Abstract
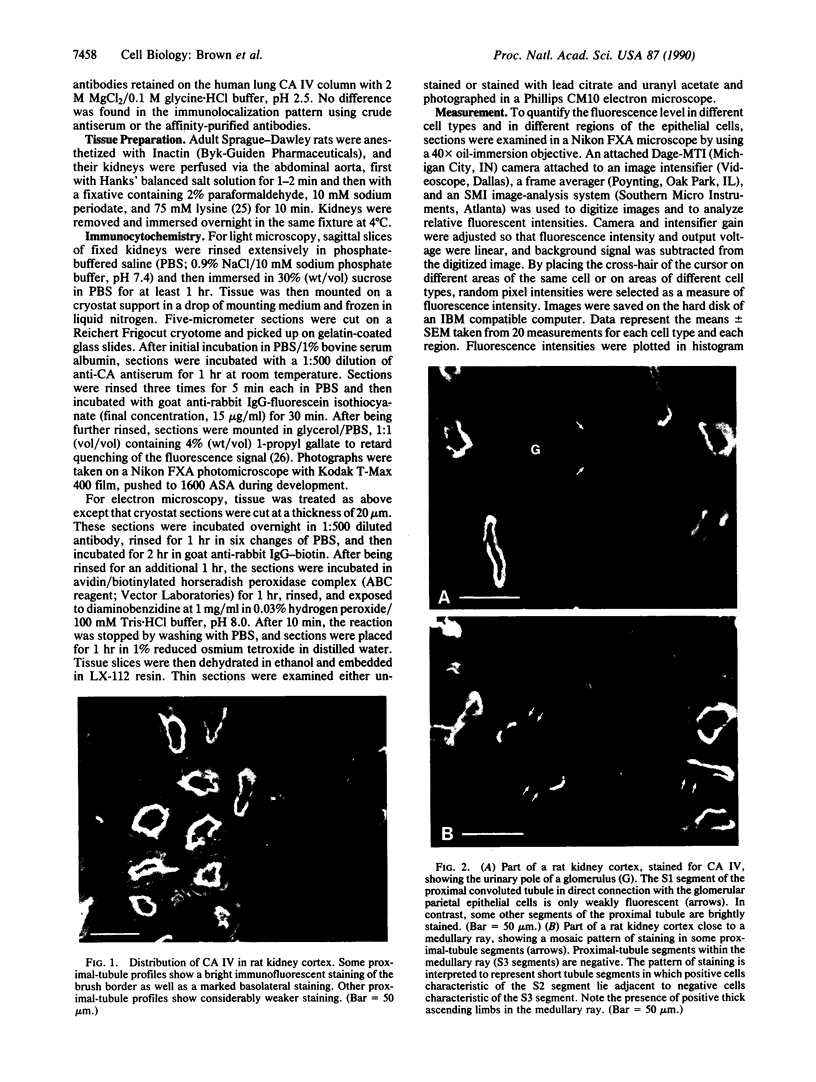
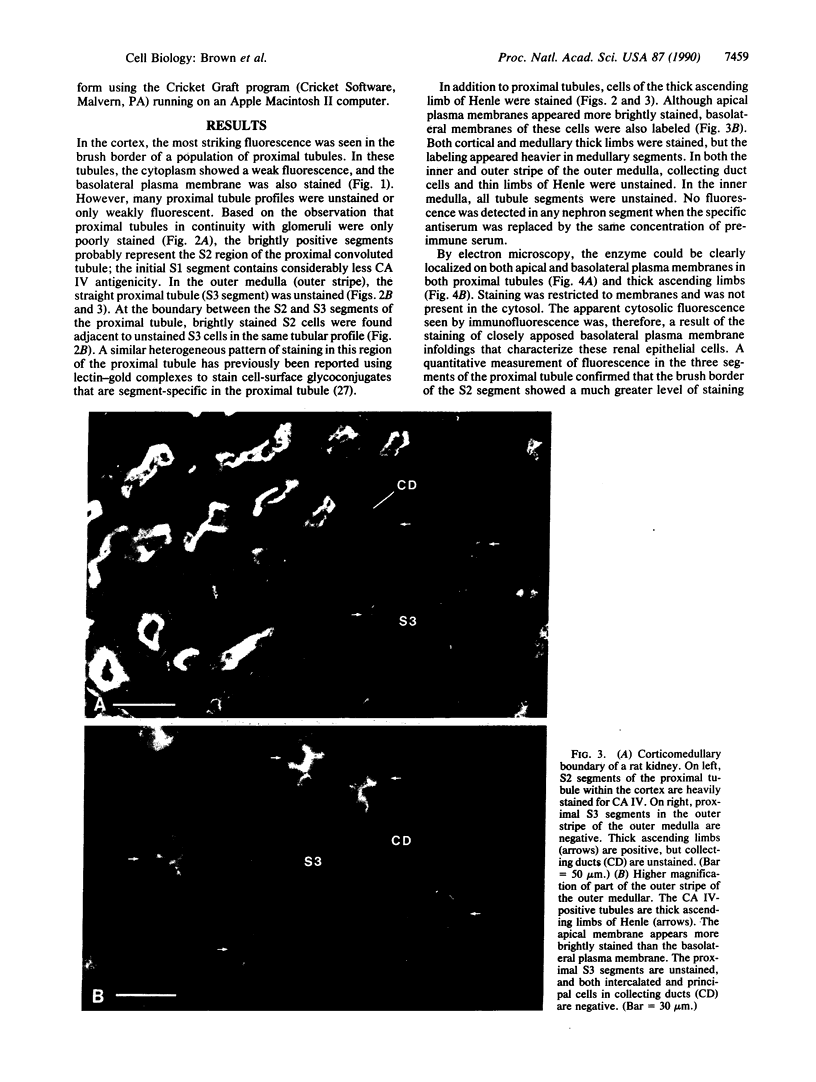
Rat carbonic anhydrase (CA) IV was purified by affinity chromatography and used to produce a specific antiserum in rabbits for immunolocalization studies in rat kidney. CA IV was localized in apical plasma membranes of the proximal convoluted tubule and the thick ascending limb of Henle. Both of these segments are involved in bicarbonate reabsorption in the rat. Immunofluorescent staining of the brush border was faint in the S1 segment, greatest in the S2 segment, and absent from the S3 segment of the proximal tubule. CA IV was also detected in the basolateral plasma membrane of proximal-tubule and thick-ascending-limb epithelial cells by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy. In the proximal tubule, an extracellular membrane CA had been previously suggested on the basis of electrophysiological studies. CA IV was not detected in intercalated cells of the collecting ducts. These cells contain, in contrast, abundant cytosolic CA II. Thus, the distribution of CA IV is quite distinct from that of CA II; it corresponds with the localization of an isoenzyme(s) that did not stain with antibodies against CA II but that was revealed by histochemical-staining procedures. We conclude that the apical CA IV is the luminal CA responsible for bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal tubule and the thick ascending limb in the rat kidney. These studies also suggest that CA IV plays a role in bicarbonate transport across the basolateral plasma membrane in these two segments of the rat nephron.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D., Hirsch S., Gluck S. An H+-ATPase in opposite plasma membrane domains in kidney epithelial cell subpopulations. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):622–624. doi: 10.1038/331622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Kumpulainen T., Roth J., Orci L. Immunohistochemical localization of carbonic anhydrase in postnatal and adult rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):F110–F118. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.1.F110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Kunz A., Wohlwend A., Vassalli J. D., Orci L. Détection ultrastructurale de l'hétérogénéité du glycocalyx dans les tubes contournés et droits proximaux du rein de Rat par la technique de la lectine couplée à l'or [1]. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1983;297(10):501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Roth J., Kumpulainen T., Orci L. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of carbonic anhydrase. Presence in intercalated cells of the rat collecting tubule. Histochemistry. 1982;75(2):209–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00496012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt B. C., Sato K., Frömter E. Electrophysiological analysis of bicarbonate permeation across the peritubular cell membrane of rat kidney proximal tubule. I. Basic observations. Pflugers Arch. 1984 May;401(1):34–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00581530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyan D. C., Bulger R. E. Renal carbonic anhydrase. Am J Physiol. 1982 Oct;243(4):F311–F324. