Abstract
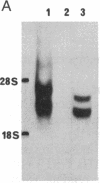
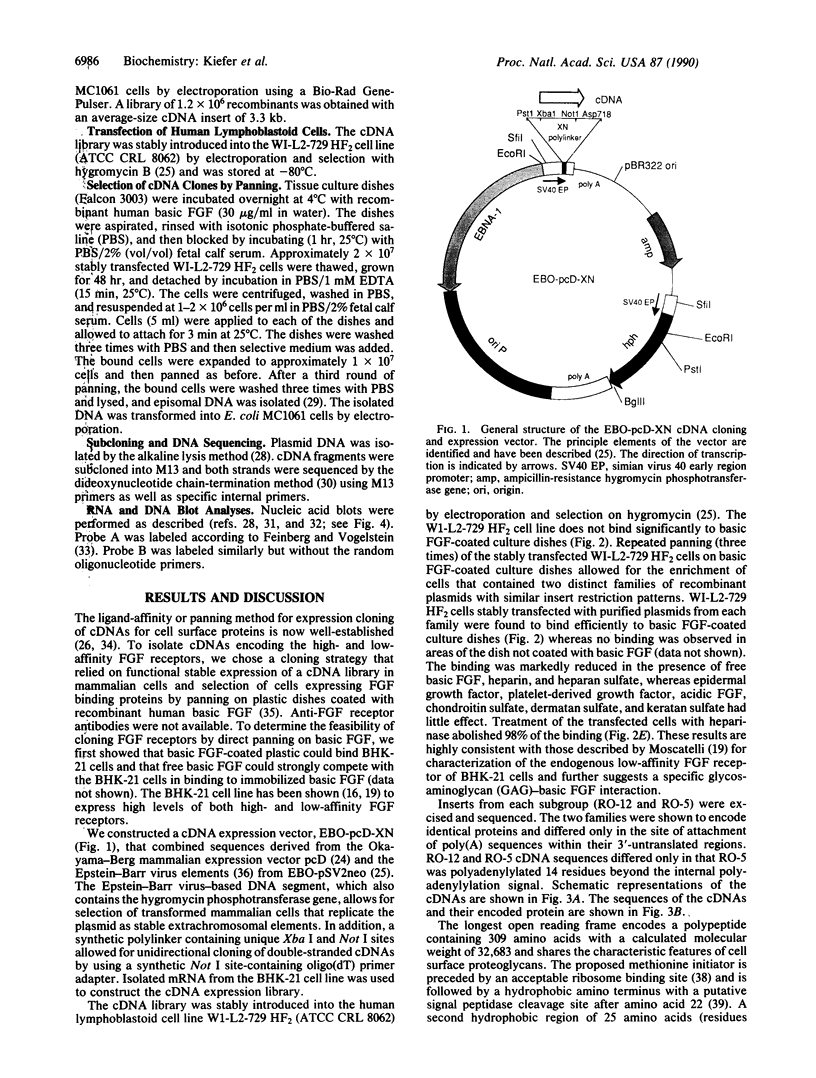
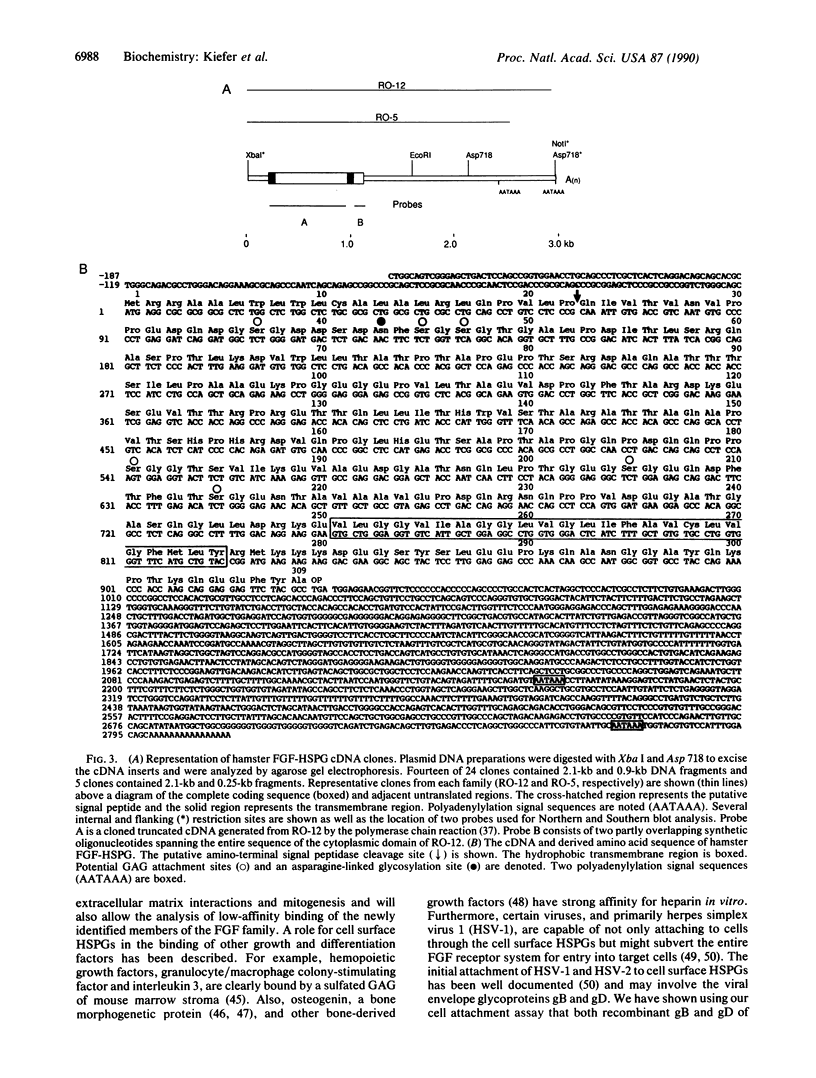
Expression cloning of cDNAs encoding a basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) binding protein confirms previous hypotheses that this molecule is a cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan. A cDNA library constructed from a hamster kidney cell line rich in FGF receptor activity was transfected into a human lymphoblastoid cell line. Clones expressing functional basic FGF binding proteins at their surfaces were enriched by panning on plastic dishes coated with human basic FGF. The amino acid sequence deduced from the isolated cDNAs revealed several interesting features, including hydrophobic signal and transmembrane domains that flank an extracellular region containing six potential attachment sites for glycosaminoglycan side chains. The structure also contains a short hydrophilic cytoplasmic tail sequence homologous to previously reported actin binding domains. Binding of basic FGF to cells expressing the binding protein could be inhibited by heparin and heparan sulfate but not by chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, or keratan sulfate. In addition to binding basic FGF, this protein or related surface proteins may function as an initial cellular attachment site for other growth factors and for viruses, such as herpes simplex virus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham J. A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Mergia A., Friedman J., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Human basic fibroblast growth factor: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2523–2528. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr P. J., Cousens L. S., Lee-Ng C. T., Medina-Selby A., Masiarz F. R., Hallewell R. A., Chamberlain S. H., Bradley J. D., Lee D., Steimer K. S. Expression and processing of biologically active fibroblast growth factors in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16471–16478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdon M. A., Krusius T., Campbell S., Schwartz N. B., Ruoslahti E. Identification and synthesis of a recognition signal for the attachment of glycosaminoglycans to proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3194–3198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandan E., Hirschberg C. B. Differential association of rat liver heparan sulfate proteoglycans in membranes of the Golgi apparatus and the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10520–10526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buntrock P., Jentzsch K. D., Heder G. Stimulation of wound healing, using brain extract with fibroblast growth factor (FGF) activity. II. Histological and morphometric examination of cells and capillaries. Exp Pathol. 1982;21(1):62–67. doi: 10.1016/s0232-1513(82)80054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas P., Burgos J., Baird A. Basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) promotes cartilage repair in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):611–618. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80887-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delli Bovi P., Curatola A. M., Kern F. G., Greco A., Ittmann M., Basilico C. An oncogene isolated by transfection of Kaposi's sarcoma DNA encodes a growth factor that is a member of the FGF family. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Rubin J. S., Miki T., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.2475908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Isolation and characterization of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor. Methods Enzymol. 