Abstract
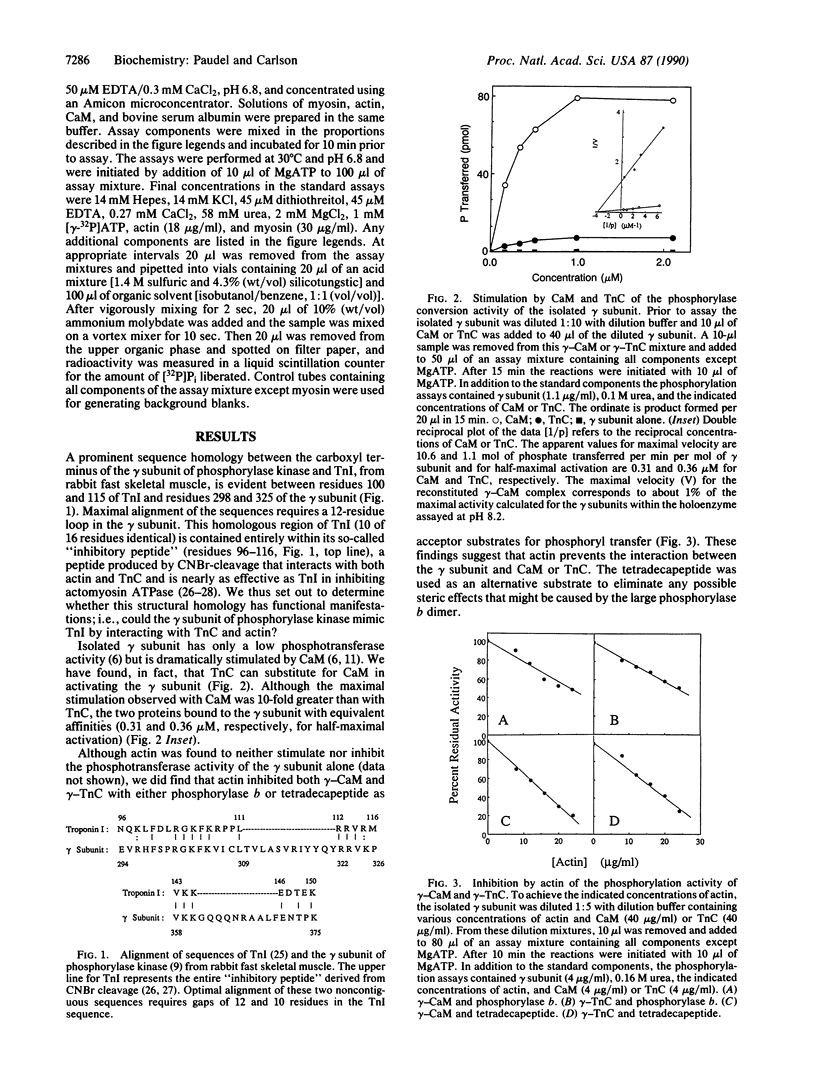
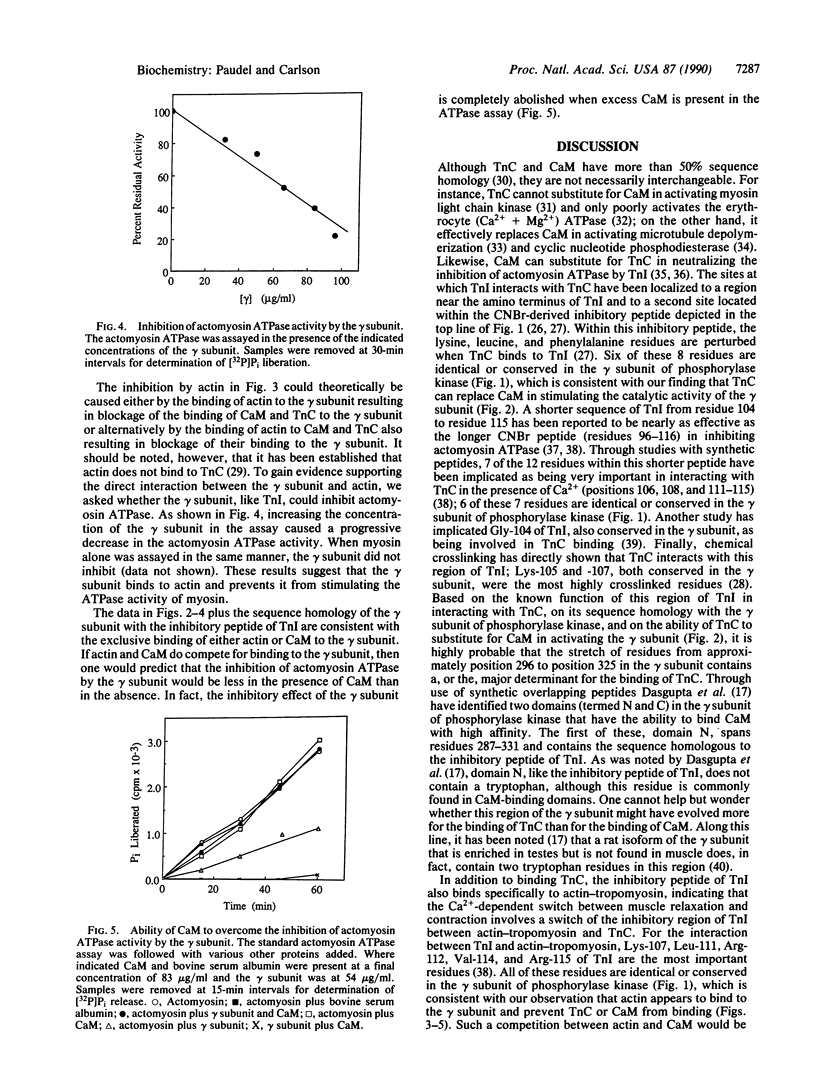
A sequence homology has been noted between the carboxyl quarter of the catalytic gamma subunit of phosphorylase kinase and the region of troponin I coded by exon VII. Because this portion of troponin I contains the inhibitory region that interacts with actin and troponin C, we have examined whether the gamma subunit of phosphorylase kinase can functionally mimic troponin I by also interacting with actin and troponin C. We have found that troponin C not only activates the isolated gamma subunit of phosphorylase kinase but also binds with approximately the same affinity as calmodulin. Although actin had no effect on the activity of the gamma subunit alone, it did inhibit the activity of gamma-calmodulin and gamma-troponin C complexes. Conversely, the gamma subunit was able to inhibit actomyosin ATPase in a process that could be overcome by calmodulin. These results suggest that actin and calmodulin (or troponin C) compete for binding to the gamma subunit. Moreover, the structural and functional similarities between the gamma subunit and troponin I suggest that the gamma subunit of phosphorylase kinase may have evolved from the fusion of a protein kinase protogene with a progenitor of exon VII of troponin I.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amphlett G. W., Vanaman T. C., Perry S. V. Effect of the troponin C-like protein from bovine brain (brain modulator protein) on the Mg2+-stimulated ATPase of skeletal muscle actinomyosin. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80836-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Kittler E. L., Emerson C. P., Jr Structure, evolution, and regulation of a fast skeletal muscle troponin I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8080–8084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Hunkeler F. L., Krebs E. G. The regulation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschmeier B., Meyer H. E., Mayr G. W. Characterization of the calmodulin-binding sites of muscle phosphofructokinase and comparison with known calmodulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9454–9462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachia P. J., Sykes B. D., Hodges R. S. Calcium-dependent inhibitory region of troponin: a proton nuclear magnetic resonance study on the interaction between troponin C and the synthetic peptide N alpha-acetyl[FPhe106]TnI-(104-115) amide. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 16;22(17):4145–4152. doi: 10.1021/bi00286a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachia P. J., Van Eyk J., Ingraham R. H., McCubbin W. D., Kay C. M., Hodges R. S. Calmodulin and troponin C: a comparative study of the interaction of mastoparan and troponin I inhibitory peptide [104-115]. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3553–3562. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Burchell A., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. T., Vanaman T. C., Nairn C. Identification of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein as the fourth subunit of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80772-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Picton C., Klee C. B. Activation of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle by calmodulin and troponin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of calcium ions, calmodulin and troponin in the regulation of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):563–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta M., Honeycutt T., Blumenthal D. K. The gamma-subunit of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase contains two noncontiguous domains that act in concert to bind calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17156–17163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGrado W. F., Erickson-Viitanen S., Wolfe H. R., Jr, O'Neil K. T. Predicted calmodulin-binding sequence in the gamma subunit of phosphorylase b kinase. Proteins. 