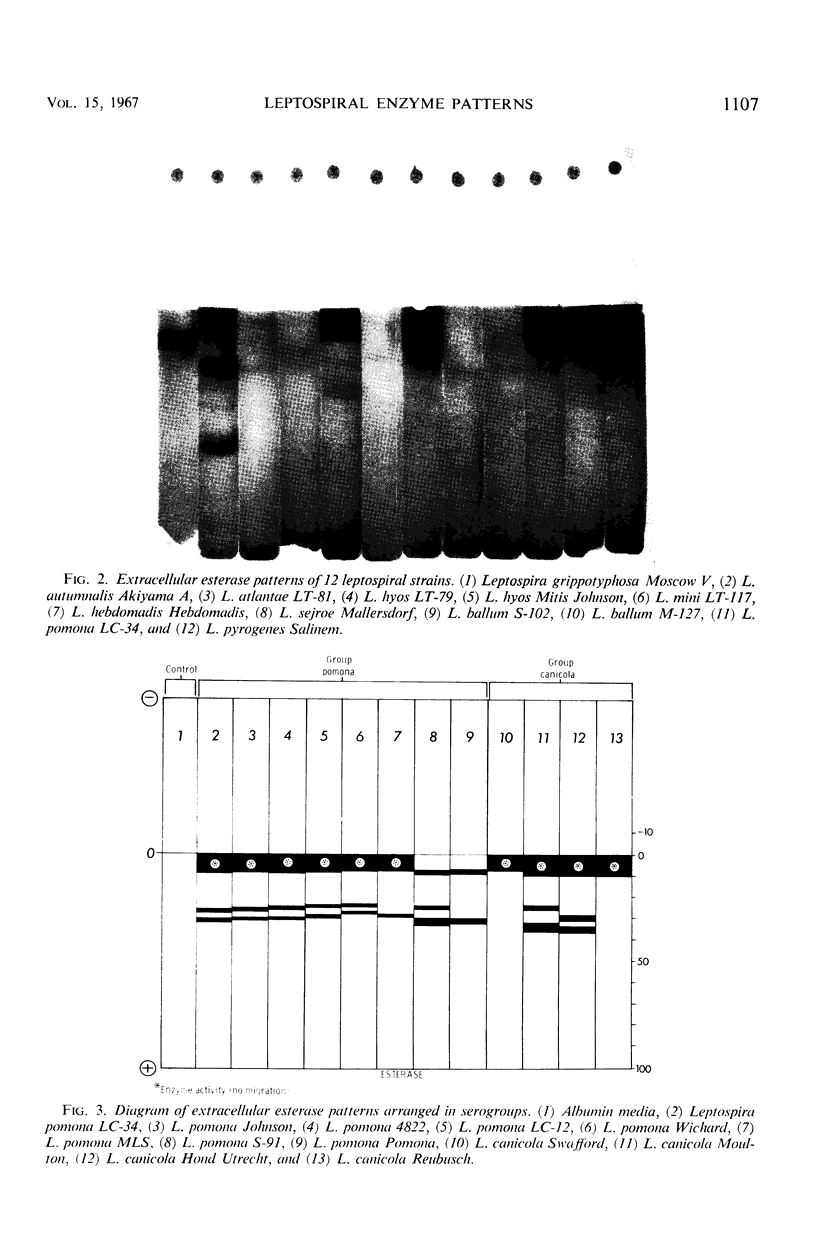
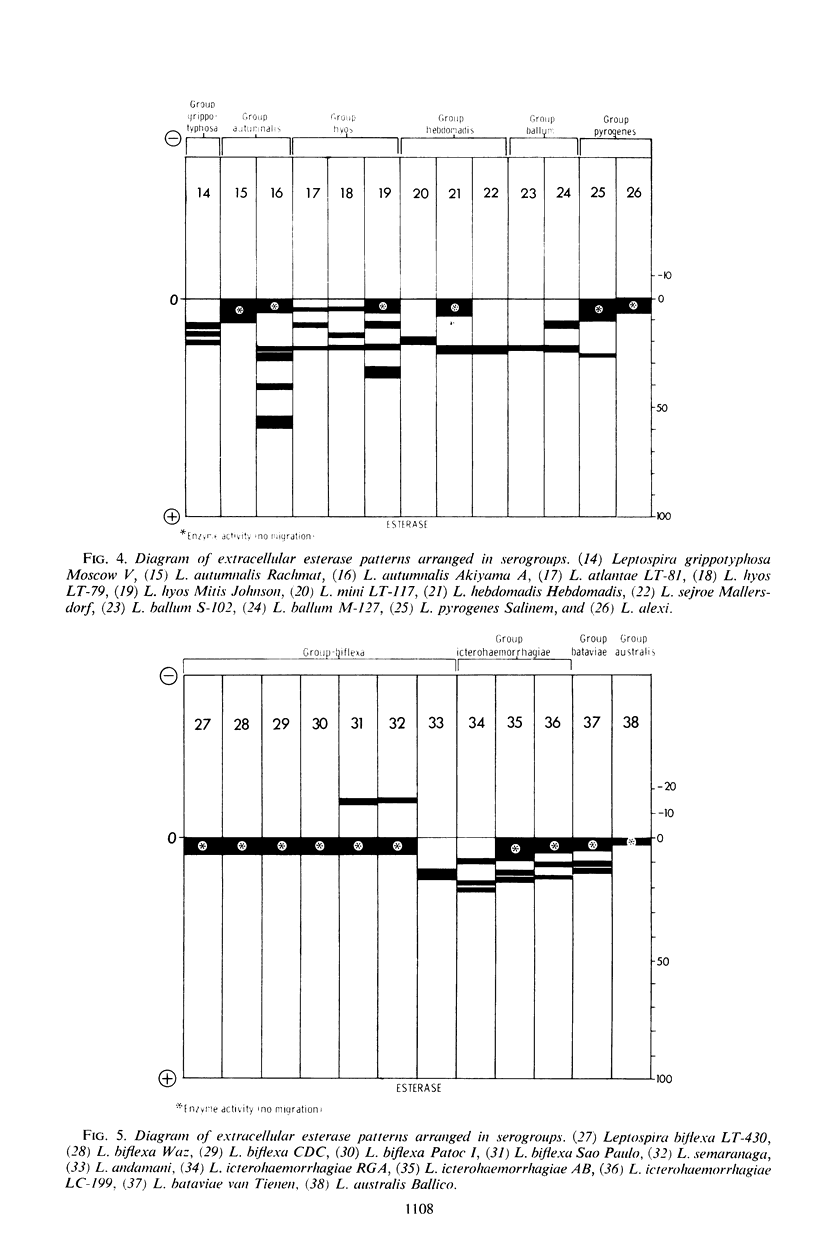
Abstract
An analysis of intracellular and extracellular leptospiral enzymes was made by use of starch-gel electrophoresis with natural and synthetic substrates. Of 37 serotypes examined for extracellular exterase, all had activity of varying mobility and degree. All extracellular preparations were negative for catalase, phosphatase, and naphthylamidase. Intracellularly, five serotypes were examined, including Leptospira biflexa Patoc I, L. biflexa Waz, L. canicola Moulton, L. icterohaemorrhagiae RGA, and L. pomona S91. Among the enzymes detected by this electrophoretic technique were transaminase and catalase, confirming the results of previous investigators. Further, other enzymes heretofore unreported have been detected. These include esterases, phosphatases, lactic, malic, glutamic, succinic, α-glycerophosphate, and 6-phosphogluconic dehydrogenases, and a naphthylamidase. The presence of these enzymes suggests the existence of tricarboxylic acid, glycolytic, and pentose-related pathways in Leptospira. In addition, enzyme patterns show promise in leptospiral classification.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CZEKALOWSKI J. W., McLEOD J. W., RODICAN J. The growth and respiration of Leptospira in solid or semi-solid media with special reference to Dinger's phenomenon. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Dec;34(6):588–595. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DECKER L. E., RAU E. M. Multiple forms of glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase in tissues. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jan;112:144–149. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-27975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWEY M. M., CONKLIN J. L. Starch gel electrophoresis of lactic dehydrogenase from rat kidney. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Dec;105:492–494. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DYMOWSKA Z., ZAKRZEWSKA A. PR'OBY USTALENIA PEWNYCH WLA'SIWO'SCI ENZYMATYCZNYCH SZCZEP'OW LEPTOSPIROWYCH. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 1964;16:79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLINGHAUSEN H. C., Jr, MCCULLOUGH W. G. NUTRITION OF LEPTOSPIRA POMONA AND GROWTH OF 13 OTHER SEROTYPES: A SERUM-FREE MEDIUM EMPLOYING OLEIC ALBUMIN COMPLEX. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Jan;26:39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinghausen H. C., Jr, Sandvik O. Tributyrinase activity of leptospires: fixed and soluble tributyrinase demonstrated by means of an agar diffusion test. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;65(2):259–270. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.65.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAINE S. Catalase activity in pathogenic Leptospira. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:1–9. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON J. D., SPOONER D. F. The metabolism of leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1956 Mar;5(2):154–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(56)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUZI M., CSOKA R. An egg-yolk reaction test for the differentiation of Leptospirae. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:208–212. doi: 10.1002/path.1700820129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUZI M., CSOKA R. Rapid method for the differentiation of parasitic and saprophytic leptospirae. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:1008–1008. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.1008-1008.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG H. S., ARMSTRONG J. C. Oxidase reaction with leptospiral colonies and its adaptation to antibiotic sensitivity testing. J Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(4):512–513. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.4.512-513.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb D., Hepden P. M. The electrophoretic movement of proteins from various Streptomyces species as a taxonomic criterion. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jul;44(1):95–104. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. S., Goldberg H. S. Electrophoretic determination of leptospiral enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1739–1740. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1739-1740.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. C., ROGERS P. DIFFERENTIATION OF PATHOGENIC AND SAPROPHYTIC LEPTOSPIRES WITH 8-AZAGUANINE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1618–1623. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1618-1623.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B. M. A comparison by the use of gel electrophoresis of soluble protein components and esterase enzymes of some group D Streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):413–419. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKERT C. L., HUNTER R. L. The distribution of esterases in mouse tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1959 Jan;7(1):42–49. doi: 10.1177/7.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOVETZ A. J., LARSON A. D. Transamination in Leptospira biflexa. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:638–640. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muftic M., Schröder E. Peptidasegram in the differentiation of bacilli species. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1966;29(2):252–256. doi: 10.1159/000161907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATEL V., GOLDBERG H. S., BLENDEN D. CHARACTERIZATION OF LEPTOSPIRAL LIPASE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:877–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.877-884.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAO P. J., LARSON A. D., COX C. D. CATALASE ACTIVITY IN LEPTOSPIRA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1045–1048. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1045-1048.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. E., Rutenburg A. M. Starch-gel electrophoresis of human tissue enzymes which hydrolyze L-leucyl-beta-naphthylamide. Science. 1966 May 27;152(3726):1256–1257. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3726.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URABE K., TAKEI N., SAITO H. FORMAMIDASE ACTIVITY OF MYCOBACTERIA. I. SIGNIFICANCE AS A MARKER FOR DIFFERENTIATING MYCOBACTERIA. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Jan;91:120–124. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.91.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. J. X-linked electrophoretic variation in 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster. J Hered. 1966 Mar-Apr;57(2):58–60. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a107466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




