Abstract
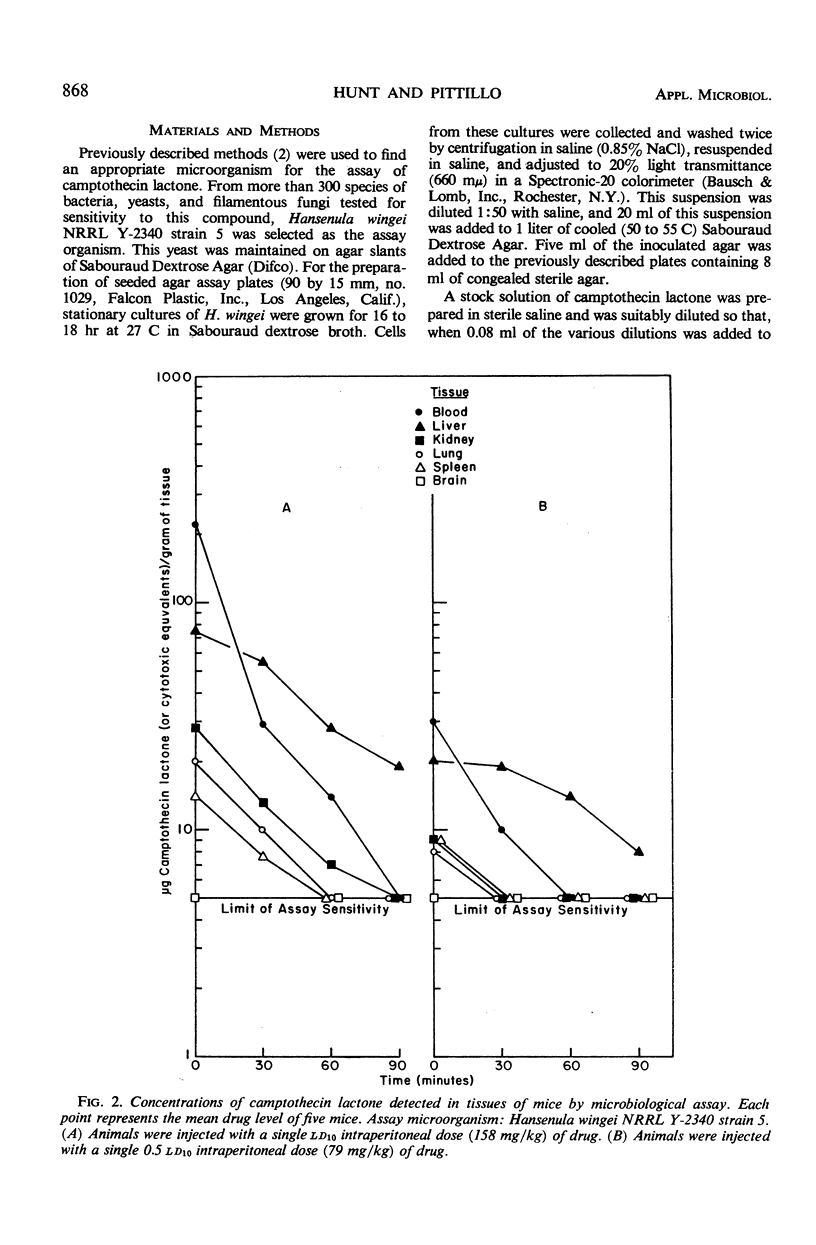
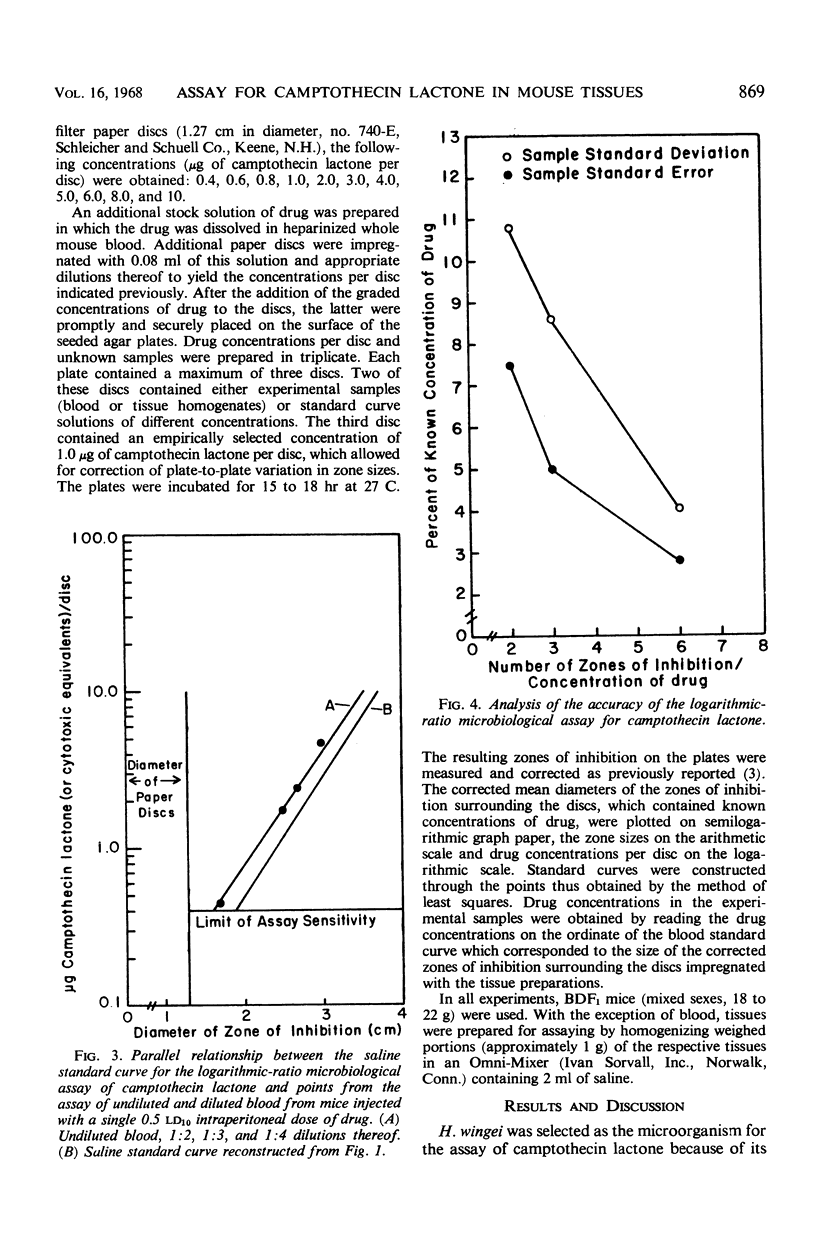
The marked sensitivity of the yeast Hansenula wingei NRRL Y-2340 strain 5 to a new antineoplastic alkaloid served as the basis for a logarithmic-ratio microbiological assay which has been developed for the estimation of concentrations of camptothecin lactone (or cytotoxic equivalents) in tissues of mice. The utility of this assay has been demonstrated by presenting data which show the concentrations of camptothecin lactone (or cytotoxic equivalents) detected in various tissues of mice at intervals following intraperitoneal injection of a 1 or 0.5 ld10 dose of this drug.
