ABSTRACT
Nontoxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans cause invasive disease in humans and animals. Host sensing of corynebacteria is largely uncharacterized, albeit the recognition of lipoglycans by Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) appears to be important for macrophage activation by corynebacteria. The members of the order Corynebacterineae (e.g., mycobacteria, nocardia, and rhodococci) share a glycolipid-rich cell wall dominated by mycolic acids (termed corynomycolic acids in corynebacteria). The mycolic acid-containing cord factor of mycobacteria, trehalose dimycolate, activates the C-type lectin receptor (CLR) Mincle. Here, we show that glycolipid extracts from the cell walls of several pathogenic and nonpathogenic Corynebacterium strains directly bound to recombinant Mincle in vitro. Macrophages deficient in Mincle or its adapter protein Fc receptor gamma chain (FcRγ) produced severely reduced amounts of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and of nitric oxide (NO) upon challenge with corynebacterial glycolipids. Consistently, cell wall extracts of a particular C. diphtheriae strain (DSM43989) lacking mycolic acid esters neither bound Mincle nor activated macrophages. Furthermore, TLR2 but not TLR4 was critical for sensing of cell wall extracts and whole corynebacteria. The upregulation of Mincle expression upon encountering corynebacteria required TLR2. Thus, macrophage activation by the corynebacterial cell wall relies on TLR2-driven robust Mincle expression and the cooperative action of both receptors.
KEYWORDS: C-type lectin receptor, Mincle, Toll-like receptor, macrophage, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, cell wall lipids, mycolate, mycolic acid, corynomycolate
INTRODUCTION
Diphtheria caused by toxin-producing Corynebacterium diphtheriae is a severe, life-threatening infection, which has become rare in Europe due to the efficacy and coverage of toxoid immunization but still causes a considerable burden of disease globally. Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis can also harbor the tox gene encoding diphtheria toxin (1) and in addition may secrete the exotoxin phospholipase D, a virulence factor involved in caseous lymphadenitis of sheep and goats (2, 3). Rates of infections with nontoxigenic strains of C. diphtheriae, including bloodstream infections and endocarditis, appear to be increasing in Europe (4, 5). Of the 90 species that comprise the genus Corynebacterium, many inhabit the human skin or mucosa as commensals (6), with C. striatum, C. tuberculostearicum, C. amycolatum, and C. jeikeium being typical examples of skin inhabitants, whereas C. urealyticum and C. glucuronolyticum are frequently found in the urogenital tract. All these Corynebacterium spp. can cause invasive disease in patients with compromised skin or mucosal barrier function (e.g., patients suffering from burn wounds or carrying intravascular devices) or in immunocompromised patients (e.g., diabetics and cancer patients) (7–13).
While it is clear that protection against toxin-producing strains of C. diphtheriae relies on the presence of neutralizing antibodies, not much is known about the immune response against nontoxigenic Corynebacterium spp. in patients. A few studies in the mouse model have started to investigate tissue tropism and inflammatory responses (14), revealing strain-dependent arthritogenic potential independent of toxin and phospholipase D production (15, 16).
Taxonomically, Corynebacterium spp. belong to the suborder Corynebacterineae of the order Actinomycetales, which includes Mycobacterium spp., Nocardia spp., Rhodococcus spp., and Tsukamurella spp. All Corynebacterineae are characterized by a lipid-rich cell wall with an outer membrane layer dominated by long-chain α-alkyl β-hydroxy fatty acids called mycolic acids (termed corynomycolic acids in Corynebacterium) covalently linked to arabinogalactan and additionally to trehalose as trehalose monomycolate (TMM) and trehalose dimycolate (TDM) (17). Among the Corynebacterineae, Corynebacterium spp. have the shortest chain length, with corynomycolic acids comprising a total carbon length of 22 to 38 carbons, whereas Mycobacterium spp. harbor mycolic acids with a total carbon length of 60 to 90 carbons (17). TDM from pathogenic mycobacteria is known as cord factor, based on its role in the clumping of mycobacteria during in vitro culture, and has been recognized for decades for its role in inducing the inflammatory response, granuloma formation, and adjuvant activity for T cell responses during mycobacterial infection (18–20). Recently, the direct recognition of TDM by the C-type lectin receptor (CLR) Mincle was shown to trigger macrophage activation through the adapter protein Fc receptor gamma chain (FcRγ), the kinase Syk, and the Card9-Bcl10-Malt1 complex (21–23). Mincle, the related CLR Mcl, and the components of this signaling pathway are essential for granuloma formation and adjuvant effects in response to TDM in mice (20, 22, 24–26) and mediate the response of human macrophages to TDM and the synthetic glycolipid trehalose dibehenate (TDB) (27).
However, the mechanisms of innate immune recognition of corynebacteria are not well studied. Early work from the 1960s to the 1980s in the last century described surface lipids of C. pseudotuberculosis as virulence factors with toxic activity toward macrophages and correlated the lipid content to abscess formation in vivo (28, 29). Toll-like receptors (TLRs) mediate C. diphtheriae-driven macrophage activation in a TLR2-dependent yet TLR4-independent manner (30). Mishra et al. demonstrated that lipomannan (LM) and lipoarabinomannan (LAM) of C. glutamicum interact with TLR2 (31). In addition, TLR2-activating lipoglycans of C. glutamicum include glycosylated diacylglycerol-anchored lipids (32). A stimulatory effect of purified trehalose dicorynomycolate (TDCM) from C. glutamicum on macrophages was shown previously, without characterization of the receptors involved (33). Recently, synthetic corynomycolates were demonstrated to be recognized through mouse and human Mincle by using a reporter cell system (34). However, the role for Mincle and other CLRs in the recognition of corynebacteria by innate immune cells has not been tested.
Here, we used cell wall preparations of specific isolates of C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans, and C. glutamicum to comparatively address the roles of TLR2 and Mincle receptors in macrophage activation by corynebacteria. Mincle directly bound glycolipid cell wall extracts and was required for cytokine and nitric oxide (NO) production in response to lipid extracts but not to whole bacteria. Consistently, one isolate of C. diphtheriae lacking cell wall mycolates was deficient in Mincle binding and macrophage activation in response to its glycolipid extracts. TLR2 was essential for macrophage activation by corynebacteria and upregulated Mincle expression, suggesting a synergistic recognition of corynebacterial glycolipids via a feed-forward loop of TLR2-dependent Mincle induction.
RESULTS
Mincle-Fc binds to cell wall extracts of corynebacteria.
To test for the presence of Mincle ligands in the cell wall of corynebacteria, chloroform-methanol extracts were prepared and used in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)-based Mincle-Fc binding assay (35, 36). Plate-bound lipid extracts of several strains of C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans, and C. glutamicum dose-dependently bound to Mincle-Fc (Fig. 1A). Binding activity was detectable starting at a concentration of around 1 μg/ml of the extract. Corynebacterial glycolipids bound specifically to Mincle-Fc, as no signal was obtained by using Clec9a-Fc or the Fc protein alone (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). The synthetic Mincle ligand TDB, which was used as a positive control, yielded detectable signals at lower concentrations and reached somewhat higher signals at saturation. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and staining of fatty acid methyl esters (FAMES) and mycolic acid methyl esters (MAMES) from cell wall lipid extracts with molybdophosphoric acid (MPA) gave overall similar results for the different corynebacterial strains, with prominent signals representing FAMES and MAMES (Fig. 1B). Together, the data from Mincle-Fc binding assay clearly demonstrated the presence of ligands for this CLR among the complex mixture of corynebacterial cell wall glycolipids.
FIG 1.
