Abstract
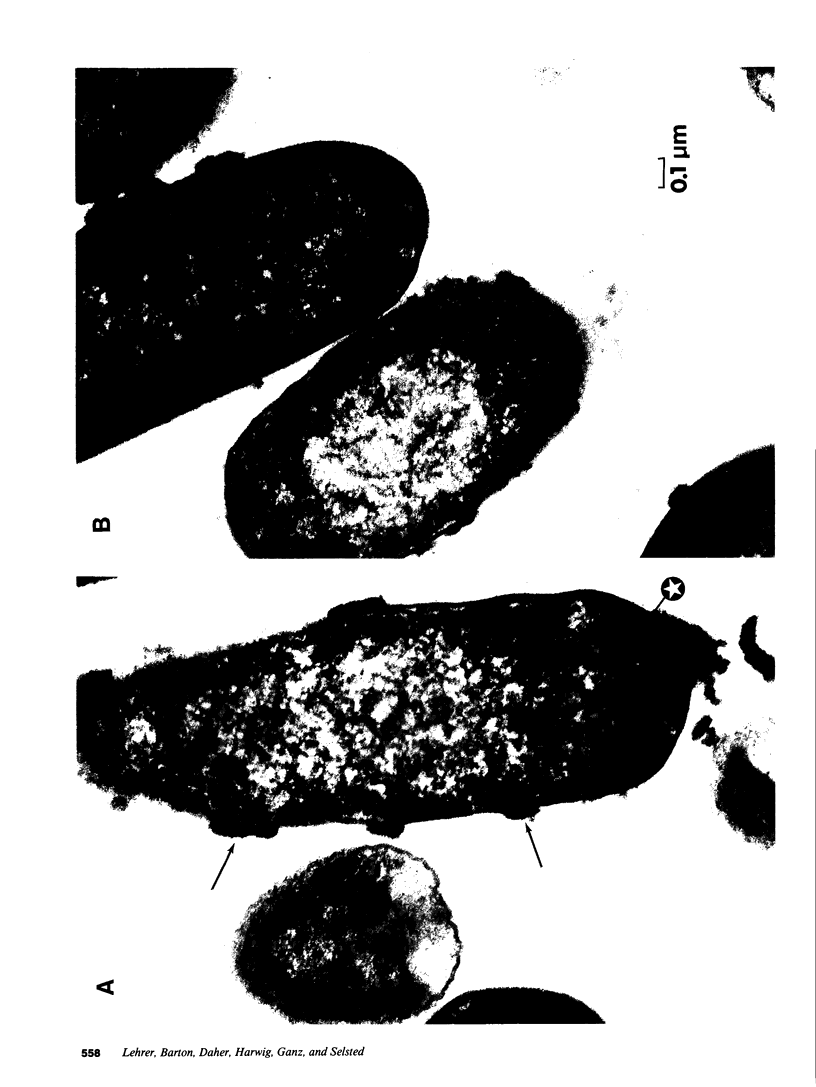
Defensins are small, cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides that are abundant in human, rabbit, and guinea pig neutrophils (PMN). Three defensins (human neutrophil peptide defensin [HNP]-1, HNP-2, and HNP-3) constitute between 30 and 50% of the total protein in azurophil granules of human PMN. We examined the mechanism of HNP-mediated bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli ML-35 (i-, y-, z+) and its pBR322-transformed derivative, E. coli ML-35p. Under conditions that supported bactericidal activity, HNP-1 sequentially permeabilized the outer membrane (OM) and inner membrane (IM) of E. coli. Coincident with these events, bacterial synthesis of DNA, RNA, and protein ceased and the colony count fell. Although these events were closely coupled under standard assay conditions, OM permeabilization was partially dissociated from IM permeabilization when experiments were performed with E. coli that had been plasmolyzed by mannitol. Under such conditions, the rate and extent of bacterial death more closely paralled loss of IM integrity than OM permeabilization. Electron microscopy of E. coli that had been killed by defensins revealed the presence of striking electron-dense deposits in the periplasmic space and affixed to the OM. Overall, these studies show that HNP-mediated bactericidal activity against E. coli ML-35 is associated with sequential permeabilization of the OM and IM, and that inner membrane permeabilization appears to be the lethal event.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Kuller G., Muhly M., Fromm S., Seibert G., Parrisius J. Formation of transmural complement pores in serum-sensitive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):206–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.206-210.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey S. G., Shafer W. M., Spitznagel J. K. Neisseria gonorrhoeae survive intraleukocytic oxygen-independent antimicrobial capacities of anaerobic and aerobic granulocytes in the presence of pyocin lethal for extracellular gonococci. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.384-389.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daher K. A., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Direct inactivation of viruses by human granulocyte defensins. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1068-1074.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R. E., Lehrer R. I. Fungicidal properties of a chymotrypsin-like cationic protein from human neutrophils: adsorption to Candida parapsilosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):382–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.382-388.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg D., Friedberg I., Shilo M. Interaction of Gram-Negative Bacteria with the Lysosomal Fraction of Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes II. Changes in the Cell Envelope of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):311–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.311-318.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg D., Shilo M. Interaction of Gram-Negative Bacteria with the Lysosomal Fraction of Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes I. Role of Cell Wall Composition of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):305–310. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.305-310.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Metcalf J. A., Gallin J. I., Boxer L. A., Lehrer R. I. Microbicidal/cytotoxic proteins of neutrophils are deficient in two disorders: Chediak-Higashi syndrome and "specific" granule deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):552–556. doi: 10.1172/JCI113631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Antimicrobial activity of phagocyte granule proteins. Semin Respir Infect. 1986 Jun;1(2):107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamers M. N., Bot A. A., Weening R. S., Sips H. J., Roos D. Kinetics and mechanism of the bactericidal action of human neutrophils against Escherichia coli. Blood. 1984 Sep;64(3):635–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovde C. J., Gray B. H. Physiological effects of a bactericidal protein from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):90–95. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.90-95.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Jetten M. E. Energy requirement for the initiation of colicin action in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 14;387(1):12–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamaya T. Lytic action of lysozyme on Candida albicans. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1970 Dec 29;42(3):197–207. doi: 10.1007/BF02051947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordel M., Benz R., Sahl H. G. Mode of action of the staphylococcinlike peptide Pep 5: voltage-dependent depolarization of bacterial and artificial membranes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):84–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.84-88.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Barton A., Ganz T. Concurrent assessment of inner and outer membrane permeabilization and bacteriolysis in E. coli by multiple-wavelength spectrophotometry. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Apr 6;108(1-2):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90414-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Daher K., Ganz T., Selsted M. E. Direct inactivation of viruses by MCP-1 and MCP-2, natural peptide antibiotics from rabbit leukocytes. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):467–472. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.467-472.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Selsted M. E. Oxygen-independent bactericidal systems. Mechanisms and disorders. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Mar;2(1):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Szklarek D., Selsted M. E. Modulation of the in vitro candidacidal activity of human neutrophil defensins by target cell metabolism and divalent cations. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1829–1835. doi: 10.1172/JCI113527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein A. K., Ganz T., Nguyen T. M., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Mechanism of target cytolysis by peptide defensins. Target cell metabolic activities, possibly involving endocytosis, are crucial for expression of cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2686–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J., Carroll S. F. Sequential metabolic expressions of the lethal process in human serum-treated Escherichia coli: role of lysozyme. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):735–745. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.735-745.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Antibacterial activity of cationic proteins from human granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1118–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Mechanisms for the microbicidal activity of cationic proteins of human granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Dec;14(6):1269–1275. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.6.1269-1275.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. G., Ganz T., Kinkade J. M., Jr, Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I., Parmley R. T. Defensin-rich dense granules of human neutrophils. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):757–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock J. P., Rest R. F. Rapid damage to membranes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae caused by human neutrophil granule extracts. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):509–519. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-2-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer J. G., Martin N. L., Hancock R. E. Interaction of macrophage cationic proteins with the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):693–698. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.693-698.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Brown D. M., DeLange R. J., Harwig S. S., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of six antimicrobial peptides of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4579–4584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S., Ganz T., Schilling J. W., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of three human neutrophil defensins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1436–1439. doi: 10.1172/JCI112121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S. Purification, primary structure, and antimicrobial activities of a guinea pig neutrophil defensin. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2281–2286. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2281-2286.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Ganz T., Lehrer R. I. Activity of rabbit leukocyte peptides against Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):202–206. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.202-206.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antibacterial activity of antimicrobial peptides of rabbit granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):150–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.150-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic antimicrobial proteins isolated from human neutrophil granulocytes in the presence of diisopropyl fluorophosphate. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):29–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.29-35.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sips H. J., Hamers M. N. Mechanism of the bactericidal action of myeloperoxidase: increased permeability of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):11–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.11-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W., Kroll H. P. Killing of an encapsulated strain of Escherichia coli by human serum. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):122–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.122-131.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljanen P., Koski P., Vaara M. Effect of small cationic leukocyte peptides (defensins) on the permeability barrier of the outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2324–2329. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2324-2329.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton E., Gladstone G. P. Factors affecting the susceptibility of staphylococci to killing by the cationic proteins from rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes: the effects of alteration of cellular energetics and of various iron compounds. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Oct;57(5):560–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton E. The preparation, properties and action on Staphylococcus aureus of purified fractions from the cationic proteins of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Br J Exp Pathol. 1978 Aug;59(4):416–431. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A., Geerts W., Vogels G. D. Energy requirements for the action of staphylococcin 1580 in Staphyloccus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 20;539(3):372–385. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Elsbach P. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to purified bactericidal leukocyte proteins: relation to binding and bacterial lipopolysaccharide structure. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):619–628. doi: 10.1172/JCI109707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Olsson I., Odeberg H. Purification and characterization of a potent bactericidal and membrane active protein from the granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2664–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Kao L., Victor M., Elsbach P. Oxygen-independent intracellular and oxygen-dependent extracellular killing of Escherichia coli S15 by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):206–212. doi: 10.1172/JCI111947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEYA H. I., SPITZNAGEL J. K. ANTIBACTERIAL AND ENZYMIC BASIC PROTEINS FROM LEUKOCYTE LYSOSOMES: SEPARATION AND IDENTIFICATION. Science. 1963 Nov 22;142(3595):1085–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3595.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Arginine-rich proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. Antimicrobial specificity and biochemical heterogeneity. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):927–941. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. II. Composition, properties, and mechanism of antibacterial action. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):755–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.755-762.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Rosselet A. Function of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli as a permeability barrier to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):368–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]