Abstract
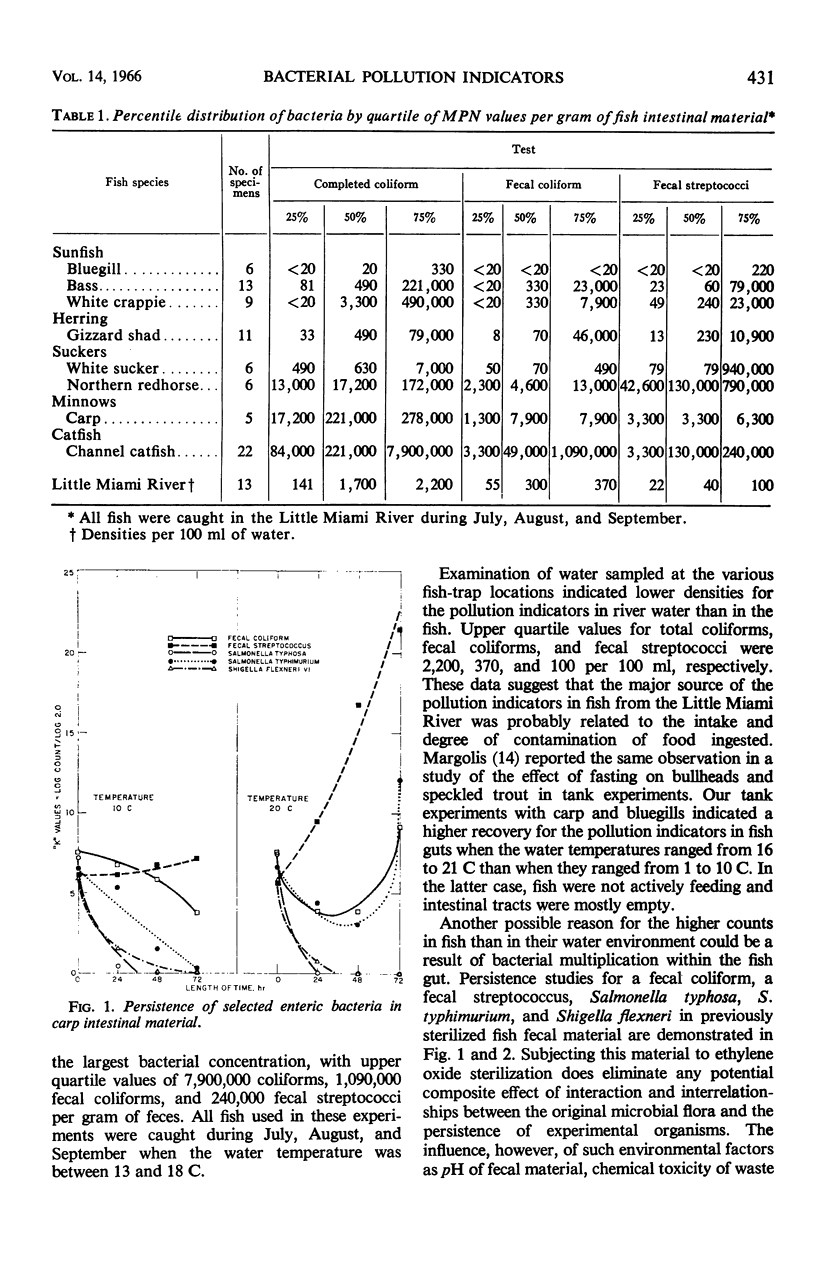
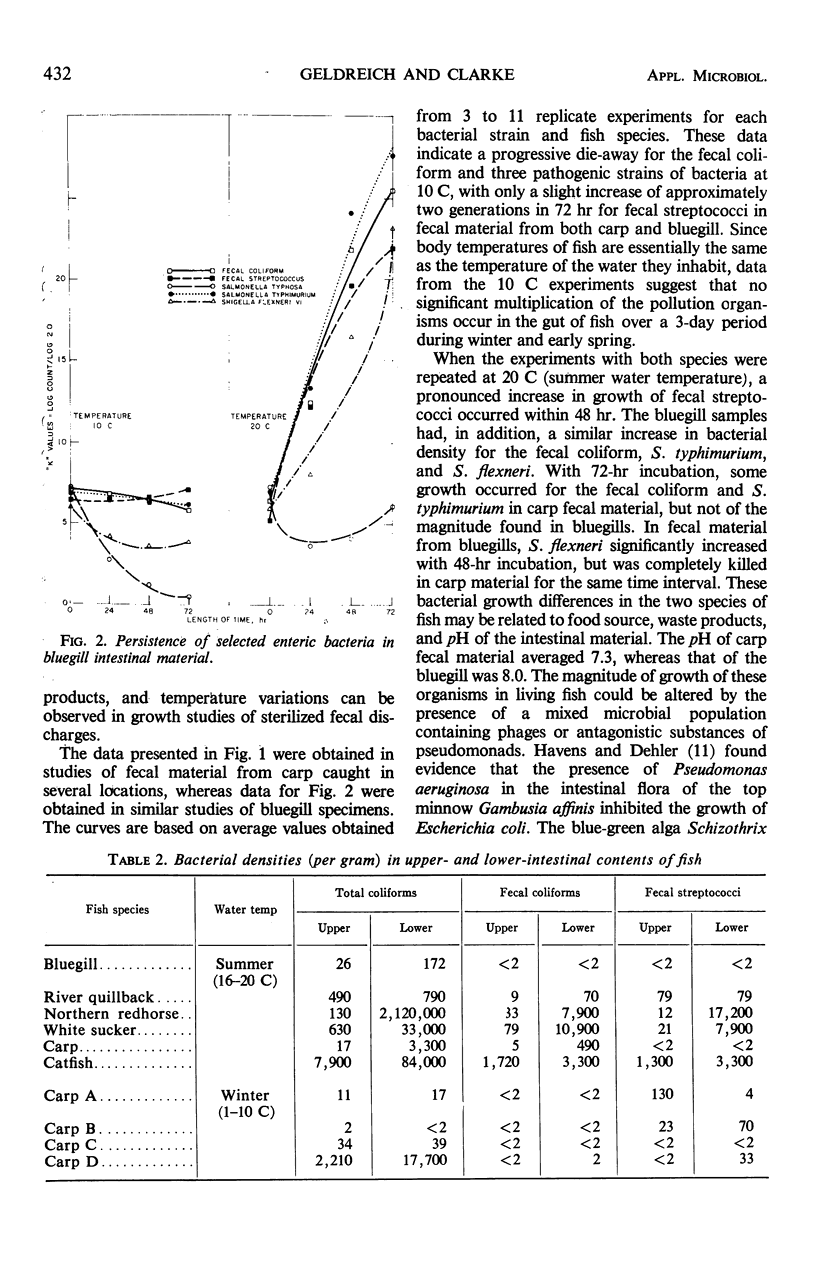
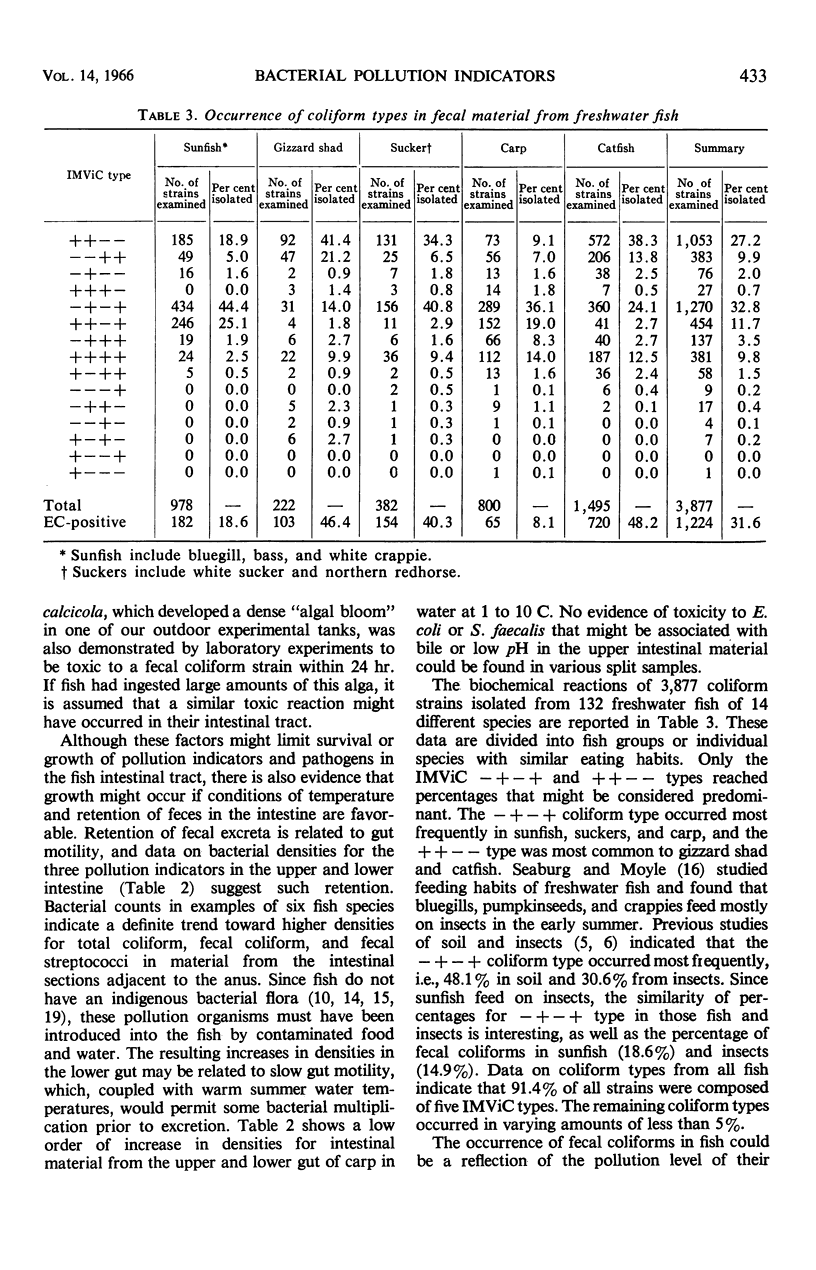
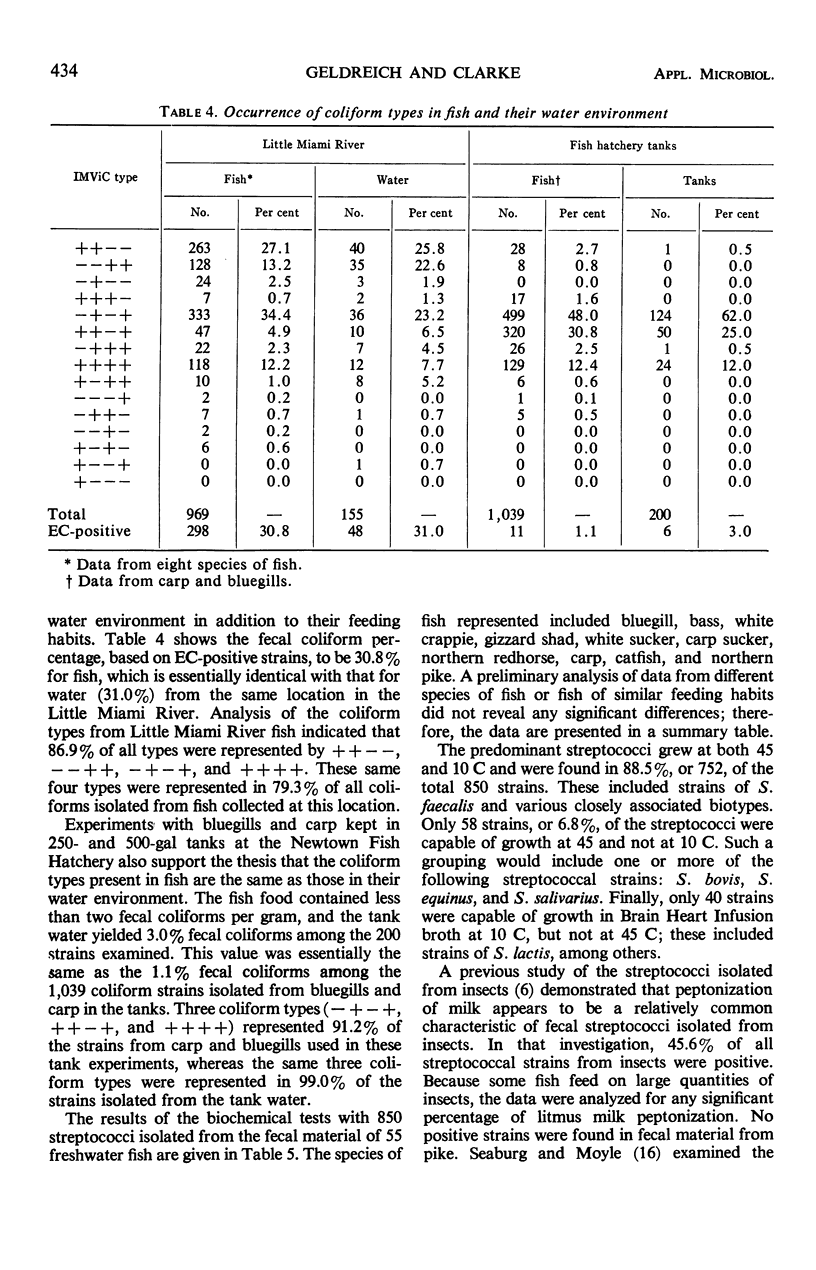
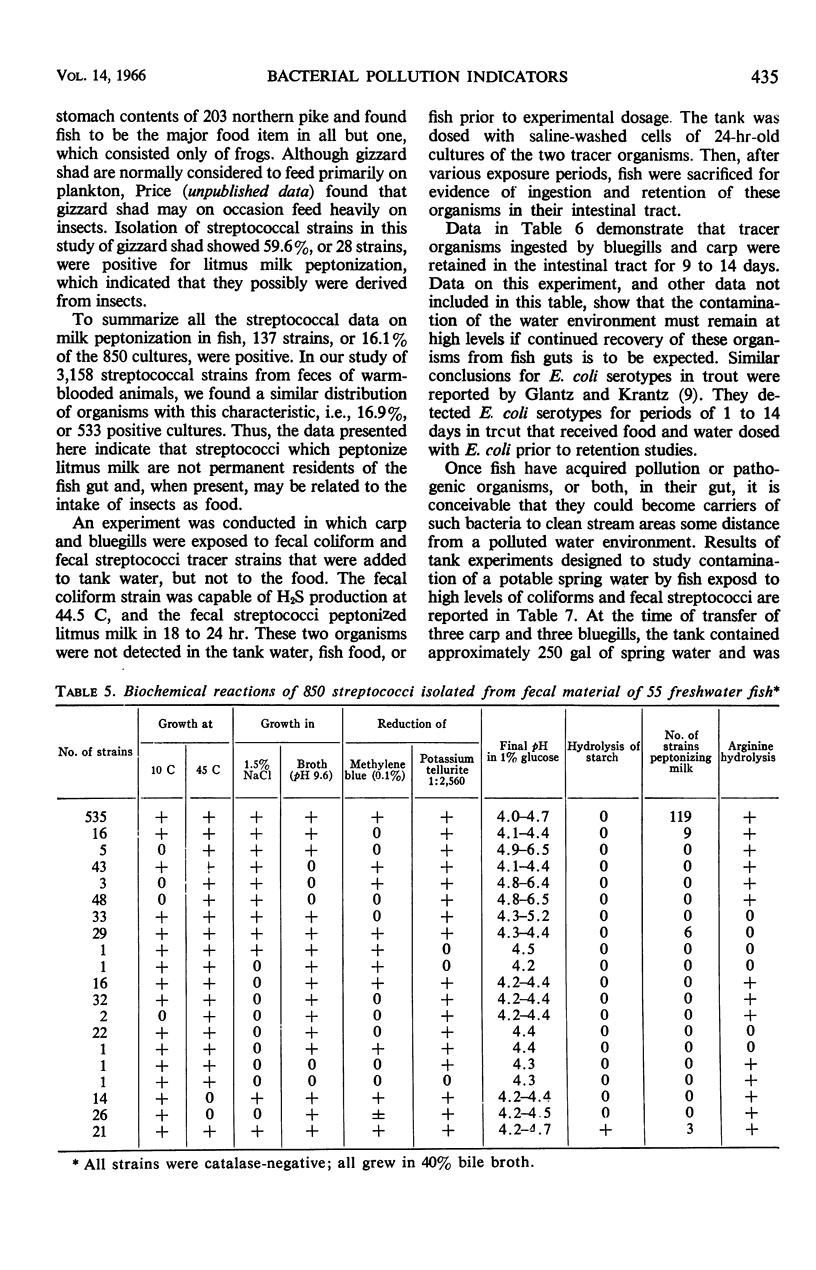
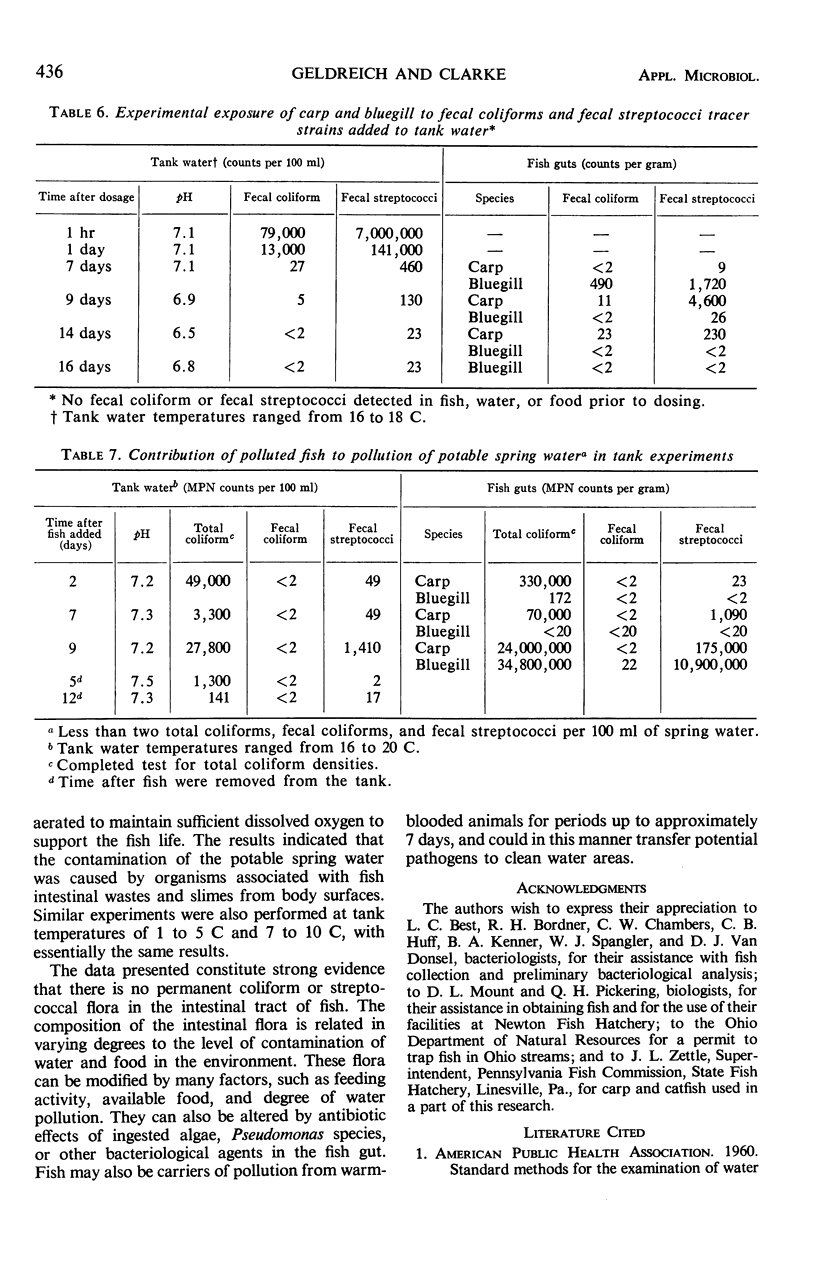
A study was made of the occurrence, distribution, and persistence of coliforms, fecal coliforms, and fecal streptococci in the intestinal tract of freshwater fish. A total of 132 fish representing 14 different species were used in various phases of these experiments. Examination of the intestinal contents of 78 fish from moderately