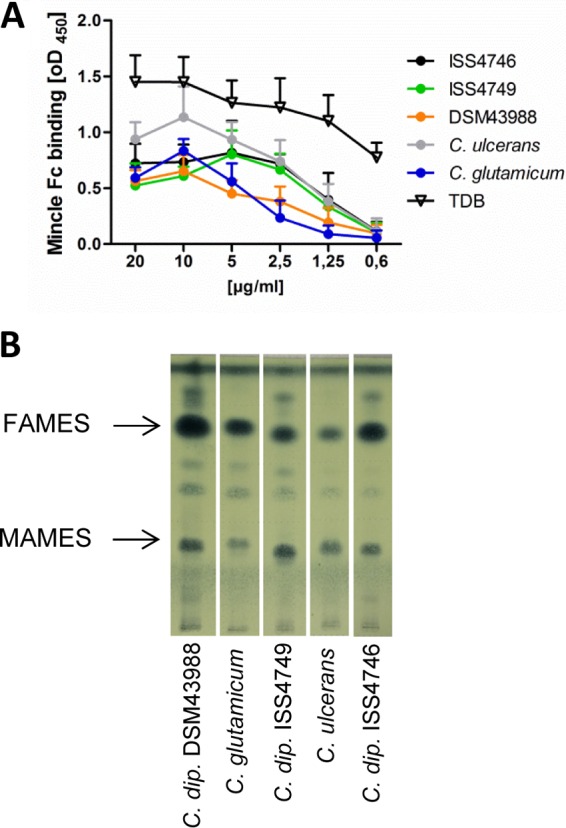
Cell wall extracts of corynebacteria bind the Mincle-Fc fusion protein in vitro. (A) The binding affinity of the Mincle-Fc fusion protein for different concentrations of corynebacterial glycolipid extracts was analyzed by using a Mincle-Fc binding assay. Data are depicted as mean values and standard deviations from 3 experiments performed in duplicates (n = 6). (B) TLC of fatty acid and mycolic acid methyl esters stained with MPA. C. dip., C. diphtheriae.
Mincle-FcRγ signaling is required for the response to corynebacterial cell wall glycolipids.
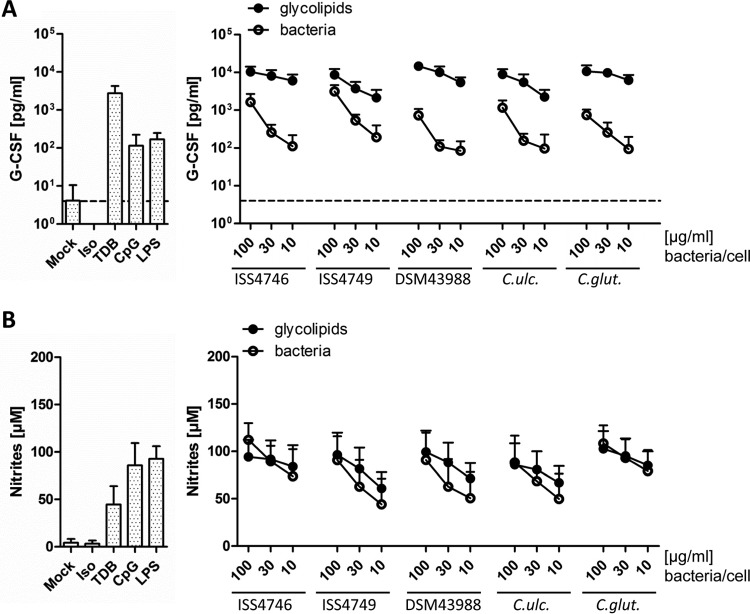
To assess the response of innate immune cells to corynebacteria and their cell wall, bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMM) were stimulated with titrated amounts of plate-bound glycolipid extracts or heat-inactivated corynebacteria, followed by measurement of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) release as a robust readout of Mincle-dependent BMM activation (22, 37) (Fig. 2A) and nitrites as an indicator of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activity (Fig. 2B). As positive controls, ligands for TLR4 and TLR9 (lipopolysaccharide [LPS] and CpG oligodeoxynucleotide [ODN], respectively) and for Mincle (TDB) were included. While all synthetic ligands triggered both G-CSF from resting BMM and NO release from gamma interferon (IFN-γ)-cotreated BMM, TDB more potently induced G-CSF, and the TLR ligands induced higher levels of NO. G-CSF production was induced very robustly and dose dependently by the glycolipid extracts of corynebacteria independent of the species tested. Whole corynebacteria also triggered G-CSF production, yet even at a high bacterium-to-cell ratio of 100, the levels were not as high as those with relatively small amounts of glycolipids. In contrast, NO production from BMM cotreated with IFN-γ was induced to similar levels by cell wall extracts and whole corynebacteria.
FIG 2.
Corynebacterial glycolipids induce G-CSF and NO production in macrophages in a concentration-dependent manner. BMM from C57BL/6 mice were stimulated with different concentrations of glycolipids (100, 30, or 10 μg/ml) or heat-killed bacteria (100, 30, or 10 bacteria per cell), followed by determination of G-CSF (A) and nitrite (B) levels in cell culture supernatants via an ELISA and a Griess assay, respectively. The detection limit for G-CSF was 4 pg/ml (dotted line). For comparison, unstimulated cells or TDB-, CpG-, or LPS-stimulated cells were used as controls. Data are represented as means and standard deviations of results from 6 independent experiments performed in duplicates (n = 12). Iso, isopropanol; C. ulc., C. ulcerans; C. glut., C. glutamicum.
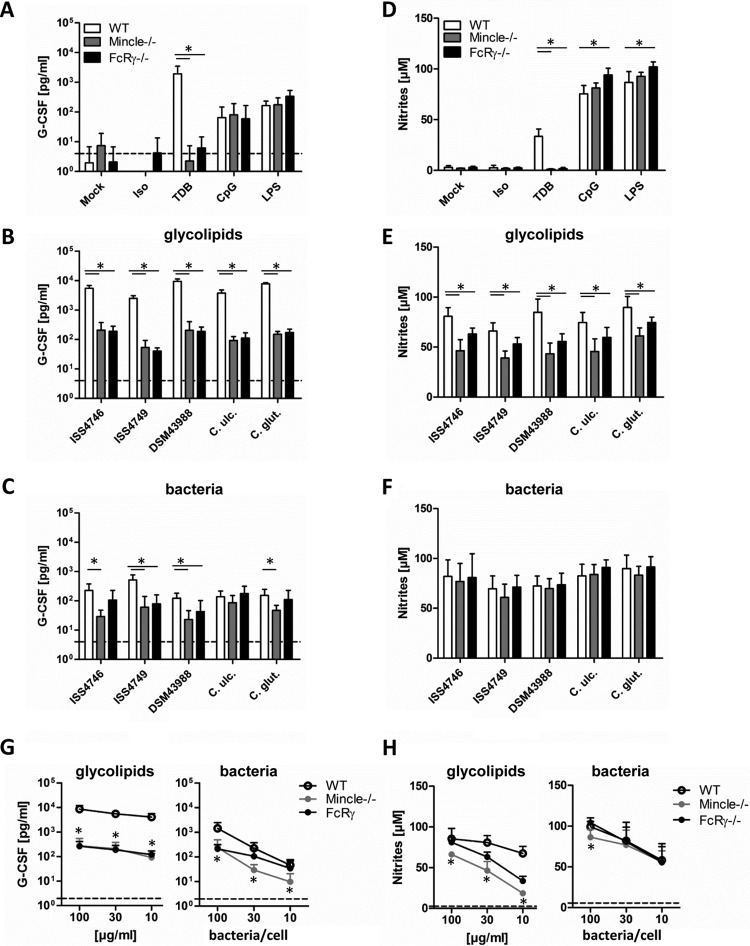
We next asked whether the recognition of cell wall glycolipids by Mincle and signaling via its adapter protein FcRγ were required for the macrophage response to corynebacteria. As expected, BMM lacking Mincle or FcRγ did not produce G-CSF or NO upon stimulation with TDB but responded normally to CpG or LPS (Fig. 3A and D). The release of G-CSF after stimulation with glycolipid extracts was strongly attenuated (20-fold reduction on average) but not completely abrogated in the absence of Mincle or FcRγ (Fig. 3B). In contrast, the comparably weak induction of G-CSF by whole corynebacteria was only partially Mincle-FcRγ dependent (Fig. 3C). NO release from IFN-γ-cotreated BMM was significantly reduced in the absence of Mincle or FcRγ after glycolipid stimulation (Fig. 3E) but not when whole corynebacteria were used (Fig. 3F). Mincle-FcRγ deficiency especially impaired the G-CSF response to glycolipid extracts over a broad range of concentrations (Fig. 3G), whereas for NO production, a shift in the dose response to glycolipids was apparent (Fig. 3H). Results for C. diphtheriae strain ISS4746 are shown in Fig. 3G and H as a representative example, since a similar pattern was observed for C. diphtheriae strains ISS4749 and DSM43988, C. ulcerans, and C. glutamicum.