1987;2(1):20–33. doi: 10.1002/prot.340020104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedman J. R., Jackson R. L., Schreiber W. E., Means A. R. Sequence homology of the Ca2+-dependent regulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from rat testis with other Ca2+-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):343–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedman J. R., Potter J. D., Means A. R. Biological cross-reactivity of rat testis phosphodiesterase activator protein and rabbit skeletal muscle troponin-C. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2437–2440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson-Viitanen S., DeGrado W. F. Recognition and characterization of calmodulin-binding sequences in peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1987;139:455–478. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)39106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. The isolation and crystallization of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase b. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath R. M., Vincenzi F. F. Phosphodiesterase protein activator mimics red blood cell cytoplasmic activator of (Ca2+-Mg2+)ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1203–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Levine B. A., Perry S. V. Proton-magnetic-resonance studies on the interaction of rabbit skeletal-muscle troponin I with troponin C and actin. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):61–68. doi: 10.1042/bj2030061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K. Messenger ribonucleic acid encoding an apparent isoform of phosphorylase kinase catalytic subunit is abundant in the adult testis. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;3(1):110–116. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-1-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessová Z., Varsányi M., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Dual function of calmodulin (delta) in phosphorylase kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 2;146(1):107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastenschmidt L. L., Kastenschmidt J., Helmreich E. Subunit interactions and their relationship to the allosteric properties of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase b. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3590–3608. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kee S. M., Graves D. J. Isolation and properties of the active gamma subunit of phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4732–4737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. M., Carlson G. M. Synergistic activation by Ca2+ and Mg2+ as the primary cause for hysteresis in the phosphorylase kinase reactions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11058–11064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leszyk J., Grabarek Z., Gergely J., Collins J. H. Characterization of zero-length cross-links between rabbit skeletal muscle troponin C and troponin I: evidence for direct interaction between the inhibitory region of troponin I and the NH2-terminal, regulatory domain of troponin C. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):299–304. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livanova N. B., Silonova G. V., Solovyeva N. V., Andreeva I. E., Ostrovskaya M. V., Poglazov B. F. Regulation of muscle phosphorylase kinase by actin and calmodulin. Biochem Int. 1983 Jul;7(1):95–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas T. J., Burgess W. H., Prendergast F. G., Lau W., Watterson D. M. Calmodulin binding domains: characterization of a phosphorylation and calmodulin binding site from myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1458–1464. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. M., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Control of microtubule assembly-disassembly by calcium-dependent regulator protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3771–3775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikovits W., Jr, Kuncio G., Ordahl C. P. The chicken fast skeletal troponin I gene: exon organization and sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3377–3390. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paudel H. K., Carlson G. M. Inhibition of the catalytic subunit of phosphorylase kinase by its alpha/beta subunits. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11912–11915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paudel H. K., Carlson G. M. Renaturation of phosphorylase kinase activity from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Aug 1;264(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paudel H. K., Carlson G. M. The quaternary structure of phosphorylase kinase as influenced by low concentrations of urea. Evidence suggesting a structural role for calmodulin. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):393–399. doi: 10.1042/bj2680393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. Assays for myosin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Gergely J. Troponin, tropomyosin, and actin interactions in the Ca2+ regulation of muscle contraction. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 18;13(13):2697–2703. doi: 10.1021/bi00710a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Wade R. D., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Homology of the gamma subunit of phosphorylase b kinase with cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4185–4192. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr Assays of protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:3–6. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuster J. R., Chan K. F., Graves D. J. Isolation and properties of the catalytically active gamma subunit of phosphorylase b kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2203–2210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syska H., Wilkinson J. M., Grand R. J., Perry S. V. The relationship between biological activity and primary structure of troponin I from white skeletal muscle of the rabbit. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):375–387. doi: 10.1042/bj1530375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot J. A., Hodges R. S. Synthetic studies on the inhibitory region of rabbit skeletal troponin I. Relationship of amino acid sequence to biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2798–2802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Gong B. J., Leavis P. C. Calcium-induced movement of troponin-I relative to actin in skeletal muscle thin filaments. Science. 1990 Mar 16;247(4948):1339–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.2138356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Gowell E., Strasburg G. M., Gergely J., Leavis P. C. Ca2+ dependence of the distance between Cys-98 of troponin C and Cys-133 of troponin I in the ternary troponin complex. Resonance energy transfer measurements. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5902–5908. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessmer G., Graves D. J. The phosphorylase kinase reaction on a peptide derived from glycogen phosphorylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 4;50(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempe M. R., Carlson G. M., Hainfeld J. F., Furcinitti P. S., Wall J. S. Analyses of phosphorylase kinase by transmission and scanning transmission electron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2882–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eyk J. E., Hodges R. S. The biological importance of each amino acid residue of the troponin I inhibitory sequence 104-115 in the interaction with troponin C and tropomyosin-actin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1726–1732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Vallet B., Cavadore J. C., Demaille J. G. Homologous calcium-binding proteins in the activation of skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle myosin light chain kinases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):335–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Grand R. J. Comparison of amino acid sequence of troponin I from different striated muscles. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):31–35. doi: 10.1038/271031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


