Abstract
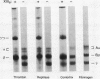
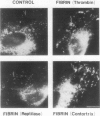
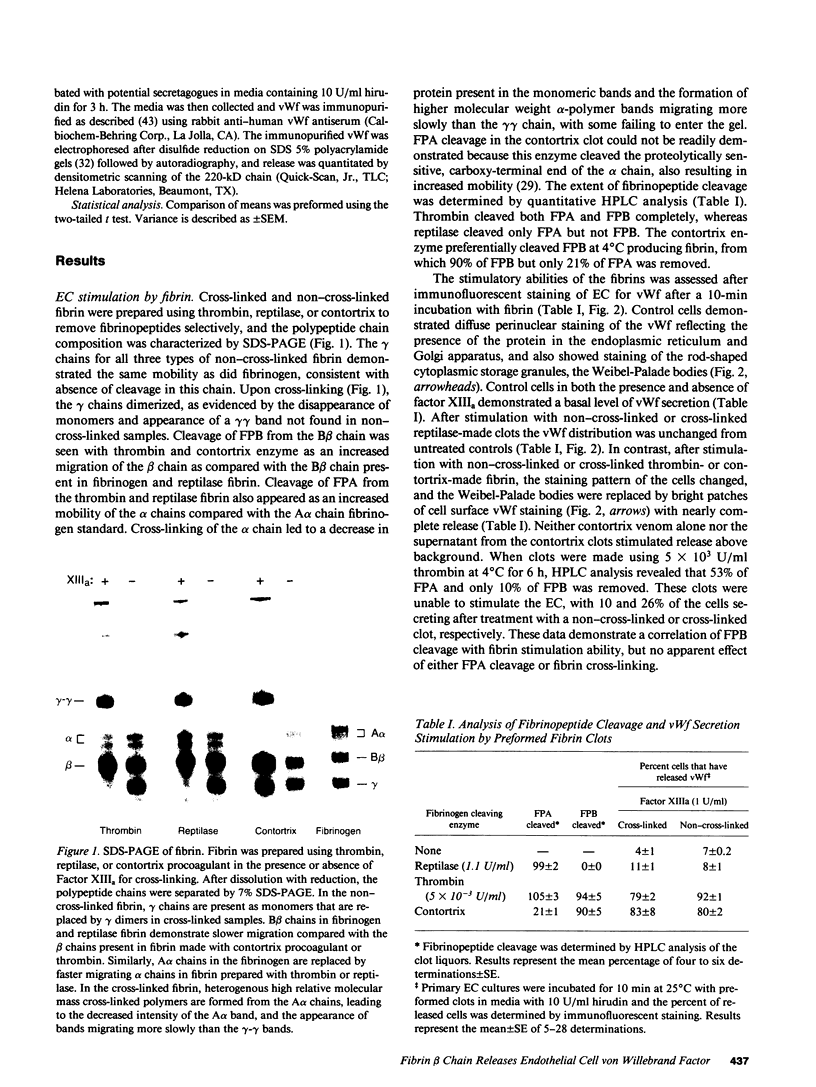
The exposure of endothelial cells (EC) to fibrin has been shown to stimulate the rapid release of von Willebrand factor (vWf) from storage sites in Weibel-Palade bodies. We have now investigated the fibrin structural features required for stimulation of release. The role of fibrinopeptide cleavage was examined by preparing fibrin with thrombin to remove both fibrinopeptide A (FPA) and fibrinopeptide B (FPB) and with reptilase or Agkistrodon contortrix procoagulant to selectively remove FPA or FPB, respectively. vWf release was found to require FPB cleavage, whereas removal of FPA and Factor XIIIa cross-linking of fibrin were without effect. The dependence of release on FPB cleavage suggested that a site involving the NH2 terminus of the beta chain could mediate vWf secretion. To test this hypothesis, B beta chain derivatives were prepared and examined for their capacity to induce release. Purified B beta chain had no effect on release at a concentration of 20 nM but stimulated release from 26 +/- 6% of cells at 200 nM, the maximum solubility. However, after thrombin cleavage of FPB, release occurred from 36 +/- 9% of cells at 20 nM and from 60 +/- 7% at 200 nM, both significantly greater than before cleavage. FPB and B beta 1-42 showed no activity, whereas beta 15-42, representing the NH2 terminus of the thrombin cleaved beta chain, stimulated significant release at concentrations of 0.1 and 1 mM. We conclude that FPB cleavage from fibrin is required for stimulation of vWf release from EC and that this is mediated by a site that includes the NH2 terminus of the beta chain.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson R. G., Saldeen K., Saldeen T. A fibrin(ogen) derived pentapeptide induces vasodilation, prostacyclin release and an increase in cyclic AMP. Thromb Res. 1983 May 1;30(3):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belew M., Gerdin B., Porath J., Saldeen T. Isolation of vasoactive peptides from human fibrin and fibrinogen degraded by plasmin. Thromb Res. 1978 Dec;13(6):983–994. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Hessel B., Iwanaga S. Structure of N-terminal fragments of fibrinogen and specificity of thrombin. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1445–1448. doi: 10.1038/2151445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Hessel B., Hogg D., Therkildsen L. A two-step fibrinogen--fibrin transition in blood coagulation. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):501–505. doi: 10.1038/275501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. S., Chou S. H., Thiagarajan P. Fibrin(ogen) peptide B beta 15-42 inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):6121–6126. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Doolittle R. F. - cross-linking sites in human and bovine fibrin. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4487–4491. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:195–229. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Harvey V. S., Estrella P., Brown L. F., McDonagh J., Dvorak A. M. Fibrin containing gels induce angiogenesis. Implications for tumor stroma generation and wound healing. Lab Invest. 1987 Dec;57(6):673–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewenstein B. M., Warhol M. J., Handin R. I., Pober J. S. Composition of the von Willebrand factor storage organelle (Weibel-Palade body) isolated from cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1423–1433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Rupp C., Beck E. A. Inhibition of fibrin polymerization by fragment d is affected by calcium, Gly-Pro-Arg and Gly-His-Arg. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 12;742(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90354-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdin B., Saldeen T., Roszkowski W., Szmigielski S., Stachurska J., Kopeć M. Immunosuppressive effect of vasoactive peptides derived from human fibrinogen. Thromb Res. 1980 May 1;18(3-4):461–468. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90341-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Growth and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna L. S., Scheraga H. A., Francis C. W., Marder V. J. Comparison of structures of various human fibrinogens and a derivative thereof by a study of the kinetics of release of fibrinopeptides. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4681–4687. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzig R. H., Ratnoff O. D., Shainoff J. R. Studies on a procoagulant fraction of southern copperhead snake venom: the preferential release of fibrinopeptide B. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Sep;76(3):451–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovig T., Stormorken H. Ultrastructural studies on the platelet plug formation in bleeding time wounds from normal individuals and patients with von Willebrand's disease. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1974;Suppl 248:105–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Shainoff J. R. Factor VIII-related protein circulates in normal human plasma as high molecular weight multimers. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):1056–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadish J. L., Butterfield C. E., Folkman J. The effect of fibrin on cultured vascular endothelial cells. Tissue Cell. 1979;11(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(79)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudryk B., Rohoza A., Ahadi M., Chin J., Wiebe M. E. Specificity of a monoclonal antibody for the NH2-terminal region of fibrin. Mol Immunol. 1984 Jan;21(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. E., Marder V. J., Francis C. W., Barlow G. H. Structural studies of the functional heterogeneity of von Willebrand protein polymers. Blood. 1981 Feb;57(2):313–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A., Mattock P., Hill R. L. Subunit structure of human fibrinogen, soluble fibrin, and cross-linked insoluble fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):738–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Automated synthesis of peptides. Science. 1965 Oct 8;150(3693):178–185. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3693.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R., Levine R., Jaffe E. A. Synthesis of factor VIII antigen by cultured guinea pig megakaryocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):914–921. doi: 10.1172/JCI108846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olander J. V., Bremer M. E., Marasa J. C., Feder J. Fibrin-enhanced endothelial cell organization. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Oct;125(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Freaney D., Edgington T. S. Inhibition of lymphocyte protein synthesis by fibrinogen-derived peptides. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1595–1598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes J. A., Francis C. W., Wagner D. D. Fibrin induces release of von Willebrand factor from endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):117–123. doi: 10.1172/JCI112771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. L., Pepper D. S., Kay A. B. Chemotaxis for human monocytes by fibrinogen-derived peptides. Br J Haematol. 1976 Apr;32(4):507–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland F. N., Donovan M. J., Picciano P. T., Wilner G. D., Kreutzer D. L. Fibrin-mediated vascular injury. Identification of fibrin peptides that mediate endothelial cell retraction. Am J Pathol. 1984 Dec;117(3):418–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Variant von Willebrand's disease: characterization of two subtypes by analysis of multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in plasma and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1318–1325. doi: 10.1172/JCI109795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Bolhuis P. A., Sixma J. J. Human blood platelet adhesion to artery subendothelium is mediated by factor VIII-Von Willebrand factor bound to the subendothelium. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):636–638. doi: 10.1038/279636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saldeen K., Christie N., Nelson W. R., Movat H. Z. Effect of a fibrin(ogen)-derived vasoactive peptide on polymorphonuclear leukocyte emigration. Thromb Res. 1985 Jan 1;37(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of fibrin-stabilizing factor on the subunit structure of human fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1506–1513. doi: 10.1172/JCI106636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Skogen W. F., Griffin G. L., Wilner G. D. Effects of fibrinogen derivatives upon the inflammatory response. Studies with human fibrinopeptide B. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):1014–1019. doi: 10.1172/JCI112353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Dardik B. N. Fibrinopeptide B and aggregation of fibrinogen. Science. 1979 Apr 13;204(4389):200–202. doi: 10.1126/science.155308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogen W. F., Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Wilner G. D. Fibrinogen-derived peptide B beta 1-42 is a multidomained neutrophil chemoattractant. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1475–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogen W. F., Wilner G. D. A simple one-step HPLC procedure for the purification of the NH2-terminal plasmin-derived B beta 1-42 peptide of human fibrinogen. Thromb Res. 1986 Jan 15;41(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn L. A., Chavin S. I., Marder V. J., Wagner D. D. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human megakaryocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1102–1106. doi: 10.1172/JCI112064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn L. A., Marder V. J., Wagner D. D. Inducible secretion of large, biologically potent von Willebrand factor multimers. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90735-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stathakis N. E., Mosesson M. W., Galanakis D. K., Ménaché D. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. Preparation and characterization of gamma and gamma' chains. Thromb Res. 1978 Sep;13(3):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. D., Campbell R., Evans T. Fibrin degradation and angiogenesis: quantitative analysis of the angiogenic response in the chick chorioallantoic membrane. J Pathol. 1985 Jan;145(1):27–37. doi: 10.1002/path.1711450103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp T. B., Weiss H. J., Baumgartner H. R. Decreased adhesion of platelets to subendothelium in von Willebrand's disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Feb;83(2):296–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turitto V. T., Weiss H. J., Baumgartner H. R. Platelet interaction with rabbit subendothelium in von Willebrand's disease: altered thrombus formation distinct from defective platelet adhesion. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1730–1741. doi: 10.1172/JCI111591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich M. M., Furie B., Jacobs M. R., Vermeer C., Furie B. C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. A synthetic peptide based upon the gamma-carboxylation recognition site sequence of the prothrombin propeptide is an active substrate for the carboxylase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9697–9702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Marder V. J. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human endothelial cells: processing steps and their intracellular localization. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Olmsted J. B., Marder V. J. Immunolocalization of von Willebrand protein in Weibel-Palade bodies of human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):355–360. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Tanaka K. Influence of fibrin, fibrinogen and fibrinogen degradation products on cultured endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 1983 Jul;48(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(83)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimar B., Delvos U. The mechanism of fibrin-induced disorganization of cultured human endothelial cell monolayers. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):139–145. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. von Willebrand disease. Hum Pathol. 1987 Feb;18(2):140–152. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]