Full text
PDF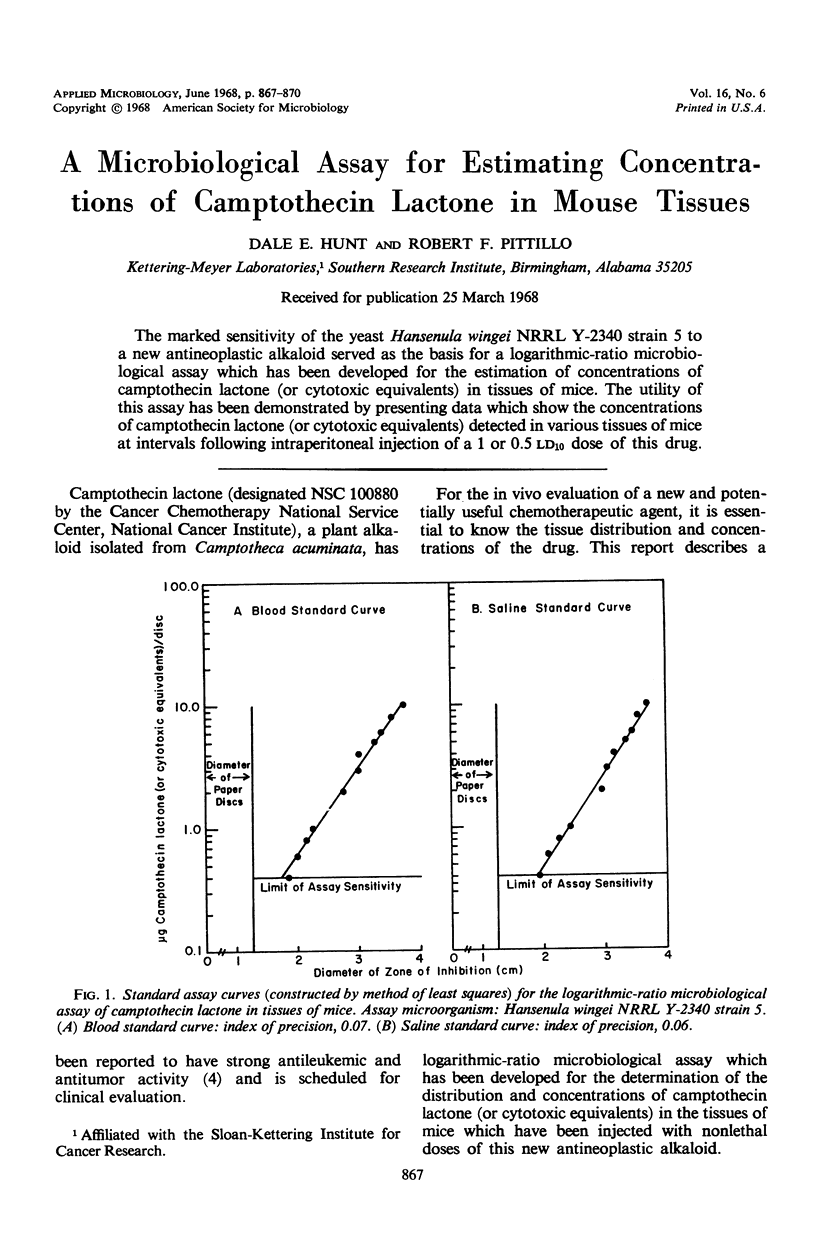

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hunt D. E., Pittillo R. F. Antifungal action of 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:710–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittillo R. F., Hunt D. E. Cytosine arabinoside sensitivity in actinobolin-resistant Streptococcus faecalis: the basis of a utilitarian microbiological assay. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):636–640. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


