Abstract
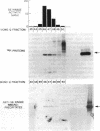
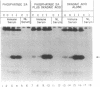
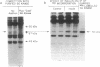
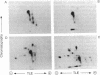
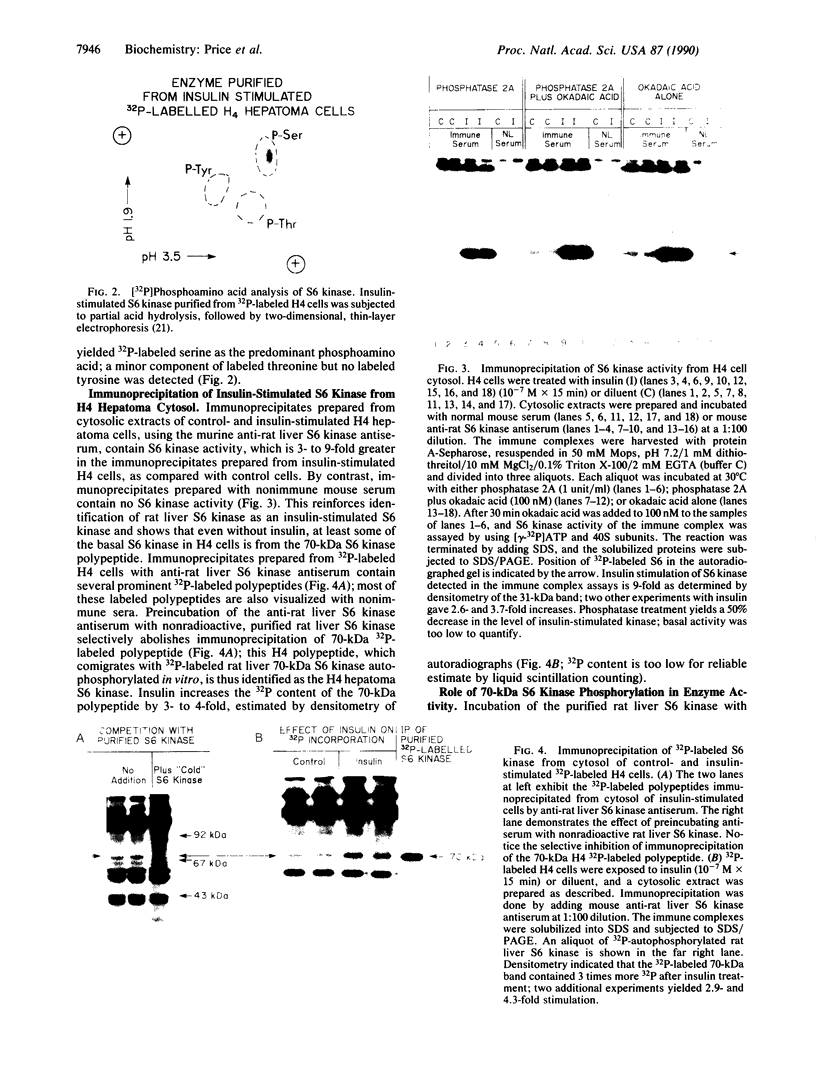
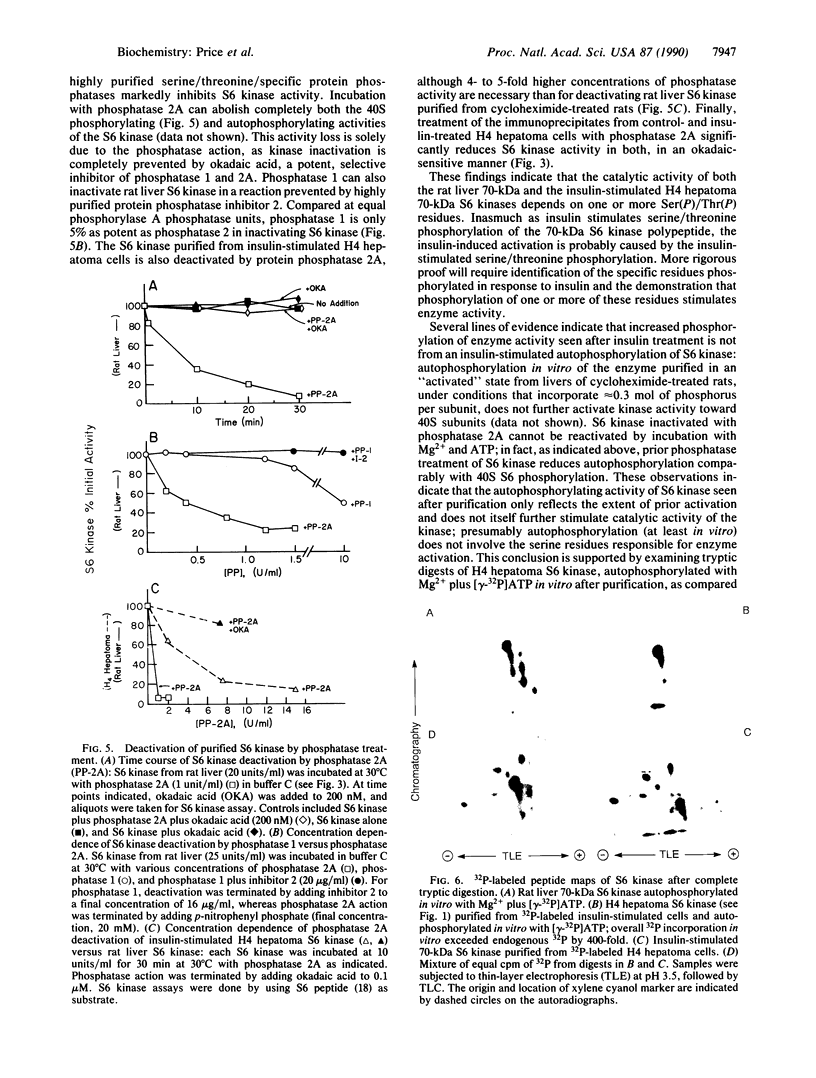
The dominant insulin-stimulated ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity was purified to near homogeneity from insulin-treated 32P-labeled rat H4 hepatoma cells and found to copurify with a 70-kDa 32P-labeled polypeptide. The dominant S6 kinase purified from livers of cycloheximide-treated rats is also a 70-kDa polypeptide. Antiserum raised against rat liver S6 kinase specifically immunoprecipitates the purified 32P-labeled H4 hepatoma insulin-stimulated S6 kinase. This antiserum also specifically precipitates insulin-stimulated S6 kinase activity directly from cytosolic extracts of H4 cells. Immune complexes prepared from the cytosol of 32P-labeled H4 cells contain several 32P-labeled polypeptides; only a 70-kDA 32P-labeled peptide, however, is specifically displaced by preadsorption of the antiserum with nonradioactive rat liver S6 kinase. Insulin treatment increases the 32P content of the immunoprecipitated 70-kDa S6 kinase polypeptide 3- to 4-fold over basal levels; 32P-labeled serine, some 32P-labeled threonine, but no 32P-labeled tyrosine are detected after partial acid hydrolysis. Tryptic peptide maps indicate that the insulin-stimulated S6 kinase purified from 32P-labeled H4 cells is phosphorylated at multiple sites distinct from those which participate in autophosphorylation in vitro. Autophosphorylation of rat liver S6 kinase in vitro does not modify S6 kinase activity. The S6 kinases purified from liver of cycloheximide-treated rat and H4 hepatoma insulin-stimulated enzyme are each completely deactivated by incubation with protein phosphatase type 2A in both autophosphorylating and 40S S6 phosphorylating activities. The phosphatase 2A-deactivated 70-kDa S6 kinase is neither reactivated nor phosphorylated by partially purified insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase, in experiments where Xenopus S6 kinase II undergoes phosphorylation and partial reactivation. Thus insulin activates the 70-kDa S6 kinase by promoting phosphorylation of specific serine/threonine residues on the enzyme polypeptide, probably through activating an as-yet-unidentified serine/threonine protein kinase distinct from microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcorta D. A., Crews C. M., Sweet L. J., Bankston L., Jones S. W., Erikson R. L. Sequence and expression of chicken and mouse rsk: homologs of Xenopus laevis ribosomal S6 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Nemenoff R. A., Blackshear P. J., Pierce M. W., Osathanondh R. Insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in detergent extracts of human placental membranes. Comparison to epidermal growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15162–15166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Siegmann M., Thomas G. S6 kinase in quiescent Swiss mouse 3T3 cells is activated by phosphorylation in response to serum treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7154–7158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Kuo C. J., Erikson R. L. Identification of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase regulated by transformation and growth-promoting stimuli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14373–14376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Klarlund J. K., Yagaloff K. A., Bradford A. P., Lewis R. E. Insulin receptor signaling. Activation of multiple serine kinases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11017–11020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degerman E., Smith C. J., Tornqvist H., Vasta V., Belfrage P., Manganiello V. C. Evidence that insulin and isoprenaline activate the cGMP-inhibited low-Km cAMP phosphodiesterase in rat fat cells by phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):533–537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. In vivo phosphorylation and activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinases during Xenopus oocyte maturation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13711–13717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenö P., Ballou L. M., Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Identification and characterization of a mitogen-activated S6 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):406–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson E., Blenis J., Maller J. L., Erikson R. L. A Xenopus ribosomal protein S6 kinase has two apparent kinase domains that are each similar to distinct protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Gunsalus J. R., Avruch J. An insulin-stimulated (ribosomal S6) protein kinase from soluble extracts of H4 hepatoma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 15;245(1):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Price D. J., Mendelsohn M. J., Carter E. A., Avruch J. An S6 kinase activated during liver regeneration is related to the insulin-stimulated S6 kinase in H4 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19455–19460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. An activated S6 kinase in extracts from serum- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5995–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. J., Nemenoff R. A., Avruch J. Purification of a hepatic S6 kinase from cycloheximide-treated Rats. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13825–13833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Wejksnora P. J., Warner J. R., Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2725–2729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Activation of S6 kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Gordon J. Multiple phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of quiescent 3T3 cells into early G1, and cellular compartmentalization of the phosphate donor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Gunsalus J. R., Nemenoff R. A., Frackelton A. R., Pierce M. W., Avruch J. Identification of the insulin receptor tyrosine residues undergoing insulin-stimulated phosphorylation in intact rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):350–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]