FIG 3.
Mincle/FcRγ deficiency impairs G-CSF and NO production in macrophages stimulated with corynebacteria or their cell wall glycolipids. (A to C) BMM from Mincle- or FcRγ-deficient mice and their respective wild-type controls were stimulated with different glycolipid extracts (30 μg/ml) or the corresponding heat-killed bacteria (30 bacteria per cell) as well as controls for 48 h, as indicated. G-CSF cytokine levels in cell culture supernatants were determined by using an ELISA. The detection limit was 4 pg/ml (dotted line). (D to F) NO production in cell culture supernatants was determined by using a Griess assay. BMM were cotreated with 10 ng/ml IFN-γ. (G and H) BMM were stimulated with different concentrations of glycolipids (100, 30, or 10 μg/ml) or heat-killed bacteria (100, 30, or 10 bacteria per cell). Data shown were obtained with glycolipids from C. diphtheriae ISS4746; extracts from the other corynebacterial strains/species showed similar dose-response curves (not shown for clarity). G-CSF and NO production was analyzed as described above. Dotted lines represent G-CSF or nitrite levels from unstimulated BMM. Note that data points for some Mincle−/− and FcRγ−/− BMM overlap in panel G. Data are depicted as means and standard deviations of results from 3 independent experiments performed in duplicates (n = 6). In panels B to H, * indicates a P value of <0.05 for the indicated comparison between genotypes.
Absence of corynomycolic acid-derived glycolipids, lack of Mincle binding, and macrophage activation in the cell wall of C. diphtheriae strain DSM43989.
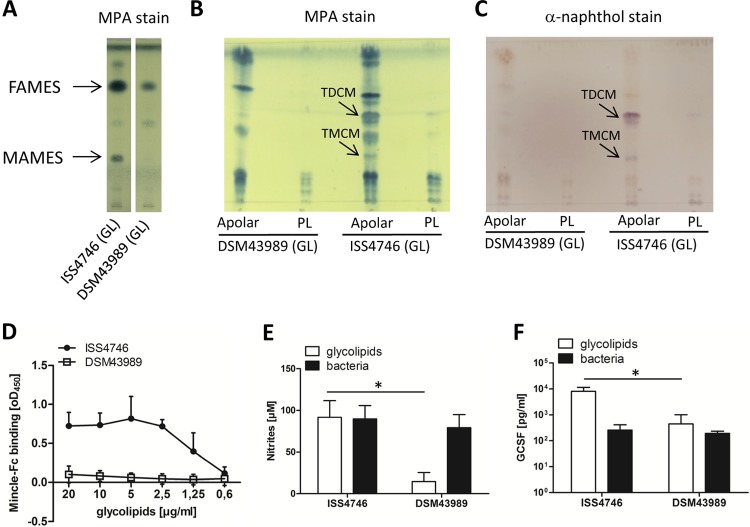
Our present studies with DSM43989, a tox+ C. diphtheriae isolate (identical to ATCC 13812, a PW8 strain used for toxoid production [38]), revealed a lack of corynomycolic acids in this strain (L. Ott, E. Hacker, T. Kunert, I. A. Kline, P. Etschel, R. Lang, V. Wiesmann, T. Wittenberg, A. C. Varela, A. Bhatt, V. Sangal, and A. Burkovski, submitted for publication) (Fig. 4A). This strain, which lacks TMM and TDM, provided us with an opportunity to probe the role of corynomycolic acid-derived glycolipids in Mincle signaling. Indeed, analysis of fractions from whole lipids revealed the absence of TDCM and trehalose monocorynomycolate (TMCM) in the apolar fraction of DSM43989 cells (Fig. 4B and C). Whole-lipid extracts from this isolate did not bind the Mincle-Fc protein even at high concentrations (Fig. 4D), consistent with the notion that the MAMES and TDCM/TMCM visible by TLC analysis represent the major Mincle ligands of the corynebacterial cell wall. The capacity of the cell wall glycolipids of DSM43989 to stimulate NO release and G-CSF production from BMM was strongly attenuated, whereas heat-killed whole DSM43989 cells activated macrophages as potently as did cells of a representative MAMES-positive C. diphtheriae strain (Fig. 4E and F).
FIG 4.
Cell wall extracts of C. diphtheriae DSM43989 fail to activate macrophages and do not bind Mincle-Fc. (A) TLC of different lipid extracts stained by using MPA. (B and C) Apolar compounds and phospholipids (PL) of glycolipid (GL) extracts were purified and also detected by TLC using MPA (B) or α-naphthol (C). (D) The binding affinity of the Mincle-Fc fusion protein for different concentrations of C. diphtheriae ISS4746 and DSM43989 glycolipid extracts was analyzed by using a Mincle-Fc binding assay. Shown are means and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments performed in duplicates (n = 6). (E and F) Bone marrow-derived murine macrophages from C57BL/6 mice were stimulated with lipid extracts (30 μg/ml) or the corresponding heat-killed bacteria (30 bacteria per cell) from C. diphtheriae ISS4746 or DSM43989 in the presence (E) or absence (F) of 10 ng/ml IFN-γ. NO production (E) and G-CSF levels (F) were measured in the supernatant 48 h after stimulation. Data are depicted as means and standard deviations of results from 6 independent experiments performed in duplicates (n = 12).
TLR2 is essential for macrophage activation by whole corynebacteria and cell wall glycolipids.
