Abstract
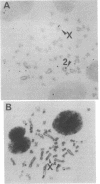
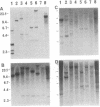
Eight genes, located on the long arm of the human X chromosome and present on the marsupial X chromosome, were mapped by in situ hybridization to the chromosomes of the platypus Ornithorhynchus anatinus, one of the three species of monotreme mammals. All were located on the X chromosome. We conclude that the long arm of the human X chromosome represents a highly conserved region that formed part of the X chromosome in a mammalian ancestor at least 150 million years ago. Since three of these genes are located on the long arm of the platypus X chromosome, which is G-band homologous to the Y chromosome and apparently exempt from X chromosome inactivation, the conservation of this region has evidently not depended on isolation by X-Y chromosome differentiation and X chromosome inactivation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Air G. M., Thompson E. O., Richardson B. J., Sharman G. B. Amino-acid sequences of kangaroo myoglobin and haemoglobin and the date of marsupial-eutherian divergence. Nature. 1971 Feb 5;229(5284):391–394. doi: 10.1038/229391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcalay M., Toniolo D. CpG islands of the X chromosome are gene associated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9527–9543. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Gould K. G., Rees D. J., Brownlee G. G. Molecular cloning of the gene for human anti-haemophilic factor IX. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):178–180. doi: 10.1038/299178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Davison M. T., Graves J. A., O'Brien S. J., Womack J. E., Roderick T. H., Creau-Goldberg N., Hillyard A. L., Doolittle D. P., Rogers J. A. Report of the committee on comparative mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):503–532. doi: 10.1159/000132806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naismith A. L., Hoffman-Chudzik E., Tsui L. C., Riordan J. R. Study of the expression of myelin proteolipid protein (lipophilin) using a cloned complementary DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7413–7425. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Piantanida T. P., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of inherited variation in human color vision. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):203–210. doi: 10.1126/science.3485310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S. J., Seuánez H. N., Womack J. E. Mammalian genome organization: an evolutionary view. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:323–351. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Viglietto G., Martini G., Toniolo D., Paonessa G., Moscatelli C., Dono R., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., D'Urso M. Isolation of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) cDNA clones: primary structure of the protein and unusual 5' non-coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2511–2522. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rofe R., Hayman D. G-banding evidence for a conserved complement in the Marsupialia. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(1):40–50. doi: 10.1159/000132101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Wrigley J. M., Marshall Graves J. A. Autosomal assignment of OTC in marsupials and monotremes: implications for the evolution of sex chromosomes. Genet Res. 1987 Oct;50(2):131–136. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300023533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., Persico M., Alcalay M. A "housekeeping" gene on the X chromosome encodes a protein similar to ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):851–855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Martin B. M., Kaslow D. C., Migeon B. R., Choudary P. V., Stubbleflied B. K., Mayor J. A., Murray G. J., Barranger J. A., Ginns E. I. Signal sequence and DNA-mediated expression of human lysosomal alpha-galactosidase A. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 1;165(2):275–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VandeBerg J. L., Cooper D. W. Possible autosomal inheritance of erythrocyte phosphoglycerate kinase A in echidnas. Biochem Genet. 1978 Oct;16(9-10):1031–1034. doi: 10.1007/BF00483753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VandeBerg J. L., Robinson E. S., Samollow P. B., Johnston P. G. X-linked gene expression and X-chromosome inactivation: marsupials, mouse, and man compared. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1987;15:225–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. M., Graves J. A. Gene mapping in marsupials and monotremes, V. Synteny between hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase and phosphoglycerate kinase in the platypus. Aust J Biol Sci. 1988;41(2):231–237. doi: 10.1071/bi9880231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley J. M., Graves J. A. Karyotypic conservation in the mammalian order monotremata (subclass Prototheria). Chromosoma. 1988;96(3):231–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00302363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley J. M., Graves J. A. Sex chromosome homology and incomplete, tissue-specific X-inactivation suggest that monotremes represent an intermediate stage of mammalian sex chromosome evolution. J Hered. 1988 Mar-Apr;79(2):115–118. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a110464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley J. M., Graves J. A. Two monotreme cell lines, derived from female platypuses (Ornithorhynchus anatinus; Monotremata, Mammalia). In Vitro. 1984 Apr;20(4):321–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02618595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]