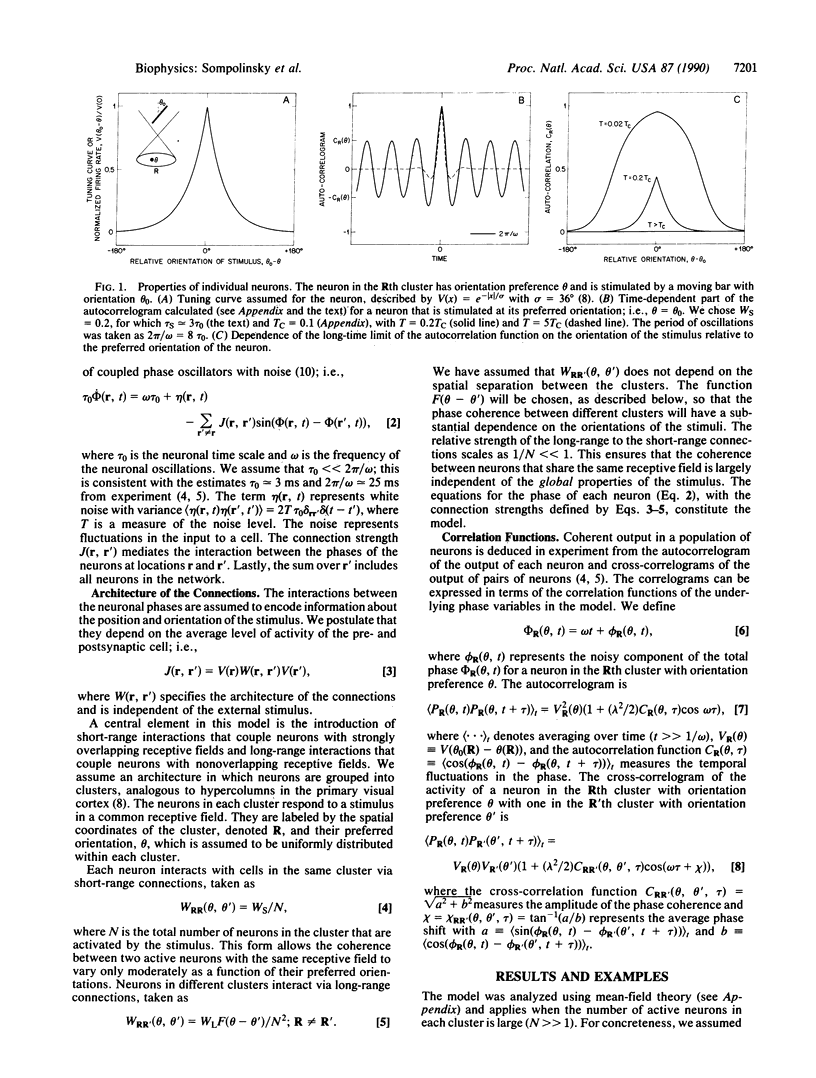
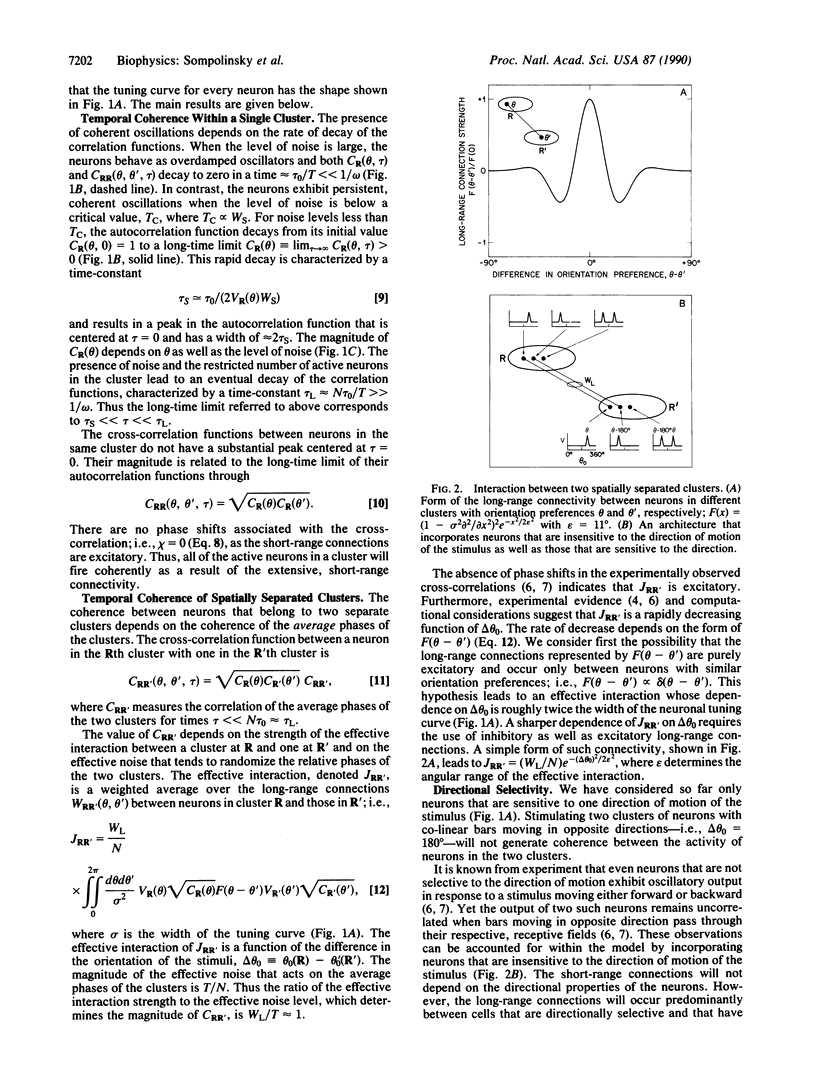
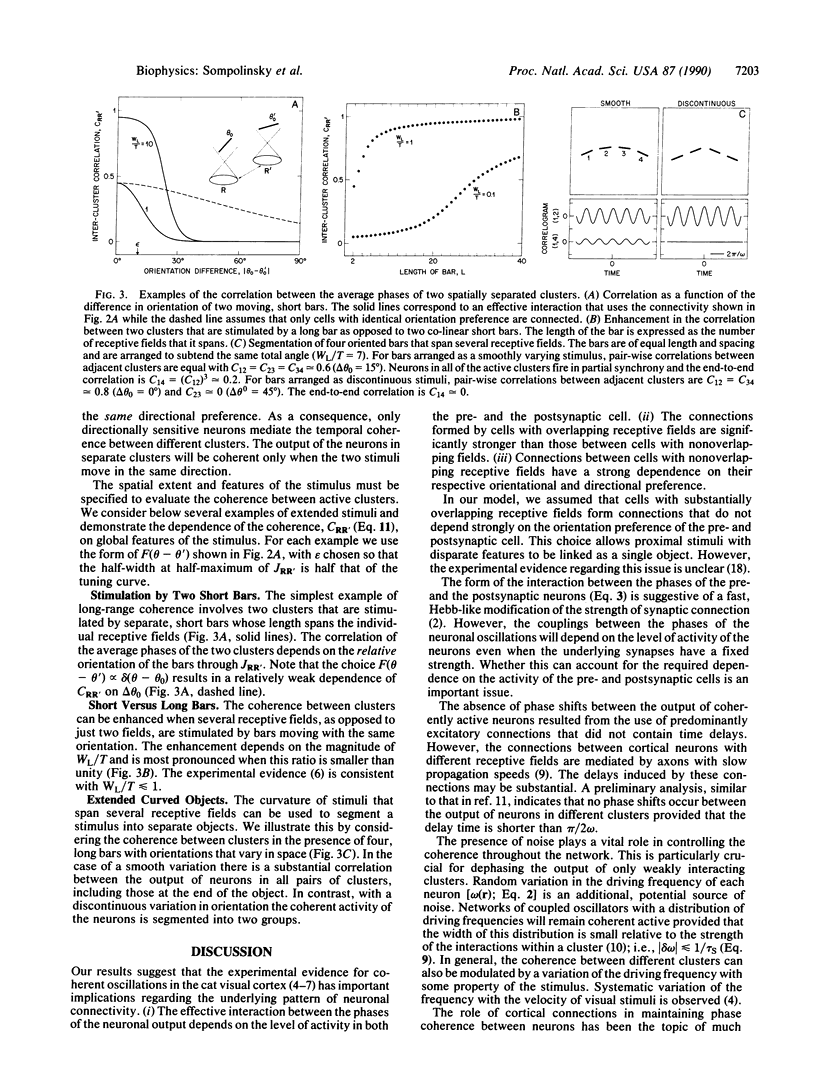
Abstract
An oscillator neural network model is presented that is capable of processing local and global attributes of sensory input. Local features in the input are encoded in the average firing rate of the neurons while the relationships between these features can modulate the temporal structure of the neuronal output. Neurons that share the same receptive field interact via relatively strong feedback connections, while neurons with different fields interact via specific, relatively weak connections. This pattern of connectivity mimics that of primary visual cortex. The model is studied in the context of processing visual stimuli that are coded for orientation. We compare our theoretical results with recent experimental evidence on coherent oscillatory activity in the cat visual cortex. The computational capabilities of the model for performing discrimination and segmentation tasks are demonstrated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eckhorn R., Bauer R., Jordan W., Brosch M., Kruse W., Munk M., Reitboeck H. J. Coherent oscillations: a mechanism of feature linking in the visual cortex? Multiple electrode and correlation analyses in the cat. Biol Cybern. 1988;60(2):121–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00202899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel Andreas K., König Peter, Gray Charles M., Singer Wolf. Stimulus-Dependent Neuronal Oscillations in Cat Visual Cortex: Inter-Columnar Interaction as Determined by Cross-Correlation Analysis. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(7):588–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. M., König P., Engel A. K., Singer W. Oscillatory responses in cat visual cortex exhibit inter-columnar synchronization which reflects global stimulus properties. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):334–337. doi: 10.1038/338334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. M., Singer W. Stimulus-specific neuronal oscillations in orientation columns of cat visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1698–1702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporns O., Gally J. A., Reeke G. N., Jr, Edelman G. M. Reentrant signaling among simulated neuronal groups leads to coherency in their oscillatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7265–7269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Malsburg C., Schneider W. A neural cocktail-party processor. Biol Cybern. 1986;54(1):29–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00337113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


