Abstract
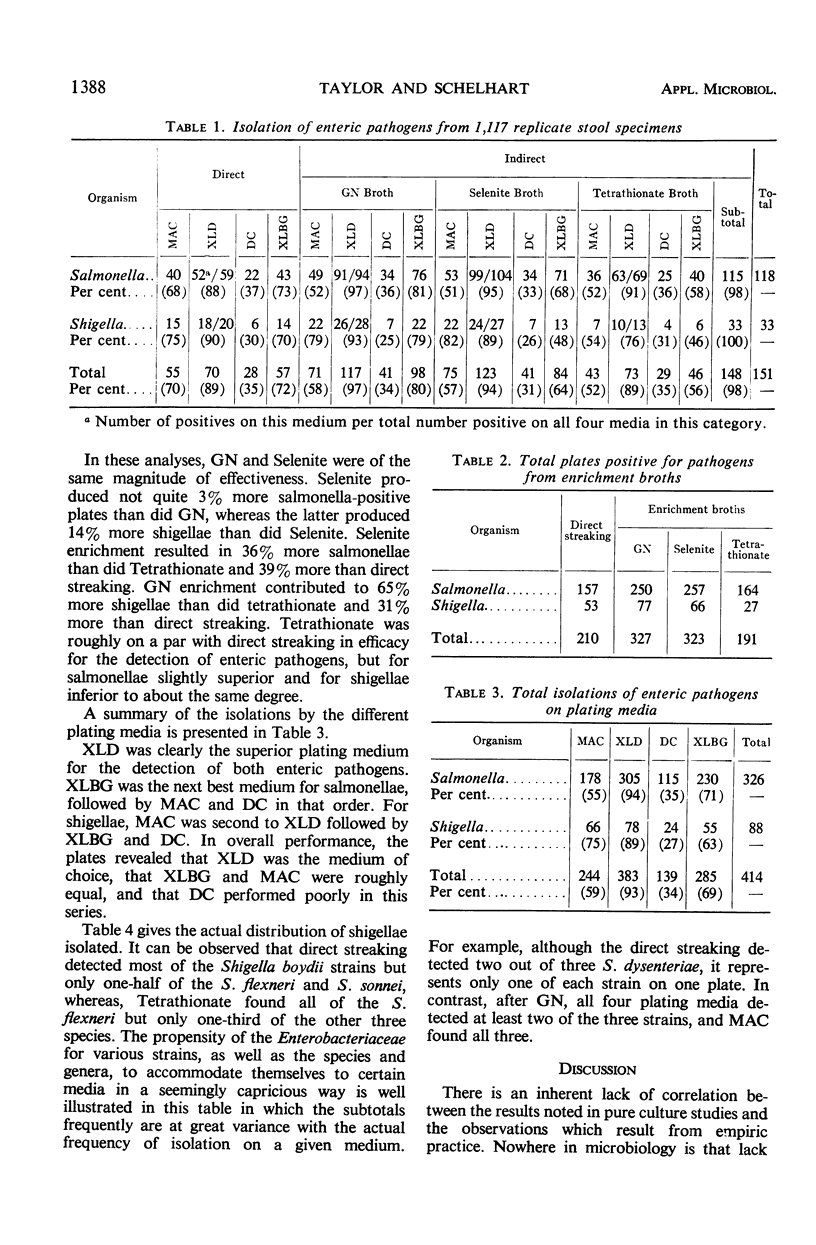
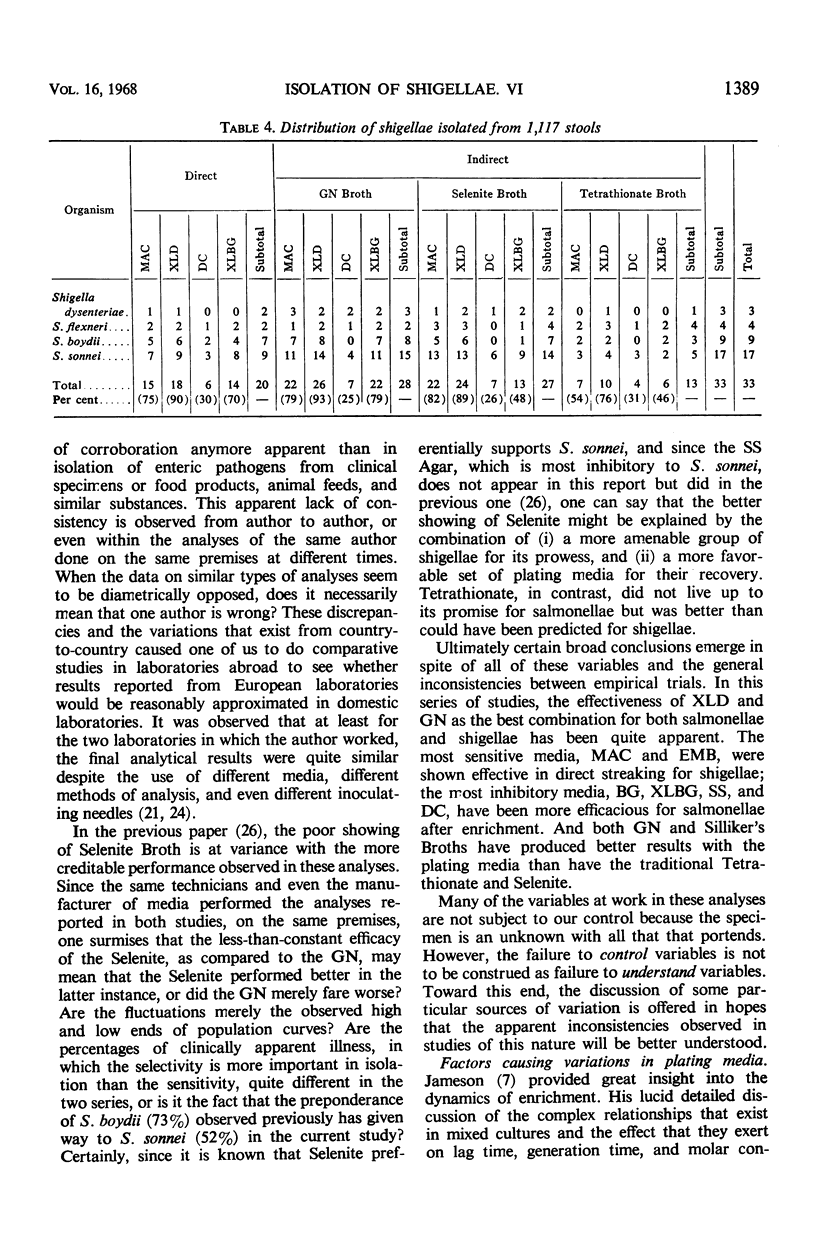
The efficiencies of three enrichment broths and four plating media for isolation of enteric pathogens were compared from 1,117 stool specimens. Direct streaking proved to be inferior to enrichment, detecting only 50% of the salmonellae and 61% of the shigellae. By contrast, Selenite Broth (SF) found 90% of the total salmonellae isolates and 82% of the shigellae isolates. Gram-Negative Broth (GN) found 82% and 85%, respectively, but Tetrathionate found only 60% and 39%. Thus, SF and GN were comparable for both salmonellae and shigellae and significantly better than Tetrathionate Broth for both. The plating media compared were MacConkey (MAC), deoxycholate citrate (DC), xylose lysine deoxycholate (XLD), and xylose lysine Brilliant Green (XLBG) Agars. Of the total salmonellae isolated, XLD produced 94%; XLBG, 71%; MAC, 55%; and DC, only 35%. Of shigellae, XLD found 89%; MAC, 75%; XLBG, 63%; and DC, but 27%. The efficacy of XLD is observed to be almost threefold that of DC. The most successful combination of media for the detection of fecal pathogens was GN or SF enrichment broths streaked to XLD plates. These analyses resulted in the isolation of 118 strains of salmonellae and 33 of shigellae.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLLARD P., UNWIN M. A trial of Rappaport's medium. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Sep;11(5):426–427. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.5.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUINEE P. A., KAMPELMACHER E. H., HOEJENBOS SPITHOUT H. H. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE INFLUENCE OF VARIATIONS IN THE ENRICHMENT METHOD FOR THE DETECTION OF SALMONELLAE. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1965;31:1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02045871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUINEE P. A., KAMPELMACHER E. H. Influence of variations of the enrichment method for detection of Salmonella. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1962;28:417–427. doi: 10.1007/BF02538757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iveson J. B., Kovacs N. A comparative trial of Rappaport enrichment medium for the isolation of Salmonellae from faeces. J Clin Pathol. 