Abstract
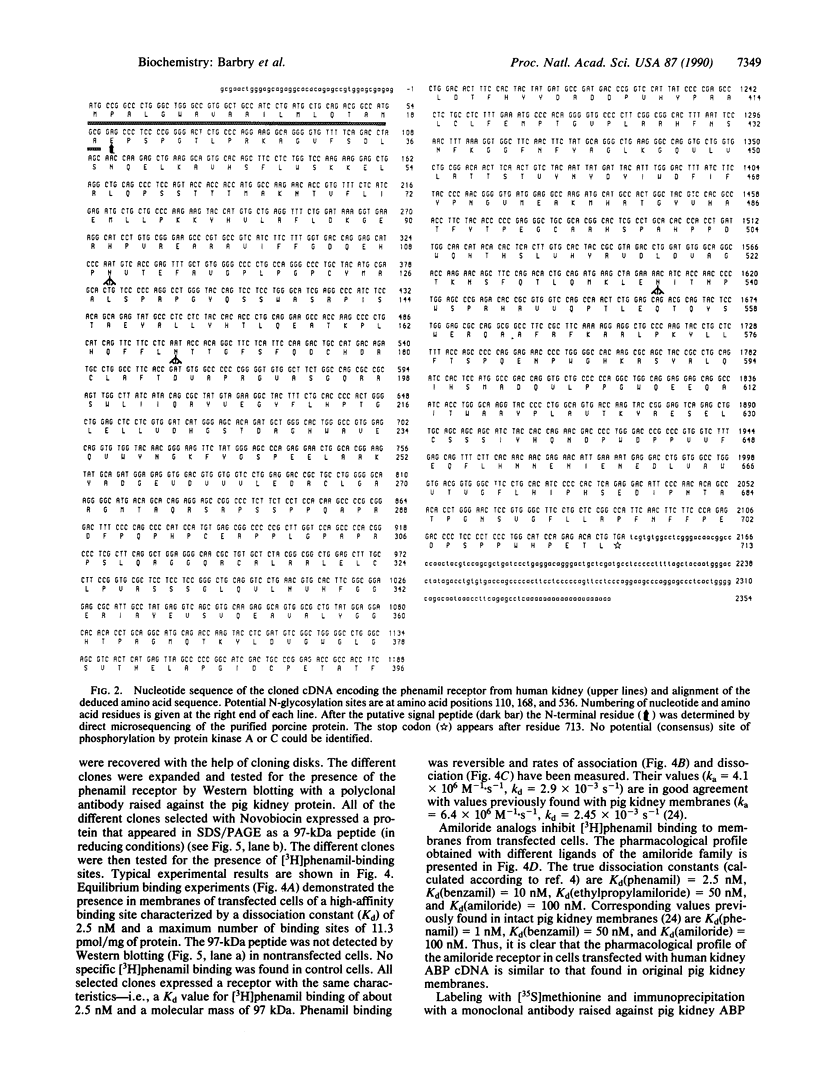
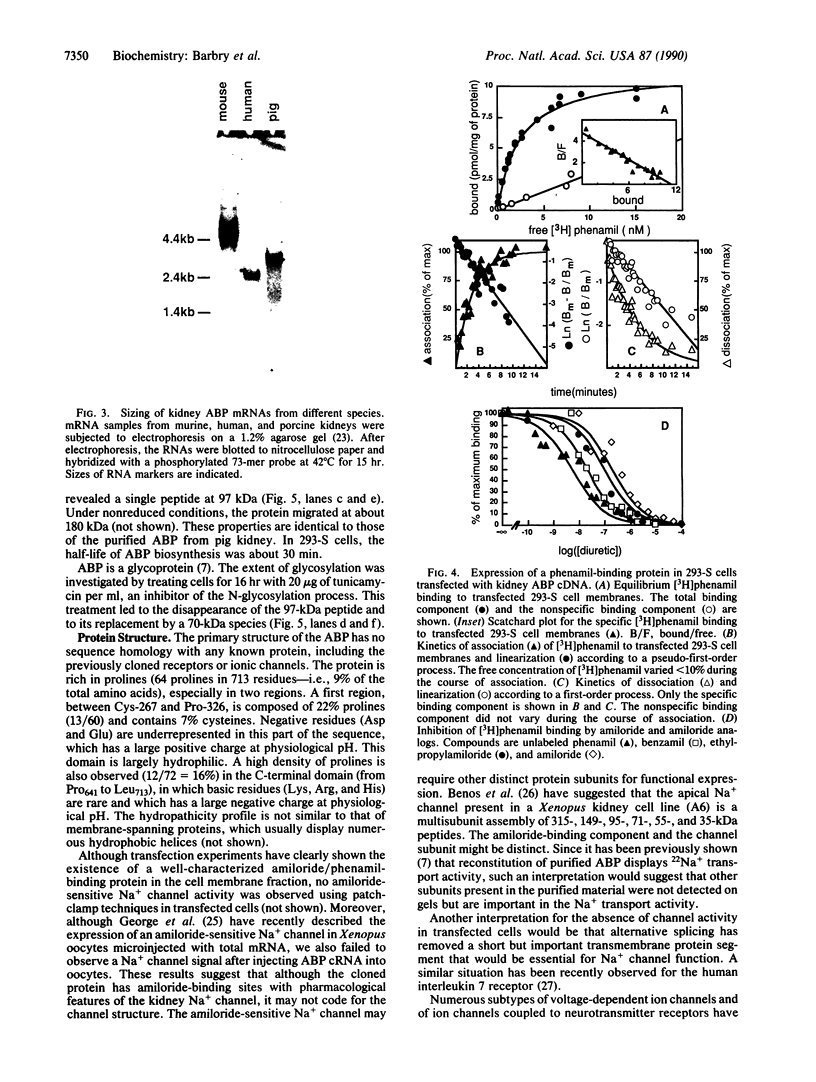
Phenamil, an analog of amiloride, is a potent blocker of the epithelial Na+ channel. It has been used to purify the porcine kidney amiloride-binding protein. Synthetic oligonucleotides derived from partial sequences have been used to screen a human kidney cDNA library and to isolate the cDNA encoding the human amiloride-binding protein. The primary structure was deduced from the DNA sequence analysis. The protein is 713 residues long, with a 19-amino acid signal peptide. The mRNA was expressed in 293-S and NIH 3T3 cells, yielding a glycoprotein (i) that binds amiloride and amiloride analogs with affinities similar to the amiloride receptor associated with the apical Na+ channel in pig kidney membranes and (ii) that is immunoprecipitated with monoclonal antibodies raised against pig kidney amiloride-binding protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avenet P., Lindemann B. Amiloride-blockable sodium currents in isolated taste receptor cells. J Membr Biol. 1988 Nov;105(3):245–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01871001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbry P., Chassande O., Duval D., Rousseau B., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. Biochemical identification of two types of phenamil binding sites associated with amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3744–3749. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbry P., Chassande O., Marsault R., Lazdunski M., Frelin C. [3H]phenamil binding protein of the renal epithelium Na+ channel. Purification, affinity labeling, and functional reconstitution. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 30;29(4):1039–1045. doi: 10.1021/bi00456a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbry P., Chassande O., Vigne P., Frelin C., Ellory C., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lazdunski M. Purification and subunit structure of the [3H]phenamil receptor associated with the renal apical Na+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4836–4840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbry P., Frelin C., Vigne P., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lazdunski M. [3H]phenamil, a radiolabelled diuretic for the analysis of the amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels in kidney membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90937-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Saccomani G., Sariban-Sohraby S. The epithelial sodium channel. Subunit number and location of the amiloride binding site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10613–10618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Cantley L., Gatzy J. T. Na+ transport in cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelia. Abnormal basal rate and response to adenylate cyclase activation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1245–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI112708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Van Beveren C., Smith D., Chen E., Mitchell R. L., Isacke C. M., Verma I. M., Ullrich A. Structural alteration of viral homologue of receptor proto-oncogene fms at carboxyl terminus. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):277–280. doi: 10.1038/320277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W. An upper limit to the number of sodium channels in frog skin epithelium. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;228(3):681–692. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:321–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frings S., Lindemann B. Odorant response of isolated olfactory receptor cells is blocked by amiloride. J Membr Biol. 1988 Nov;105(3):233–243. doi: 10.1007/BF01871000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Welsh M. J., Smith P. L. Hormonal control of chloride secretion by canine tracheal epithelium: an electrophysiologic analysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:558–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. L., Jr, Staub O., Geering K., Rossier B. C., Kleyman T. R., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Functional expression of the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7295–7298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Friend D., Ziegler S. F., Jerzy R., Falk B. A., Gimpel S., Cosman D., Dower S. K., March C. J., Namen A. E. Cloning of the human and murine interleukin-7 receptors: demonstration of a soluble form and homology to a new receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90342-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs E., Clad A. Electroelution of fixed and stained membrane proteins from preparative sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels into a membrane trap. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 1;154(2):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M. R., Church N. L., Waltner W. E., Yankaskas J. R., Gilligan P., King M., Edwards L. J., Helms R. W., Boucher R. C. A pilot study of aerosolized amiloride for the treatment of lung disease in cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 26;322(17):1189–1194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004263221704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg W. H., Henderson L. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:254–259. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Doucet A. Hormonal control of kidney functions at the cell level. Physiol Rev. 1986 Apr;66(2):377–468. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.2.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Edelman I. S. Control of apical sodium permeability in the toad urinary bladder by aldosterone. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Amiloride-sensitive Na channels from the apical membrane of the rat cortical collecting tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Shivers B. D., Seeburg P. H. The role of receptor subtype diversity in the CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jan;13(1):8–11. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90052-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel M. B., Sinha Y. N., VanderLaan W. P. Production of antibodies by inoculation into lymph nodes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;93:3–12. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)93031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Bauw G., Puype M., Van Damme J., Van Montagu M. Protein-blotting on Polybrene-coated glass-fiber sheets. A basis for acid hydrolysis and gas-phase sequencing of picomole quantities of protein previously separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):9–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrier B., Champigny G., Barbry P., Gerard C., Mauchamp J., Lazdunski M. Identification and properties of a novel type of Na+-permeable amiloride-sensitive channel in thyroid cells. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):499–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Champigny G., Marsault R., Barbry P., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. A new type of amiloride-sensitive cationic channel in endothelial cells of brain microvessels. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7663–7668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Frelin C., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lazdunski M. Structure-activity relationships of amiloride and certain of its analogues in relation to the blockade of the Na+/H+ exchange system. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;25(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