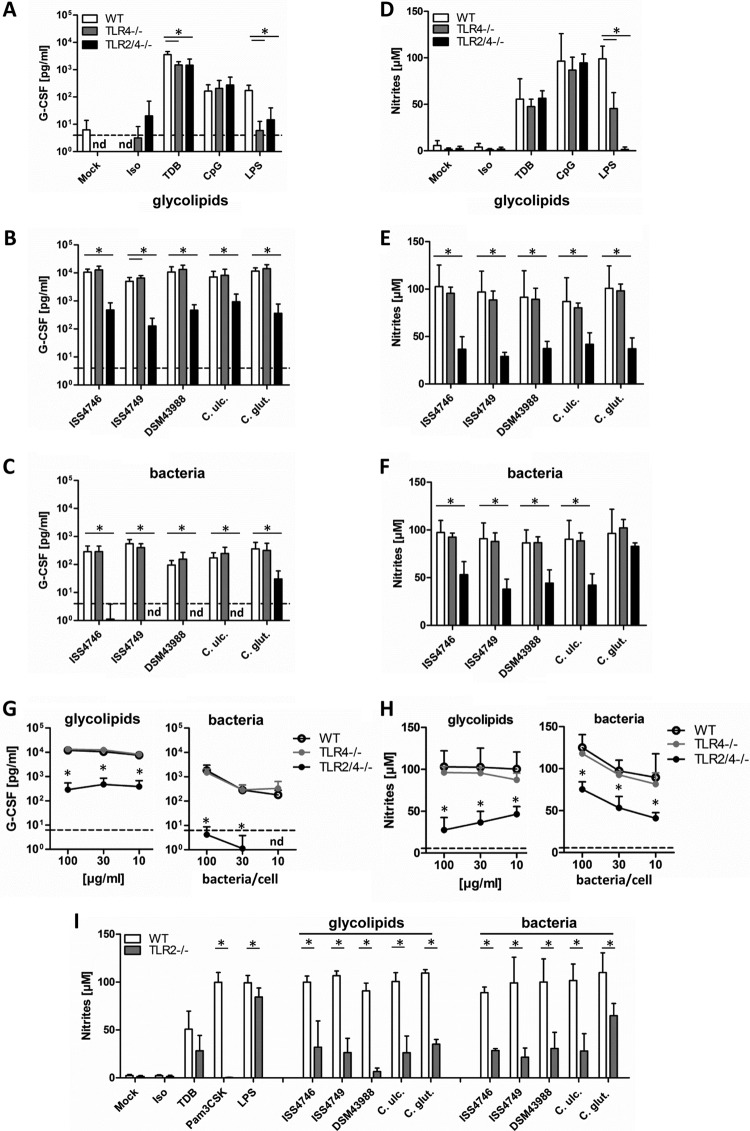
BMM from Tlr4−/− and Tlr2−/−;Tlr4−/− mice were employed to test the role of these TLRs in macrophage activation by corynebacteria and their cell wall glycolipids (Fig. 5). Control stimulations with ligands for Mincle, TLR4, and TLR9 showed no effect on TDB and CpG responses, as expected, yet strongly reduced responses to LPS in Tlr4−/− and no response in Tlr2−/−;Tlr4−/− BMM (Fig. 5A and D). The residual production of NO in Tlr4−/− BMM might be attributable to potential contaminating TLR2 ligands in the LPS preparation used or contributive LPS recognition through TLR2 (39). Tlr4−/− macrophage responsiveness to the glycolipid extract as well as to whole heat-inactivated corynebacteria, in terms of both G-CSF production (Fig. 5B and C) as well as NO release (Fig. 5E and F), equaled that of wild-type (WT) controls. In contrast, Tlr2−/−;Tlr4−/− BMM secreted substantially less G-CSF in response to cell wall glycolipids and no detectable G-CSF after stimulation with whole corynebacteria (Fig. 5B and C). In addition, the levels of nitrites were significantly reduced in supernatants of double-deficient BMM (Fig. 5E and F), except for C. glutamicum. Dose-response experiments confirmed that Tlr2−/−;Tlr4−/− but not Tlr4−/− BMM lack responsiveness to both cell wall extracts and whole corynebacteria (Fig. 5G and H). Results for C. diphtheriae strain ISS4746 are shown in Fig. 5G and H as a representative example, since a similar pattern was observed for C. diphtheriae strains ISS4749 and DSM43988, C. ulcerans, and C. glutamicum. Furthermore, the response to glycolipid extracts of DSM43989 was further reduced in Tlr2−/−;Tlr4−/− BMM (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). Next, we applied Tlr2−/− BMM, which failed to respond to cell wall lipid extracts and whole corynebacteria (including C. glutamicum) (Fig. 5I), excluding an involvement of TLR4. Together, these results corroborate the previous implication of TLR2 as a receptor for corynebacterial cell wall lipoglycans (30, 31).
FIG 5.
TLR2 deficiency impairs G-CSF and NO production in macrophages stimulated with corynebacteria or their cell wall glycolipids. (A to C) BMM from TLR4-deficient or TLR2/4-double-deficient mice and their respective wild-type controls were stimulated with different glycolipid extracts (30 μg/ml) or the corresponding heat-killed bacteria (30 bacteria per cell) as well as controls for 48 h, as indicated. G-CSF cytokine levels in cell culture supernatants were determined by using an ELISA. The detection limit was 4 pg/ml (dotted line). nd, not detectable. (D to F) NO production in cell culture supernatants was determined by using a Griess assay. BMM were cotreated with 10 ng/ml IFN-γ. BMM were stimulated with different concentrations of glycolipids (100, 30, or 10 μg/ml) or heat-killed bacteria (100, 30, or 10 bacteria per cell). Data shown were obtained with glycolipids from C. diphtheriae ISS4746; extracts from the other corynebacterial strains/species showed similar dose-response curves (not shown for clarity). (G and H) G-CSF levels and NO production were analyzed as described above. Dotted lines represent G-CSF or nitrite levels from unstimulated BMM. Note that data points for WT and TLR4−/− BMM overlap in panel G. Data are depicted as means and standard deviations of results from 3 independent experiments performed in duplicates (n = 6). (I) Wild-type and TLR2-deficient BMM were stimulated as described above for panels A to C, followed by NO measurement. Data are depicted as means and standard deviations of results from 3 independent experiments performed in duplicates (n = 6). In panels B, C, and E to I, * indicates a P value of <0.05.
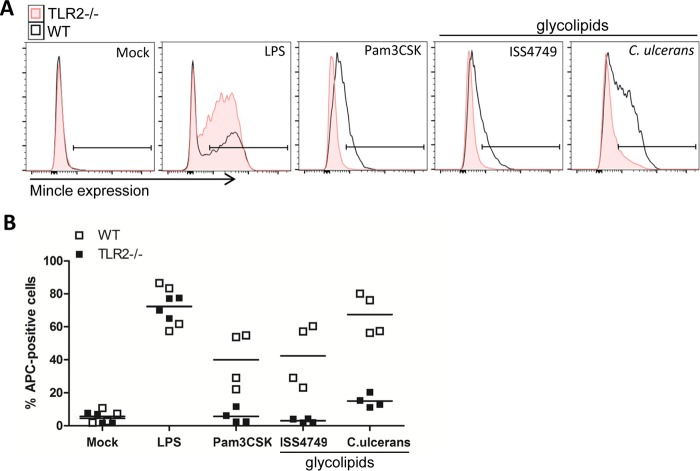
TLR2 is required for upregulation of Mincle expression on macrophages in response to corynebacteria.
The expression of Mincle can be strongly induced by LPS in a C/EBPβ-dependent manner (40), which increases the sensitivity of macrophages to the Mincle ligand mycobacterial cord factor (37). We therefore asked whether TLR2-dependent stimulation by corynebacterial ligands may similarly upregulate Mincle expression and enhance the response to Mincle ligands in a feed-forward loop. Flow cytometry of resting BMM from WT and Tlr2−/− mice showed very low levels of cell surface Mincle protein and, as expected, strong and TLR2-independent upregulation after stimulation with LPS (Fig. 6A and B). Glycolipid extracts of C. diphtheriae strain ISS4749 and of C. ulcerans led to a more moderate but clearly detectable induction of Mincle receptor levels on WT, but not Tlr2−/−, BMM (Fig. 6A and B). As expected, the widely used TLR2 ligand lipopeptide Pam3CSK4 upregulated Mincle in a TLR2-dependent manner (Fig. 6A and B). The inclusion of Mincle−/− BMM confirmed the specificity of staining with the 4A9 antibody in resting and stimulated BMM (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material), consistent with previously reported results (41). Thus, TLR2 drives high-level Mincle expression in response to corynebacteria to optimize responsiveness to cell wall glycolipids of corynebacteria.
FIG 6.
TLR2 deficiency leads to impaired Mincle upregulation on the cell surface. Shown are data from flow cytometric analysis of Mincle receptor expression on TLR2-deficient BMM and the respective wild-type controls. BMM were stimulated with 30 μg/ml cell wall extract of C. diphtheriae ISS4749 or C. ulcerans for 48 h. Unstimulated cells (mock) or BMM stimulated with 10 ng/ml LPS or 50 ng/ml Pam3CSK4 were used as controls. Panel A depicts representative histograms, indicating the gate used for the determination of Mincle-expressing macrophages shown in panel B. Data are depicted as single values from 2 independent experiments with biological duplicates (n = 4).
