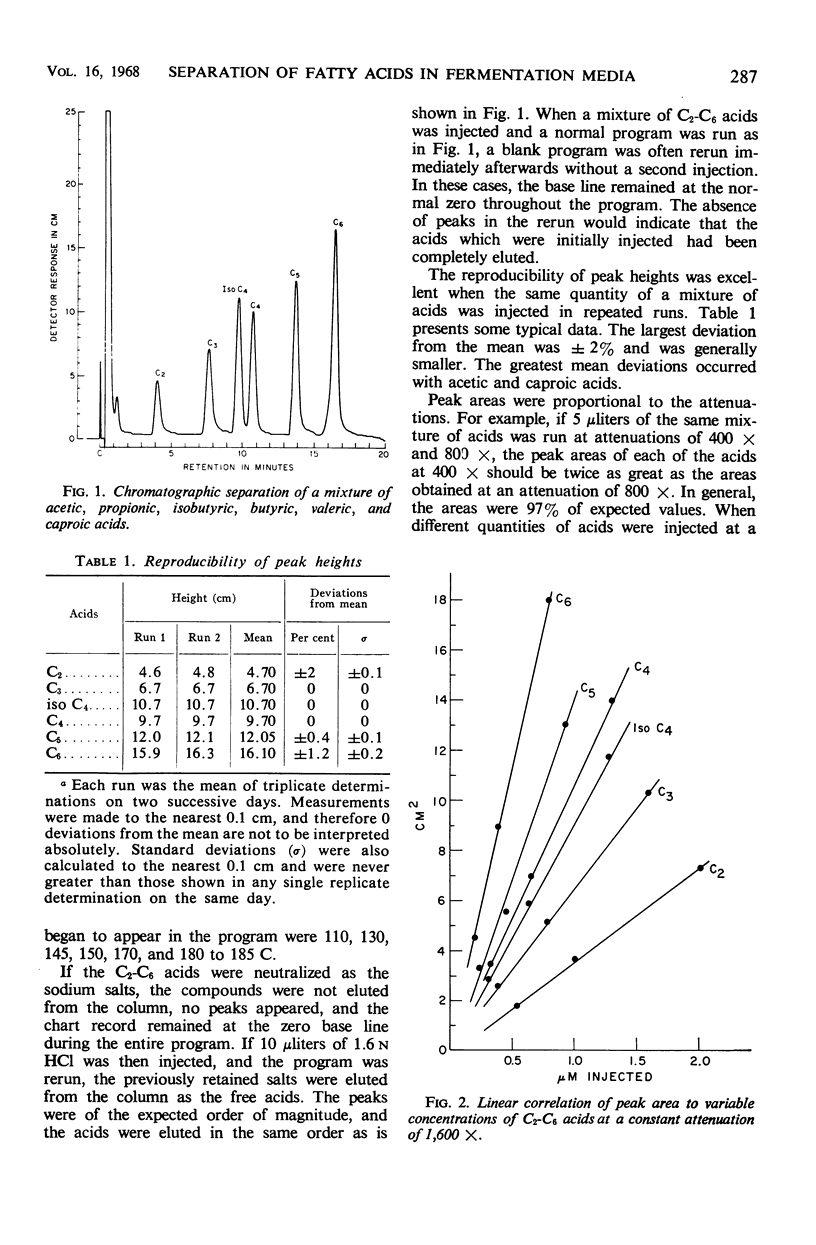
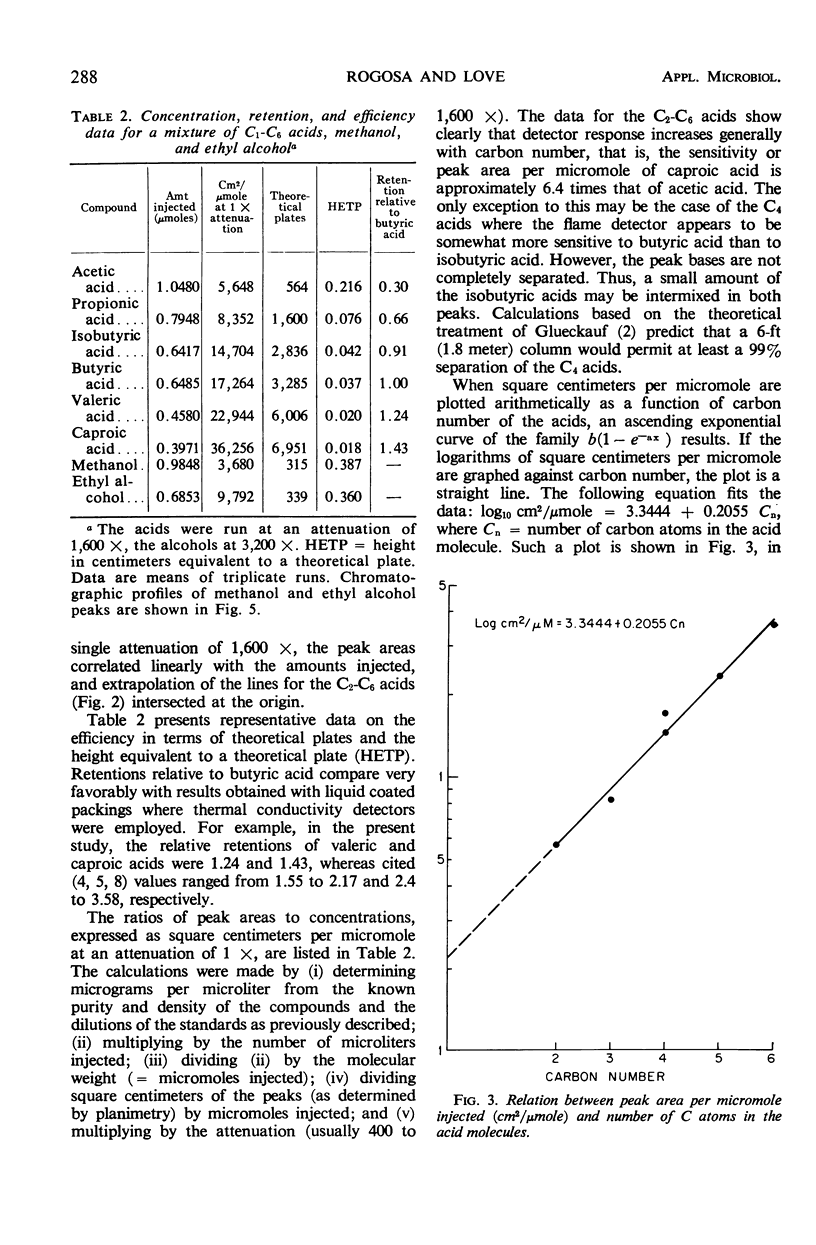
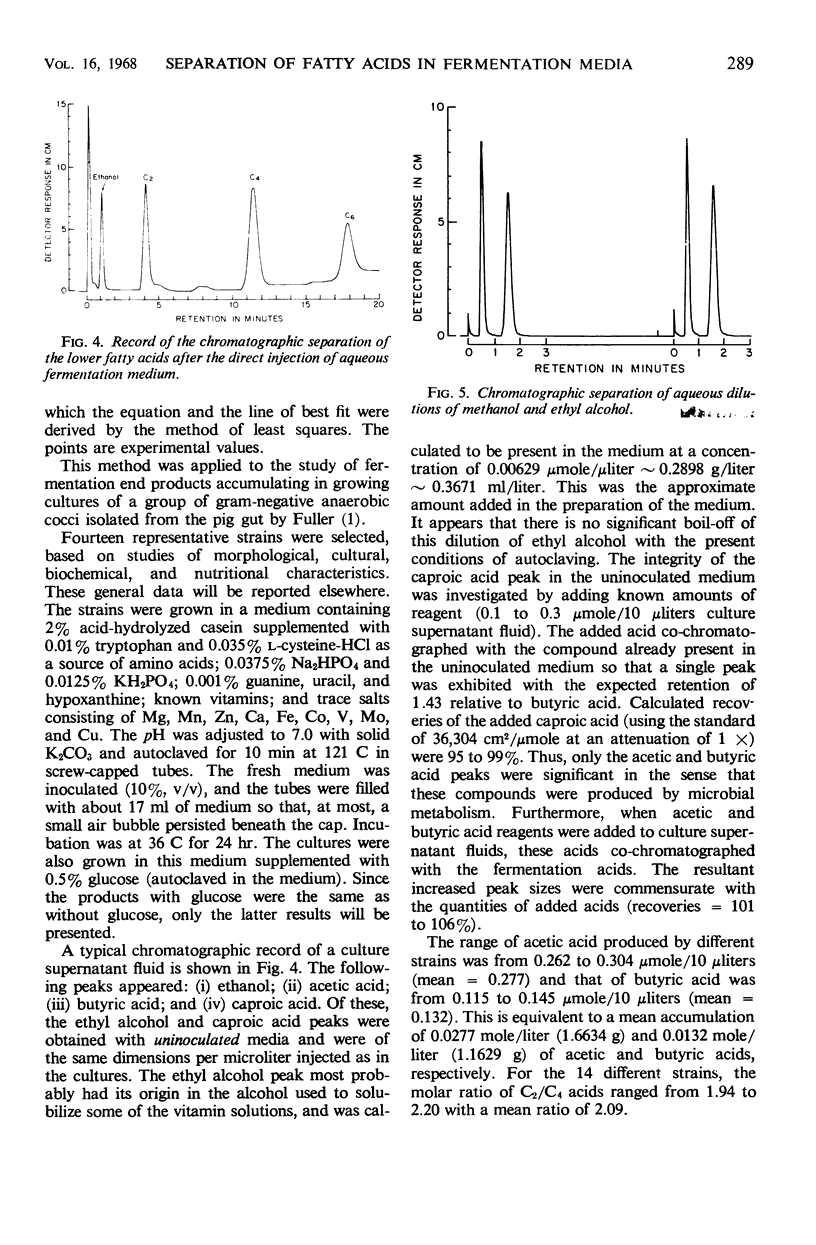
Abstract
A method is described for the direct quantitative gas chromatographic separation of C2-C6 lower fatty acid homologues, methanol, and ethyl alcohol in aqueous microbial fermentation media. A hydrogen flame detector and a single-phase solid column packing, comprising beads of a polyaromatic resin (polystyrene cross-linked with divinyl benzene), were employed. Direct injections of 1 to 10 μliters of aqueous culture supernatant fluids were made. Quantitative recoveries of C2-C6 acids added to culture supernatant fluids were obtained.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fuller R. Some morphological and physiological characteristics of gram negative anaerobic bacteria isolated from the alimentary tract of the pig. J Appl Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;29(2):375–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1966.tb03486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PACKETT L. V., MCCUNE R. W. DETERMINATION OF STEAM-VOLATILE ORGANIC ACIDS IN FERMENTATION MEDIA BY GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Jan;13:22–27. doi: 10.1128/am.13.1.22-27.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


