin C and BCG instillations versus BCG alone in treatment of carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder: a nordic study. Eur Urol. 2003;43:637–645. doi: 10.1016/S0302-2838(03)00140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhang YH, Ma LW, Wu Y, Chen JG, Luo DQ. Bacillus Calmette-Guerin vaccine and mitomycin C alternation for irrigation of bladder to prevent the recurrence of superficial bladder carcinoma. Journal Of Modern Urology. 2009;14:281–282. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sun MZ, Zhang YH. Alternating intravesical instillation of mitomycin C plus bacillus Calmette-Guerin for preventing recurrence of superficial bladder cancer. Chinese Community Doctors. 2010;12:65–66. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bao GJ. Effect of Mitomycin C Instilled after Operation Added with Bacillus Calmette-Guerir Maintenance Therapy to Prevent Recurrence of Bladder Cancer. The Chinese Journal Of Modern Applied Pharmacy. 2007;24:650–652. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fang WJ, Zhang BB, Cai SL. Prevention of recurrence of bladder cancer by intravesical instillation with combination of Mitomycin C and Bacillus Calmette-Guerir after TURBT. Zhejiang Medical Journal. 2002;24:328–329. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Weiss BE, Pietzak EJ, Wein AJ, Malkowicz SB, Guzzo TJ. Single instillation of mitomycin C plus bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) versus BCG alone in high grade non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Can J Urol. 2015;22:7876–7881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gan C, et al. Sequential bacillus Calmette-Guérin/Electromotive Drug Administration of Mitomycin C as the Standard Intravesical Regimen in High Risk Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: 2-Year Outcomes. J Urol. 2016;195:1697–703. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.01.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Witjes JA, Caris CT, Mungan NA, Debruyne FM, Witjes WP. Results of a randomized phase III trial of sequential intravesical therapy with mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin versus mitomycin C alone in patients with superficial bladder cancer. J Urol. 1998;160:1668–71. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)62377-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Van der Meijden AP, et al. Marker tumour responses to the sequential combination of intravesical therapy with mitomycin-C and BCG-RIVM in multiple superficial bladder tumours. Report from the European Organisation for Research and Treatment on Cancer-Genitourinary Group (EORTC 30897) Eur Urol. 1996;29:199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rintala E, et al. Alternating mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin instillation therapy for carcinoma in situ of the bladder. The Finnbladder Group. J Urol. 1995;154:2050–3. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)66691-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rintala E, Jauhiainen K, Kaasinen E, Nurmi M, Alfthan O. Alternating mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin instillation prophylaxis for recurrent papillary (stages Ta to T1) superficial bladder cancer. Finnbladder Group. J Urol. 1996;156:56–9. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)65936-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ratliff TL, Palmer JO, McGarr JA, Brown EJ. Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy for murine bladder tumors: initiation of the response by fibronectin-mediated attachment of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin. Cancer Res. 1987;47:1762–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hudson MA, Ritchey JK, Catalona WJ, Brown EJ, Ratliff TL. Comparison of the fibronectin-binding ability and antitumor efficacy of various mycobacteria. Cancer Res. 1990;50:3843–3847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kavoussi LR, Brown EJ, Ritchey JK, Ratliff TL. Fibronectin-mediated Calmette-Guerin bacillus attachment to murine bladder mucosa. Requirement for the expression of an antitumor response. J Clin Invest. 1990;85:62–67. doi: 10.1172/JCI114434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tan BT, Limpens J, Koken M, Valster H, Scheper RJ. Local administration of various cytostatic drugs after subcutaneous immunization enhances delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to sheep red blood cells in mice. Scand J Immunol. 1986;23:605–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nowak AK, Robinson BW, Lake RA. Gemcitabine exerts a selective effect on the humoral immune response: implications for combination chemoimmunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2002;62:2353–2358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zitvogel L, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Kroemer G. Immunological aspects of cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:59–73. doi: 10.1038/nri2216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lan Y, Liu D, Lin M. Comparison of the combination therapy of bacillus Calmette-Guérin and mitomycin C with the monotherapy for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Neoplasma. 2016;63:967–976. doi: 10.4149/neo_2016_616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Matsushima M, et al. Enhanced antitumor effect of combination intravesical mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy in an orthotopic bladder cancer model. Oncol Lett. 2011;2:13–19. doi: 10.3892/ol.2010.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Guyatt GH, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2008;336:924–926. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Higgins JP, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M. & Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–634. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