DISCUSSION
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study investigating the role of a C-type lectin receptor in innate immune recognition of corynebacteria and to bring forward a nonredundant role for Mincle and its adapter protein FcRγ in macrophage activation by cell wall glycolipids of several pathogenic and commensal corynebacterial species. Our results suggest that corynomycolate esters of trehalose constitute the Mincle ligand(s), as the glycolipids from one C. diphtheriae strain lacking corynomycolic acids failed to bind Mincle and to activate macrophages. Our findings reveal the collaborative induction of inflammatory and antimicrobial gene expression by TLR2 and Mincle in corynebacterium-challenged macrophages involving the induction of Mincle expression. These results indicate that both TLR2 and Mincle-FcRγ may be important during human and veterinary infections with C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans, and C. pseudotuberculosis.
The chemical nature of the Mincle ligand(s) from the corynebacterial cell wall preparations obtained by chloroform-methanol extraction in our study is unknown. However, the lack of stimulation by glycolipid extracts of C. diphtheriae strain DSM43989, which does not contain TMCM/TDCM (Fig. 4), suggested that mycolate-associated glycolipids confer Mincle binding and thereby activate macrophages. As reported in detail previously, the lack of cell wall mycolates in DSM43989 may be due to a deficiency in DIP0789, a putative enoyl coenzyme A (enoyl-CoA) hydratase (Ott et al., submitted). In a recent publication, van der Peet et al. reported the chemical synthesis of corynomycolic acids and tested trehalose and glucose mono- and diesters thereof for interactions with human and mouse Mincle using reporter cell lines (34). Notably, not only TDCM but also TMCM, and even glucose monocorynomycolate, triggered Mincle signaling and reporter gene activation. In contrast, when TDB was reduced toward a monosaccharide, namely, glucose behenate, it lost stimulatory activity (34). Similarly, testing of trehalose mono- and diesters of fatty acids of various lengths identified exclusively the diester forms as strong Mincle activators (36). Accordingly, a glucose monosaccharide is sufficient for binding to the carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) provided that the lipid portion is of sufficient complexity (i.e., a corynomycolic acid and not a simple fatty acid). Conversely, the disaccharide trehalose binds with higher affinity to the CRD such that diesters of simple fatty acids can also trigger Mincle signaling.
Our finding that the robust production of G-CSF and of NO in response to cell wall extracts requires both TLR2 and Mincle suggests a collaboration of these pattern recognition receptors, which may occur at different levels (Fig. 7). First, we observed that the TLR2-driven induction of Mincle surface expression is operative and consistent with data from previous reports on TLR4 action (37, 40), MyD88-dependent upregulation in response to Mycobacterium bovis BCG (42), and TLR2 activity (43). This C/EBPβ-dependent feed-forward loop enhancing the response to Mincle ligands (37) most likely accounts for the TLR2-driven G-CSF production in response to cell wall glycolipid challenge, although we acknowledge that formal proof of this mechanism would require the demonstration that the overexpression of Mincle, perhaps in association with other CLRs like Mcl, circumvents TLR2 dependence. Second, the concurrent triggering of Mincle by trehalose corynomycolates and of TLR2 by ligands such as LM/LAM (31) and phosphatidylinositol mannosides (PIMs) (44), respectively, might quantitatively, qualitatively, and synergistically enhance signaling toward transcriptional and translational immune responses. While Mincle and TLR2 showed synergism in the induction of G-CSF and NO, the dual triggering of both pathways may also have antagonistic effects on other responses and accordingly shape the output of the macrophage in terms of cytokines and antimicrobial mediators. Indeed, the Mincle ligand TDM inhibited interleukin-12p40 (IL-12p40) production induced by the TLR2 ligand Pam3CSK4 via IL-10 production in murine macrophages (45), and Wevers et al. observed that the ligation of Mincle downregulated IL-12p35 expression induced by TLR or Dectin-1 stimulation via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)–protein kinase B (PKB)-dependent MDM2-mediated degradation of IRF-1 in human dendritic cells (DC) (46). An interesting mechanism for the synergistic induction of the iNOS protein by TDM and Pam3CSK4 through increased translational efficiency dependent on hypusination of the elongation factor eukaryotic initiation factor 5 (eIF5) was recently described by Lee and colleagues (43). Thus, it will be interesting to investigate the differential regulation of a wider set of inflammatory and regulatory cytokines by Mincle and TLR2 pathways after macrophages encounter corynebacteria.
FIG 7.
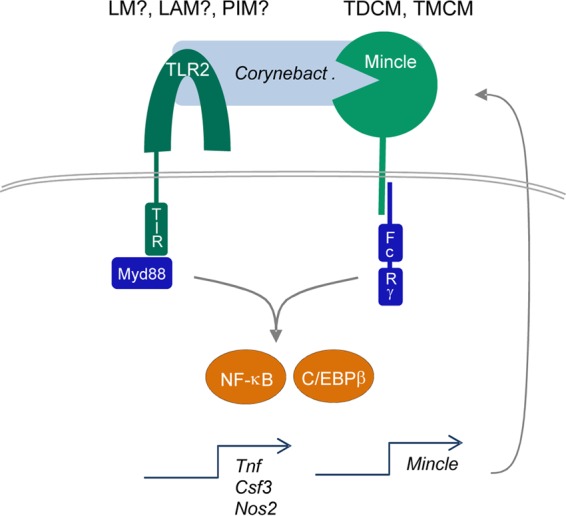
Synergistic induction of macrophage activation by the corynebacterial cell wall through TLR2 and Mincle signaling. The cell wall of corynebacteria contains TLR2 ligands, which activate macrophages through MyD88-dependent signaling. Lipomannan (LM) and Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) have been identified as TLR2 ligands from corynebacteria (31); PIMs from mycobacteria activate TLR2 (44) and are present in corynebacterial glycolipid extracts. Mincle binds to glycolipids containing mycolates (likely TDCM and TMCM), which activates FcRγ-Syk-dependent gene expression (Csf3 encodes G-CSF, and Nos2 encodes iNOS). Both pathways synergize at the level of NF-κB. In addition, TLR2- and C/EBPβ-dependent upregulation of Mincle mRNA and protein expression increases cell surface Mincle receptor expression and responsiveness to TDCM/TMCM in murine macrophages.
An important question arising is how the stimulation of the receptors Mincle and TLR2 on macrophages impacts the course of infections with corynebacterial species in vivo. C. pseudotuberculosis causes caseous lymphadenitis in sheep and goats, a chronic granulomatous infection with histopathological similarities to mycobacterial infections (47), and the amount of cell wall lipids in C. pseudotuberculosis strains has been correlated positively with the severity of abscess formation in a mouse model (29). Mice deficient in the Mincle-FcRγ and TLR2 pathways should be valuable to investigate the differential roles of glycolipid recognition in inflammation, the control of bacterial replication, and the differentiation of Th cell responses in vivo. As corynebacteria are abundant commensals on human skin and mucosal surfaces, Mincle- versus TLR2-dependent responses to their cell wall glycolipids by macrophages and DC may also contribute to protective and/or pathogenic immune responses. Therefore, it will be important to determine whether human myeloid cells respond similarly to corynebacterial cell wall components, as shown here for murine macrophages, in future experiments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reagents.
Synthetic TDB was purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, AL, USA), solubilized in isopropanol at a concentration of 2.5 mg/ml. LPS of Escherichia coli serotype O55:B5 (Sigma-Aldrich, Deisenhofen, Germany) was taken up in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at a stock concentration of 1 mg/ml. B-type CpG ODN 1826 was synthetized by TIB Molbiol (Berlin, Germany) and reconstituted to a stock concentration of 1 mM. Pam3CSK4 was obtained from EMC Microcollections GmbH (Tübingen, Germany). All TLR and CLR ligands were stored as stocks at −20°C.