polluted sections of the Little Miami River indicated that fecal coliform densities were lowest in bluegills (less than 20 per gram) and highest in catfish (1,090,000 per gram). Levels of fecal streptococci for these two species were 220 and 240,000 per gram, respectively. The occurrence of fecal coliforms in fish caught in this stream reflected the warm-blooded-animal-pollution level of the water. All fish used in this phase of the study were caught during July, August, and September when the water temperatures were between 13 and 18 C. The fate of fecal coliforms and Streptococcus faecalis in the fish intestine indicated that these organisms can probably survive and multiply when fish and water temperatures are 20 C or higher, but only when the organisms are retained in the gut for periods beyond 24 hr. Based on the biochemical reactions for 3,877 coliform strains isolated from 132 freshwater fish of 14 different species, 91.4% of all strains were composed of five IMViC types. In a similar study of the biochemical reactions of 850 streptococci isolated from the intestinal tract of 55 freshwater fish, the predominant strains included S. faecalis and various closely associated biotypes. No consistently recurring pattern for either coliforms or streptococci could be developed to identify species of fish investigated. The composition of the intestinal flora is, however, related in varying degree to the level of contamination of water and food in the environment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EVELYN T. P., McDERMOTT L. A. Bacteriological studies of fresh-water fish. I. Isolation of aerobic bacteria from several species of Ontario fish. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Jun;7:375–382. doi: 10.1139/m61-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELDREICH E. E., KENNER B. A., KABLER P. W. OCCURRENCE OF COLIFORMS, FECAL COLIFORMS, AND STREPTOCOCCI ON VEGETATION AND INSECTS. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jan;12:63–69. doi: 10.1128/am.12.1.63-69.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLANTZ P. J., KRANTZ G. E. ESCHERICHIA COLI SEROTYPES ISOLATED FROM FISH AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jan;2:54–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNER B. A., CLARK H. F., KABLER P. W. Fecal Streptococci. I. Cultivation and enumeration of Streptococci in surface waters. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Jan;9:15–20. doi: 10.1128/am.9.1.15-20.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER L. F., BAKER G. E. The role of fish as conveyors of microorganisms in aquatic environments. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Aug;7:595–605. doi: 10.1139/m61-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENKATARAMAN R., SREENIVASAN A. The bacteriology of fresh-water fish. Indian J Med Res. 1953 Oct;41(4):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]