1967 May;20(3):290–293. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.3.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMESON J. E. A discussion of the dynamics of Salmonella enrichment. J Hyg (Lond) 1962 Jun;60:193–207. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall C. E., Martin W. T., Boring J. R. Efficiency of cultures of rectal swabs and faecal specimens in detecting salmonella carriers: correlation with numbers of salmonellas excreted. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Sep;64(3):261–269. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTH W. R., BARTRAM M. T. The efficiency of selenite broth of different compositions in the isolation of Salmonella. Appl Microbiol. 1953 May;1(3):130–134. doi: 10.1128/am.1.3.130-134.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTH W. R., Jr Lactose pre-enrichment method for isolation of Samonella from dried egg albumen. Its use in a survery of commercially produced albumen. Appl Microbiol. 1961 May;9:188–195. doi: 10.1128/am.9.3.188-195.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPAPORT F., KONFORTI N. Selective enrichment medium for paratyphoid bacteria; inhibitory and growth promoting factors. Appl Microbiol. 1959 Mar;7(2):63–66. doi: 10.1128/am.7.2.63-66.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILLIKER J. H., DEIBEL R. H., FAGAN P. T. ENHANCING EFFECT OF FECES ON ISOLATION OF SALMONELLAE FROM SELENITE BROTH. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Mar;12:100–105. doi: 10.1128/am.12.2.100-105.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILLIKER J. H., DEIBEL R. H., FAGAN P. T. ISOLATION OF SALMONELLAE FROM FOOD SAMPLES. VI. COMPARISON OF METHODS FOR THE ISOLATION OF SALMONELLA FROM EGG PRODUCTS. Appl Microbiol. 1964 May;12:224–228. doi: 10.1128/am.12.3.224-228.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILLIKER J. H., TAYLOR W. I. Isolation of salmonellae from food samples. II. The effect of added food samples upon the performance of enrichment broths. Appl Microbiol. 1958 Jul;6(4):228–232. doi: 10.1128/am.6.4.228-232.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. G. On the nature of the selective action of selenite broth. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:61–71. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR W. I., BUTTIAUX R., CATSARAS M. [Technics for detection of Salmonella in meat]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 May;104:638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR W. I., HOBBS B. C., SMITH M. E. COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS FOR THE ISOLATION OF SALMONELLAE FROM IMPORTED FOODS. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jan;12:53–56. doi: 10.1128/am.12.1.53-56.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR W. I. Isolation of Salmonellae from food samples. V. Determination of the method of choice for enumeration of Salmonella. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Nov;9:487–490. doi: 10.1128/am.9.6.487-490.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR W. I., SILLIKER J. H. Isolation of Salmonellae from food samples. IV. Comparison of methods of enrichment. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Nov;9:484–486. doi: 10.1128/am.9.6.484-486.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. I., Harris B. Isolation of shigellae. II. Comparison of plating media and enrichment broths. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Oct;44(4):476–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. I. Isolation of shigellae. I. Xylose lysine agars; new media for isolation of enteric pathogens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Oct;44(4):471–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. I., Schelhart D. Isolation of shigellae. V. Comparison of enrichment broths with stools. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1383–1386. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1383-1386.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassiliadis P., Pateraki E., Politi G. Comportement des Shigella dans le milieu d'enrichissement au sélénite. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1966 Jan-Feb;59(1):31–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss K. F., Ayres J. C., Kraft A. A. Inhibitory action of selenite on Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris, and Salmonella thompson. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):857–862. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.857-862.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