Culture of corynebacteria.
Bacterial strains used in this study are shown in Table 1. All C. diphtheriae and C. ulcerans strains were grown in Bacto heart infusion (HI) broth (Becton Dickinson and Company, France) at 37°C. C. glutamicum was grown in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth (Oxoid, Hampshire, England) at 37°C.
TABLE 1.
Corynebacterium strains used
| Strain | Description | Reference and/or source |
|---|---|---|
| C. diphtheriae ISS4746 | tox negative, throat smear, C. diphtheriae subsp. gravis | 16 |
| C. diphtheriae ISS4749 | tox negative, throat smear, C. diphtheriae subsp. gravis | 16 |
| C. diphtheriae DSM43988 | Apathogenic isolate of throat smear, ATCC 11913 | DSMZ |
| C. diphtheriae DSM43989 | Pathogenic, unknown origin, ATCC 13812, tox+ | 38, DSMZ |
| C. ulcerans 809 | Patient isolate from fatal pulmonary infection | 53 |
| C. glutamicum ATCC 13032 | Wild type | 54 |
Preparation of cell wall glycolipids.
For glycolipid extraction, bacterial cultures were grown to an optical density of 0.4 to 0.6 and harvested. Cells were incubated in chloroform-methanol (1:2) overnight, followed by filtration through the appropriate filter paper. Cells were incubated in chloroform-methanol (1:1) for 5 h and filtered through the same filter paper, followed by further overnight incubation in chloroform-methanol (2:1). Filtrates were collected in round-bottom flasks. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation. Isolated glycolipids were dissolved in chloroform-methanol (2:1), sonicated, and stored at 4°C. To roughly correlate glycolipid extract amounts to the corresponding number of corynebacteria, we assumed that (i) bacterial growth stopped directly after transfer of the culture to ice and (ii) no glycolipid was lost during preparation. Calculating 5 × 108 bacteria per optical density at 600 nm (OD600) unit, we estimate that 1 μg of glycolipid extracts corresponds to 1.45 × 107 CFU. Thus, a concentration of 10 μg/ml glycolipid extract in a well with 2 × 105 BMM would roughly correspond to a bacterium-to-cell ratio of 145.
Extraction and analytical thin-layer chromatography of total lipids and fatty acid and mycolic acid methyl esters.
Total lipids were extracted from Corynebacterium spp. by using protocols described previously for C. glutamicum (48). The total lipids were further fractionated by chilled acetone precipitation to generate a predominantly phospholipid-rich, polar lipid pellet and a predominant apolar lipid-rich supernatant. Aliquots from all fractions were analyzed by TLC (silica gel 60 F254 plates) using chloroform-methanol-water (60:16:2) as the solvent system and MPA–α-naphthol as a stain to visualize lipids/glycolipids.
Methyl esters of fatty and mycolic acids were extracted by using protocols described previously for C. glutamicum (48). The bound mycolates were released from delipidated cells or free glycolipid extracts by using 2 ml of a 5% aqueous solution of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide and subsequent overnight incubation at 95°C. The cooled suspension was then mixed thoroughly with water (2 ml), CH2Cl2 (4 ml), and CH3I (500 μl) for 30 min. The lower organic phase was recovered after centrifugation and washed three times with 4 ml of water. The organic extract was then dried and resuspended in 4 ml diethyl ether. Particulate, insoluble matter was removed by centrifugation; the resultant clear supernatant was dried and resuspended in 200 μl CH2Cl2. TLC of aliquots of the extract was performed by using silica gel 60 F254 plates developed in petroleum ether-acetone (95:5, vol/vol).
Mincle-Fc binding assay.
Blocking and incubation steps were performed with Hanks' balanced salts solution (HBSS) plus 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in a working volume of 50 μl at room temperature. Washing steps were performed with HBSS only. Ninety-six-well cell culture plates were coated with glycolipids as previously described (22, 49) and blocked for 2 h. Murine Mincle-Fc and Clec9a-Fc fusion proteins or the Fc protein alone (35) was added and incubated at a final concentration of 200 ng/ml for 6 h, followed by at least 5 washing steps. Anti-human Fc horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody (Jackson) was added at a final concentration of 1.6 μg/ml and incubated for 1 h, followed by at least 8 washing steps. Detection was performed by using the 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) substrate reagent (BD Bioscience).
Isolation and culture of mouse macrophages.
Clec4e−/− mice were generated by the Consortium for Functional Glycomics and used with permission (50). Fcerg1−/− mice were described previously (51), and a breeding pair was kindly provided by Falk Nimmerjahn. C57BL/6, Clec4e−/−, and Fcerg1−/− mice were bred at the Präklinische Experimentelle Tierzentrum of the Medical Faculty of the Friedrich Alexander University Erlangen-Nürnberg. Tlr2−/−, Tlr4−/−, and TLR2−/−;Tlr4−/− mice were bred at the animal facility of the University Hospital Essen. Bone marrow cells from femurs and tibiae were differentiated to macrophages by culture in complete Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM) (Life Technologies) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Biochrome), antibiotics, and 50 μM β-mercaptoethanol (complete DMEM [cDMEM]) plus 10% L929 cell-conditioned medium as a source of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), as previously described (52). On day 7, adherent macrophages were harvested by Accutase (Sigma, Deisenhofen, Germany) treatment, washed, and counted.
Cell stimulation.
Cell wall extracts of corynebacteria (100 μg/ml, 30 μg/ml, or 10 μg/ml) as well as TDB (5 μg/ml; Polar Avanti) were used plate bound, as previously described (22, 49). For coating, cell wall extracts and TDB were dissolved in isopropanol. Isopropanol only was used as a negative control. LPS (100 ng/ml) and CpG (0.5 μM) were additionally used as positive controls. Whole bacteria were grown to an optical density (OD600) of 0.4 to 0.6, harvested, and washed in PBS. Bacteria were inactivated in a water bath for 15 min at 70°C and resuspended in cDMEM before use. For stimulation, a bacterium-to-cell ratio of 100, 30, or 10 was used.
Cytokine ELISA.
The cytokine concentration of murine G-CSF was analyzed by a sandwich ELISA (DuoSet ELISA; R&D Systems) using cell-free cell culture supernatants of cells stimulated as indicated.
Griess assay.
NO production of BMM was assessed via a Griess assay. BMM were cotreated with IFN-γ.
Flow cytometry of Mincle surface receptor levels.
A total of 2 × 105 bone marrow-derived macrophages of C57BL/6 and Tlr2−/− mice were stimulated with LPS (10 ng/ml), Pam3CSK4 (50 ng/ml), or different cell wall extracts of corynebacteria (30 μg/ml), as indicated. BMM were stimulated for 48 h in F-bottom 96-well cell culture plates. Receptor surface expression of Mincle was assessed by flow cytometry as described previously (41). Staining was performed by using anti-Mincle (clone 4A9; MBL) (24) as a primary antibody and anti-rat IgG1 conjugated to allophycocyanin (APC) as a secondary antibody (eBioscience, Frankfurt, Germany) at a final concentration of 1 μg/ml for anti-Mincle and anti-rat IgG-APC. Fc receptors were blocked by adding anti-mouse CD16/32 (clone 93; eBioscience) at a final concentration of 2.5 μg/ml before staining. Cells were stained with primary antibodies for 20 min at 4°C, washed, and then stained with secondary antibody for 20 min at 4°C. Flow cytometry data were acquired on a FACSCanto II instrument (BD), and analysis was carried out by using FlowJo (version 10).
Statistical analysis.
Statistical analysis was performed by using GraphPad Prism (version 5). A two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test was applied as indicated for nonpaired testing between two groups. P values of <0.05 were considered significant and are indicated by asterisks in the figures.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We gratefully acknowledge support by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft to the laboratory of R.L. (SFB 796 TP B6 and GRK1660 TP A2).