1987;147:106–119. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)47102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Mavrakos A. E., Iafrati M. D., Doleman S. E., Klagsbrun M. Growth factors in bone matrix. Isolation of multiple types by affinity chromatography on heparin-Sepharose. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12665–12674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E., Martin G. R. Two proto-oncogenes implicated in mammary carcinogenesis, int-1 and int-2, are independently regulated during mouse development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7806–7810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Howk R., Burgess W., Ricca G. A., Chiu I. M., Ravera M. W., O'Brien S. J., Modi W. S., Maciag T., Drohan W. N. Human endothelial cell growth factor: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and chromosome localization. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):541–545. doi: 10.1126/science.3523756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan M., DiSorbo D., Hou J. Z., Hoshi H., Mansson P. E., McKeehan W. L. High and low affinity binding of heparin-binding growth factor to a 130-kDa receptor correlates with stimulation and inhibition of growth of a differentiated human hepatoma cell. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11306–11313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaner R. J., Baird A., Mansukhani A., Basilico C., Summers B. D., Florkiewicz R. Z., Hajjar D. P. Fibroblast growth factor receptor is a portal of cellular entry for herpes simplex virus type 1. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1410–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.2162560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén L., Oldberg A., Hök M. Cell-surface heparan sulfate. Mechanisms of proteoglycan-cell association. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10407–10413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. L., Johnson D. E., Cousens L. S., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. Purification and complementary DNA cloning of a receptor for basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):57–60. doi: 10.1126/science.2544996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luyten F. P., Cunningham N. S., Ma S., Muthukumaran N., Hammonds R. G., Nevins W. B., Woods W. I., Reddi A. H. Purification and partial amino acid sequence of osteogenin, a protein initiating bone differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13377–13380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolskee R. F., Kavathas P., Berg P. Epstein-Barr virus shuttle vector for stable episomal replication of cDNA expression libraries in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2837–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marics I., Adelaide J., Raybaud F., Mattei M. G., Coulier F., Planche J., de Lapeyriere O., Birnbaum D. Characterization of the HST-related FGF.6 gene, a new member of the fibroblast growth factor gene family. Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):335–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marynen P., Zhang J., Cassiman J. J., Van den Berghe H., David G. Partial primary structure of the 48- and 90-kilodalton core proteins of cell surface-associated heparan sulfate proteoglycans of lung fibroblasts. Prediction of an integral membrane domain and evidence for multiple distinct core proteins at the cell surface of human lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7017–7024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Casey G., Brookes S., Dixon M., Peters G., Dickson C. Sequence, topography and protein coding potential of mouse int-2: a putative oncogene activated by mouse mammary tumour virus. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):919–924. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04304.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. High and low affinity binding sites for basic fibroblast growth factor on cultured cells: absence of a role for low affinity binding in the stimulation of plasminogen activator production by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neeper M. P., Kuo L. M., Kiefer M. C., Robb R. J. Structure function relationships for the IL 2 receptor system. III. Tac protein missing amino acids 102 to 173 (exon 4) is unable to bind IL 2: detection of spliced protein after L cell transfection. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3532–3538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D. The identification and partial characterization of the fibroblast growth factor receptor of baby hamster kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13860–13868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale E. B., Singer S. J. Identification of a developmentally regulated protein-tyrosine kinase by using anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies to screen a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D. Recent developments in the cell biology of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R., Gallagher J., Spooncer E., Allen T. D., Bloomfield F., Dexter T. M. Heparan sulphate bound growth factors: a mechanism for stromal cell mediated haemopoiesis. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):376–378. doi: 10.1038/332376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruta M., Burgess W., Givol D., Epstein J., Neiger N., Kaplow J., Crumley G., Dionne C., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Receptor for acidic fibroblast growth factor is related to the tyrosine kinase encoded by the fms-like gene (FLG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8722–8726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Jalkanen M., O'Farrell S., Bernfield M. Molecular cloning of syndecan, an integral membrane proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1547–1556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Yoshida T., Miyagawa K., Sakamoto H., Terada M., Sugimura T. cDNA sequence of human transforming gene hst and identification of the coding sequence required for transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A. Fibroblast growth factors. FASEB J. 1987 Dec;1(6):434–440. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.6.3315806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walicke P. A., Feige J. J., Baird A. Characterization of the neuronal receptor for basic fibroblast growth factor and comparison to receptors on mesenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4120–4126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J. M., Rosen V., Celeste A. J., Mitsock L. M., Whitters M. J., Kriz R. W., Hewick R. M., Wang E. A. Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1528–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.3201241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WuDunn D., Spear P. G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.52-58.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan X., Bates B., Hu X. G., Goldfarb M. The human FGF-5 oncogene encodes a novel protein related to fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3487–3495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]