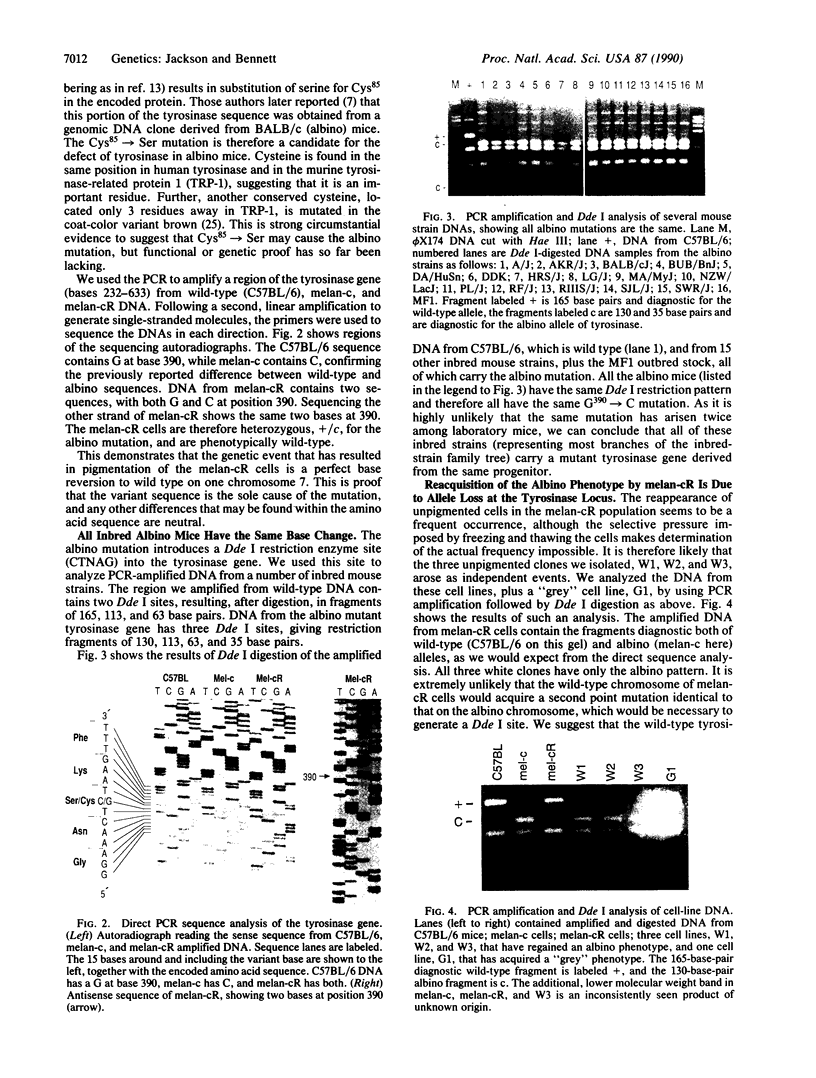
Abstract
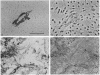
From within an albino melanocyte line grown in vitro we identified and cloned cells that apparently had reverted to wild type. We sequenced a part of the tyrosinase gene, encompassing a candidate mutation, from wild-type, albino, and revertant cell DNAs. The revertant cells contain, on one chromosome, a perfect base reversion to the wild-type sequence of this candidate mutation, proving that this is the sole defect in the tyrosinase gene of albino mutant mice. The revertant cells readily regain the albino phenotype after freezing and thawing. Taking advantage of a Dde I restriction site created by the albino mutation, we demonstrated that the regained phenotype is due to allele loss involving the wild-type chromosome. The Dde I site also allowed us to show that all inbred albino mice carry the same mutation and so must be derived from the same progenitor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett D. C., Cooper P. J., Dexter T. J., Devlin L. M., Heasman J., Nester B. Cloned mouse melanocyte lines carrying the germline mutations albino and brown: complementation in culture. Development. 1989 Feb;105(2):379–385. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. C., Cooper P. J., Hart I. R. A line of non-tumorigenic mouse melanocytes, syngeneic with the B16 melanoma and requiring a tumour promoter for growth. Int J Cancer. 1987 Mar 15;39(3):414–418. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. C. Differentiation in mouse melanoma cells: initial reversibility and an on-off stochastic model. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favor J., Neuhäuser-Klaus A., Ehling U. H. Radiation-induced forward and reverse specific locus mutations and dominant cataract mutations in treated strain BALB/c and DBA/2 male mice. Mutat Res. 1987 Mar;177(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(87)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Jiménez M. Analysis of mammalian pigmentation at the molecular level. Pigment Cell Res. 1989 Mar-Apr;2(2):75–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.1989.tb00166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Phillips P., Lutzner M. A. The fine structure of melanogenesis in coat color mutants of the mouse. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Apr;43(1):88–106. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber M., Hintermann G., Lerch K. Primary structure of tyrosinase from Streptomyces glaucescens. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6038–6044. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. J. A cDNA encoding tyrosinase-related protein maps to the brown locus in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4392–4396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreider J. W., Wade D. R., Rosenthal M., Densley T. Maturation and differentiation of B16 melanoma cells induced by theophylline treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jun;54(6):1457–1467. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.6.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Haq A. K., Pomerantz S. H., Halaban R. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone for human tyrosinase that maps at the mouse c-albino locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7473–7477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Haq A. K., Wakulchik M., Kestler D., Barton D. E., Francke U., Lamoreux M. L., Whitney J. B., 3rd, Halaban R. Isolation, chromosomal mapping, and expression of the mouse tyrosinase gene. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Nov;93(5):589–594. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12319693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Wakulchik M., Haq A. K., Halaban R., Kestler D. Sequence analysis of mouse tyrosinase cDNA and the effect of melanotropin on its gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1301–1309. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch K., Longoni C., Jordi E. Primary structure of tyrosinase from Neurospora crassa. I. Purification and amino acid sequence of the cyanogen bromide fragments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6408–6413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Ruppert S., Schmid E., Schütz G. Functional analysis of alternatively spliced tyrosinase gene transcripts. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2723–2730. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parakkal P. F. Transfer of premelanosomes into the keratinizing cells of albino hair follicle. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov;35(2):473–477. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. Cancer. Gene losses in human tumours. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):400–402. doi: 10.1038/335400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Green H. Formation of a keratinizing epithelium in culture by a cloned cell line derived from a teratoma. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):317–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert S., Müller G., Kwon B., Schütz G. Multiple transcripts of the mouse tyrosinase gene are generated by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2715–2722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlager G., Dickie M. M. Natural mutation rates in the house mouse. Estimates for five specific loci and dominant mutations. Mutat Res. 1971 Jan;11(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(71)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlager G., Dickie M. M. Spontaneous mutations and mutation rates in the house mouse. Genetics. 1967 Oct;57(2):319–330. doi: 10.1093/genetics/57.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Halaban R., Moellmann G., Cowan J. M., Lerner M. R., Lerner A. B. Normal murine melanocytes in culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 Jul;23(7):519–522. doi: 10.1007/BF02628423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terao M., Tabe L., Garattini E., Sartori D., Studer M., Mintz B. Isolation and characterization of variant cDNAs encoding mouse tyrosinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):848–853. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Takeuchi S., Kudo T., Sato C., Takeuchi T. Melanin production in cultured albino melanocytes transfected with mouse tyrosinase cDNA. Jpn J Genet. 1989 Apr;64(2):121–135. doi: 10.1266/jjg.64.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yandell D. W., Dryja T. P., Little J. B. Somatic mutations at a heterozygous autosomal locus in human cells occur more frequently by allele loss than by intragenic structural alterations. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 May;12(3):255–263. doi: 10.1007/BF01570784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]