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00075-17.
REFERENCES
- 1.Wong TP, Groman N. 1984. Production of diphtheria toxin by selected isolates of Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun 43:1114–1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dorella FA, Pacheco LG, Oliveira SC, Miyoshi A, Azevedo V. 2006. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: microbiology, biochemical properties, pathogenesis and molecular studies of virulence. Vet Res 37:201–218. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2005056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hacker E, Antunes CA, Mattos-Guaraldi AL, Burkovski A, Tauch A. 2016. Corynebacterium ulcerans, an emerging human pathogen. Future Microbiol 11:1191–1208. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2016-0085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zakikhany K, Neal S, Efstratiou A. 2014. Emergence and molecular characterisation of non-toxigenic tox gene-bearing Corynebacterium diphtheriae biovar mitis in the United Kingdom, 2003-2012. Euro Surveill 19(22):pii=20819. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES2014.19.22.20819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zasada AA. 2013. Nontoxigenic highly pathogenic clone of Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Poland, 2004-2012. Emerg Infect Dis 19:1870–1872. doi: 10.3201/eid1911.130297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tauch A, Burkovski A. 2015. Molecular armory or niche factors: virulence determinants of Corynebacterium species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362:fnv185. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chung CS, Liao CH, Cheng SL, Lin TH, Hsueh PR. 2008. Percutaneous nephrostomy tube-associated bacteremia caused by Corynebacterium urealyticum. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 41:525–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kimura SI, Gomyo A, Hayakawa J, Akahoshi Y, Harada N, Ugai T, Komiya Y, Kameda K, Wada H, Ishihara Y, Kawamura K, Sakamoto K, Sato M, Terasako-Saito K, Kikuchi M, Nakasone H, Kanda J, Kako S, Tanihara A, Kanda Y. 2017. Clinical characteristics and predictive factors for mortality in coryneform bacteria bloodstream infection in hematological patients. J Infect Chemother 23:148–153. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2016.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lee PP, Ferguson DA Jr, Sarubbi FA. 2005. Corynebacterium striatum: an underappreciated community and nosocomial pathogen. J Infect 50:338–343. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2004.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Martins C, Faria L, Souza M, Camello T, Velasco E, Hirata R Jr, Thuler L, Mattos-Guaraldi A. 2009. Microbiological and host features associated with corynebacteriosis in cancer patients: a five-year study. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 104:905–913. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762009000600015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Novo-Veleiro I, Hernandez-Cabrera M, Canas-Hernandez F, Pisos-Alamo E, Frances-Urmeneta A, Delgado-Yague M, Alvela-Suarez L, Perez-Arellano JL. 2013. Paucisymptomatic infectious prostatitis as a cause of fever without an apparent origin. A series of 19 patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32:263–268. doi: 10.1007/s10096-012-1738-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schoen C, Unzicker C, Stuhler G, Elias J, Einsele H, Grigoleit GU, Abele-Horn M, Mielke S. 2009. Life-threatening infection caused by daptomycin-resistant Corynebacterium jeikeium in a neutropenic patient. J Clin Microbiol 47:2328–2331. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00457-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shao H, Luo R, Wang X, Pan X, Chen G. 2015. Management of a patient with small-area burns, severe sepsis and superficial vein thrombosis. J Wound Care 24:73–74, 77–78. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2015.24.2.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mochizuki Y, Saeki H, Iwaki M, Takagi H, Shibayama K, Amao H, Yamamoto A. 2016. A novel experimental platform for toxigenic and non-toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans infection in mice. Pathog Dis 74:ftv109. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dias AA, Silva FC Jr, Santos LS, Ribeiro-Carvalho MM, Sabbadini PS, Santos CS, Filardy AA, Myioshi A, Azevedo VA, Hirata R Jr, Villas-Boas MH, Mattos-Guaraldi AL. 2011. Strain-dependent arthritogenic potential of the zoonotic pathogen Corynebacterium ulcerans. Vet Microbiol 153:323–331. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Puliti M, von Hunolstein C, Marangi M, Bistoni F, Tissi L. 2006. Experimental model of infection with non-toxigenic strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and development of septic arthritis. J Med Microbiol 55:229–235. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Marrakchi H, Laneelle MA, Daffe M. 2014. Mycolic acids: structures, biosynthesis, and beyond. Chem Biol 21:67–85. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Geisel RE, Sakamoto K, Russell DG, Rhoades ER. 2005. In vivo activity of released cell wall lipids of Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin is due principally to trehalose mycolates. J Immunol 174:5007–5015. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.8.5007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hunter RL, Olsen MR, Jagannath C, Actor JK. 2006. Multiple roles of cord factor in the pathogenesis of primary, secondary, and cavitary tuberculosis, including a revised description of the pathology of secondary disease. Ann Clin Lab Sci 36:371–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shenderov K, Barber DL, Mayer-Barber KD, Gurcha SS, Jankovic D, Feng CG, Oland S, Hieny S, Caspar P, Yamasaki S, Lin X, Ting JP, Trinchieri G, Besra GS, Cerundolo V, Sher A. 2013. Cord factor and peptidoglycan recapitulate the Th17-promoting adjuvant activity of mycobacteria through mincle/CARD9 signaling and the inflammasome. J Immunol 190:5722–5730. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ishikawa E, Ishikawa T, Morita YS, Toyonaga K, Yamada H, Takeuchi O, Kinoshita T, Akira S, Yoshikai Y, Yamasaki S. 2009. Direct recognition of the mycobacterial glycolipid, trehalose dimycolate, by C-type lectin Mincle. J Exp Med 206:2879–2888. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schoenen H, Bodendorfer B, Hitchens K, Manzanero S, Werninghaus K, Nimmerjahn F, Agger EM, Stenger S, Andersen P, Ruland J, Brown GD, Wells C, Lang R. 2010. Cutting edge: Mincle is essential for recognition and adjuvanticity of the mycobacterial cord factor and its synthetic analog trehalose-dibehenate. J Immunol 184:2756–2760. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0904013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Werninghaus K, Babiak A, Gross O, Holscher C, Dietrich H, Agger EM, Mages J, Mocsai A, Schoenen H, Finger K, Nimmerjahn F, Brown GD, Kirschning C, Heit A, Andersen P, Wagner H, Ruland J, Lang R. 2009. Adjuvanticity of a synthetic cord factor analogue for subunit Mycobacterium tuberculosis vaccination requires FcRgamma-Syk-Card9-dependent innate immune activation. J Exp Med 206:89–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.20081445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kerscher B, Wilson GJ, Reid DM, Mori D, Taylor JA, Besra GS, Yamasaki S, Willment JA, Brown GD. 2016. Mycobacterial receptor, Clec4d (CLECSF8, MCL), is coregulated with Mincle and upregulated on mouse myeloid cells following microbial challenge. Eur J Immunol 46:381–389. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Miyake Y, Toyonaga K, Mori D, Kakuta S, Hoshino Y, Oyamada A, Yamada H, Ono K, Suyama M, Iwakura Y, Yoshikai Y, Yamasaki S. 2013. C-type lectin MCL is an FcRgamma-coupled receptor that mediates the adjuvanticity of mycobacterial cord factor. Immunity 38:1050–1062. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wilson GJ, Marakalala MJ, Hoving JC, van Laarhoven A, Drummond RA, Kerscher B, Keeton R, van de Vosse E, Ottenhoff TH, Plantinga TS, Alisjahbana B, Govender D, Besra GS, Netea MG, Reid DM, Willment JA, Jacobs M, Yamasaki S, van Crevel R, Brown GD. 2015. The C-type lectin receptor CLECSF8/CLEC4D is a key component of anti-mycobacterial immunity. Cell Host Microbe 17:252–259. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.01.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ostrop J, Jozefowski K, Zimmermann S, Hofmann K, Strasser E, Lepenies B, Lang R. 2015. Contribution of MINCLE-SYK signaling to activation of primary human APCs by mycobacterial cord factor and the novel adjuvant TDB. J Immunol 195:2417–2428. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hard GC. 1975. Comparative toxic effect of the surface lipid of Corynebacterium ovis on peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun 12:1439–1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Muckle CA, Gyles CL. 1983. Relation of lipid content and exotoxin production to virulence of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in mice. Am J Vet Res 44:1149–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Takada H, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S. 1999. Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity 11:443–451. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mishra AK, Alves JE, Krumbach K, Nigou J, Castro AG, Geurtsen J, Eggeling L, Saraiva M, Besra GS. 2012. Differential arabinan capping of lipoarabinomannan modulates innate immune responses and impacts T helper cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 287:44173–44183. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.402396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Blanc L, Castanier R, Mishra AK, Ray A, Besra GS, Sutcliffe I, Vercellone A, Nigou J. 2013. Gram-positive bacterial lipoglycans based on a glycosylated diacylglycerol lipid anchor are microbe-associated molecular patterns recognized by TLR2. PLoS One 8:e81593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chami M, Andreau K, Lemassu A, Petit JF, Houssin C, Puech V, Bayan N, Chaby R, Daffe M. 2002. Priming and activation of mouse macrophages by trehalose 6,6′-dicorynomycolate vesicles from Corynebacterium glutamicum. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 32:141–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2002.tb00546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.van der Peet PL, Gunawan C, Torigoe S, Yamasaki S, Williams SJ. 2015. Corynomycolic acid-containing glycolipids signal through the pattern recognition receptor Mincle. Chem Commun (Camb) 51:5100–5103. doi: 10.1039/C5CC00085H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Maglinao M, Eriksson M, Schlegel MK, Zimmermann S, Johannssen T, Gotze S, Seeberger PH, Lepenies B. 2014. A platform to screen for C-type lectin receptor-binding carbohydrates and their potential for cell-specific targeting and immune modulation. J Control Release 175:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Huber A, Kallerup RS, Korsholm KS, Franzyk H, Lepenies B, Christensen D, Foged C, Lang R. 2016. Trehalose diester glycolipids are superior to the monoesters in binding to Mincle, activation of macrophages in vitro and adjuvant activity in vivo. Innate Immun 22:405–418. doi: 10.1177/1753425916651132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schoenen H, Huber A, Sonda N, Zimmermann S, Jantsch J, Lepenies B, Bronte V, Lang R. 2014. Differential control of Mincle-dependent cord factor recognition and macrophage responses by the transcription factors C/EBPbeta and HIF1alpha. J Immunol 193:3664–3675. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nakao H, Pruckler JM, Mazurova IK, Narvskaia OV, Glushkevich T, Marijevski VF, Kravetz AN, Fields BS, Wachsmuth IK, Popovic T. 1996. Heterogeneity of diphtheria toxin gene, tox, and its regulatory element, dtxR, in Corynebacterium diphtheriae strains causing epidemic diphtheria in Russia and Ukraine. J Clin Microbiol 34:1711–1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Spiller S, Dreher S, Meng G, Grabiec A, Thomas W, Hartung T, Pfeffer K, Hochrein H, Brade H, Bessler W, Wagner H, Kirschning CJ. 2007. Cellular recognition of trimyristoylated peptide or enterobacterial lipopolysaccharide via both TLR2 and TLR4. J Biol Chem 282:13190–13198. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610340200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Matsumoto M, Tanaka T, Kaisho T, Sanjo H, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Akira S. 1999. A novel LPS-inducible C-type lectin is a transcriptional target of NF-IL6 in macrophages. J Immunol 163:5039–5048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hupfer T, Schick J, Jozefowski K, Voehringer D, Ostrop J, Lang R. 2016. Stat6-dependent inhibition of Mincle expression in mouse and human antigen-presenting cells by the Th2 cytokine IL-4. Front Immunol 7:423. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kerscher B, Dambuza IM, Christofi M, Reid DM, Yamasaki S, Willment JA, Brown GD. 2016. Signalling through MyD88 drives surface expression of the mycobacterial receptors MCL (Clecsf8, Clec4d) and Mincle (Clec4e) following microbial stimulation. Microbes Infect 18:505–509. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2016.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lee WB, Kang JS, Choi WY, Zhang Q, Kim CH, Choi UY, Kim-Ha J, Kim YJ. 2016. Mincle-mediated translational regulation is required for strong nitric oxide production and inflammation resolution. Nat Commun 7:11322. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jones BW, Means TK, Heldwein KA, Keen MA, Hill PJ, Belisle JT, Fenton MJ. 2001. Different Toll-like receptor agonists induce distinct macrophage responses. J Leukoc Biol 69:1036–1044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Patin EC, Willcocks C, Orr S, Ward TH, Lang R, Schaible UE. 2 March 2016. Mincle-mediated anti-inflammatory IL-10 response counter-regulates IL-12 in vitro. Innate Immun doi: 10.1177/1753425916636671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wevers BA, Kaptein TM, Zijlstra-Willems EM, Theelen B, Boekhout T, Geijtenbeek TB, Gringhuis SI. 2014. Fungal engagement of the C-type lectin mincle suppresses dectin-1-induced antifungal immunity. Cell Host Microbe 15:494–505. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Baird GJ, Fontaine MC. 2007. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis and its role in ovine caseous lymphadenitis. J Comp Pathol 137:179–210. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2007.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gande R, Gibson KJ, Brown AK, Krumbach K, Dover LG, Sahm H, Shioyama S, Oikawa T, Besra GS, Eggeling L. 2004. Acyl-CoA carboxylases (accD2 and accD3), together with a unique polyketide synthase (Cg-pks), are key to mycolic acid biosynthesis in Corynebacterianeae such as Corynebacterium glutamicum and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem 279:44847–44857. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408648200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ozeki Y, Tsutsui H, Kawada N, Suzuki H, Kataoka M, Kodama T, Yano I, Kaneda K, Kobayashi K. 2006. Macrophage scavenger receptor down-regulates mycobacterial cord factor-induced proinflammatory cytokine production by alveolar and hepatic macrophages. Microb Pathog 40:171–176. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2005.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wells CA, Salvage-Jones JA, Li X, Hitchens K, Butcher S, Murray RZ, Beckhouse AG, Lo YL, Manzanero S, Cobbold C, Schroder K, Ma B, Orr S, Stewart L, Lebus D, Sobieszczuk P, Hume DA, Stow J, Blanchard H, Ashman RB. 2008. The macrophage-inducible C-type lectin, mincle, is an essential component of the innate immune response to Candida albicans. J Immunol 180:7404–7413. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.11.7404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Takai T, Li M, Sylvestre D, Clynes R, Ravetch JV. 1994. FcR gamma chain deletion results in pleiotrophic effector cell defects. Cell 76:519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lang R, Rutschman RL, Greaves DR, Murray PJ. 2002. Autocrine deactivation of macrophages in transgenic mice constitutively overexpressing IL-10 under control of the human CD68 promoter. J Immunol 168:3402–3411. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.7.3402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mattos-Guaraldi AL, Sampaio JL, Santos CS, Pimenta FP, Pereira GA, Pacheco LG, Miyoshi A, Azevedo V, Moreira LO, Gutierrez FL, Costa JL, Costa-Filho R, Damasco PV, Camello TC, Hirata R Jr. 2008. First detection of Corynebacterium ulcerans producing a diphtheria-like toxin in a case of human with pulmonary infection in the Rio de Janeiro metropolitan area, Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 103:396–400. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762008000400014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Abe S, Takayama K, Kinoshita S. 1967. Taxonomical studies on glutamic acid producing bacteria. J Gen Microbiol 13:279–301. doi: 10.2323/jgam.13.279. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.