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.4.F311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eveloff J., Swenson E. R., Maren T. H. Carbonic anhydrase activity of brush border and plasma membranes prepared from rat kidney cortex. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 15;28(8):1434–1437. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernley R. T. Non-cytoplasmic carbonic anhydrases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Sep;13(9):356–359. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giloh H., Sedat J. W. Fluorescence microscopy: reduced photobleaching of rhodamine and fluorescein protein conjugates by n-propyl gallate. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1252–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.7112126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., Knepper M. A., Burg M. B. Ammonia and bicarbonate transport by thick ascending limb of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):F35–F44. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W. Sodium-dependent bicarbonate absorption by cortical thick ascending limb of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 2):F821–F829. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.6.F821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson H. P. Histochemical demonstration of carbonic anhydrase activity. Histochemie. 1967;11(2):112–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00571716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett-Emmett D., Hopkins P. J., Tashian R. E., Czelusniak J. Origins and molecular evolution of the carbonic anhydrase isozymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:338–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino Y., Burg M. B. Effect of acid-base status in vivo on bicarbonate transport by rabbit renal tubules in vitro. Jpn J Physiol. 1981;31(1):99–107. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.31.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlmark B., Agerup B., Wistrand P. J. Renal proximal tubular acidification. Role of brush-border and cytoplasmic carbonic anhydrase. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Jun;106(2):145–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I., Star R., Balaban R. S., Garvin J. L., Knepper M. A. Spontaneous luminal disequilibrium pH in S3 proximal tubules. Role in ammonia and bicarbonate transport. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):989–996. doi: 10.1172/JCI112690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Caras I. W., Davitz M. A., Rodriguez-Boulan E. A glycophospholipid membrane anchor acts as an apical targeting signal in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2145–2156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Stiernberg J., Waneck G. L., Flavell R. A., Kincade P. W. Cell-specific heterogeneity in sensitivity of phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane antigens to release by phospholipase C. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Oct 4;113(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucci M. S., Tinker J. P., Weiner I. M., DuBose T. D., Jr Function of proximal tubule carbonic anhydrase defined by selective inhibition. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):F443–F449. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.4.F443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerholm G., Ridderstråle Y. Intracellular distribution of carbonic anhydrase in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1980 Feb;17(2):162–174. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerholm G., Wistrand P. J. Carbonic anhydrase in the human fetal kidney. Pediatr Res. 1983 May;17(5):390–397. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198305000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerholm G., Wistrand P. J. Carbonic anhydrase in the human kidney: a histochemical and immunocytochemical study. Kidney Int. 1984 Jun;25(6):886–898. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley D. N., Whitney P. L. Particulate carbonic anhydrase in homogenates of human kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 11;445(3):780–790. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal G., Pessah N. I., Maren T. H. Kinetics and inhibition of membrane-bound carbonic anhydrase from canine renal cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 15;657(1):128–137. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Carbonic anhydrase isozymes IV and II in urinary membranes from carbonic anhydrase II-deficient patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6073–6076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly W. S., Whyte M. P., Krupin T., Sundaram V. Positive renal response to intravenous acetazolamide in patients with carbonic anhydrase II deficiency. Pediatr Res. 1985 Oct;19(10):1033–1036. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198510000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer S. S., Sens M. A., Tashian R. E. Immunocytochemical demonstration of carbonic anhydrase in human epithelial cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Sep;30(9):864–873. doi: 10.1177/30.9.6813372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer S. S., Stoward P. J., Tashian R. E. The immunohistolocalization of carbonic anhydrase in rodent tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Apr;27(4):820–831. doi: 10.1177/27.4.109495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashian R. E. The carbonic anhydrases: widening perspectives on their evolution, expression and function. Bioessays. 1989 Jun;10(6):186–192. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. H., Silverman D. N. The carbon dioxide hydration activity of brush-border carbonic anhydrase from the dog kidney. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Nov;205(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. L., Briggle T. V. Membrane-associated carbonic anhydrase purified from bovine lung. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12056–12059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand P. J., Kinne R. Carbonic anhydrase activity of isolated brush border and basal-lateral membranes of renal tubular cells. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Aug 29;370(2):121–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00581684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand P. J., Knuuttila K. G. Renal membrane-bound carbonic anhydrase. Purification and properties. Kidney Int. 1989 Mar;35(3):851–859. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Carbonic anhydrase IV from human lung. Purification, characterization, and comparison with membrane carbonic anhydrase from human kidney. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8795–8801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]