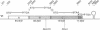Abstract
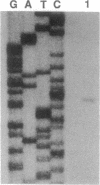
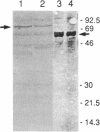
An operon encoding four proteins required for bacterial cellulose biosynthesis (bcs) in Acetobacter xylinum was isolated via genetic complementation with strains lacking cellulose synthase activity. Nucleotide sequence analysis indicated that the cellulose synthase operon is 9217 base pairs long and consists of four genes. The four genes--bcsA, bcsB, bcsC, and bcsD--appear to be translationally coupled and transcribed as a polycistronic mRNA with an initiation site 97 bases upstream of the coding region of the first gene (bcsA) in the operon. Results from genetic complementation tests and gene disruption analyses demonstrate that all four genes in the operon are required for maximal bacterial cellulose synthesis in A. xylinum. The calculated molecular masses of the proteins encoded by bcsA, bcsB, bcsC, and bcsD are 84.4, 85.3, 141.0, and 17.3 kDa, respectively. The second gene in the operon (bcsB) encodes the catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase. The functions of the bcsA, bcsC, and bcsD gene products are unknown. Bacterial strains mutated in the bcsA locus were found to be deficient in cellulose synthesis due to the lack of cellulose synthase and diguanylate cyclase activities. Mutants in the bcsC and bcsD genes were impaired in cellulose production in vivo, even though they had the capacity to make all the necessary metabolic precursors and cyclic diguanylic acid, the activator of cellulose synthase, and exhibit cellulose synthase activity in vitro. When the entire operon was present on a multicopy plasmid in the bacterial cell, both cellulose synthase activity and cellulose biosynthesis increased. When the promoter of the cellulose synthase operon was replaced on the chromosome by E. coli tac or lac promoters, cellulose production was reduced in parallel with decreased cellulose synthase activity. These observations suggest that the expression of the bcs operon is rate-limiting for cellulose synthesis in A. xylinum.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloni Y., Delmer D. P., Benziman M. Achievement of high rates of in vitro synthesis of 1,4-beta-D-glucan: activation by cooperative interaction of the Acetobacter xylinum enzyme system with GTP, polyethylene glycol, and a protein factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6448–6452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amikam D., Benziman M. Cyclic diguanylic acid and cellulose synthesis in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6649–6655. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6649-6655.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benziman M., Haigler C. H., Brown R. M., White A. R., Cooper K. M. Cellulose biogenesis: Polymerization and crystallization are coupled processes in Acetobacter xylinum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6678–6682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bureau T. E., Brown R. M. In vitro synthesis of cellulose II from a cytoplasmic membrane fraction of Acetobacter xylinum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6985–6989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukaya M., Tayama K., Tamaki T., Tagami H., Okumura H., Kawamura Y., Beppu T. Cloning of the Membrane-Bound Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Gene of Acetobacter polyoxogenes and Improvement of Acetic Acid Production by Use of the Cloned Gene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):171–176. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.171-176.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sunagawa M., Mori A., Imai C., Fukuda M., Takagi M., Yano K. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the 72-kilodalton dehydrogenase subunit of alcohol dehydrogenase from Acetobacter aceti. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3115–3122. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3115-3122.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang M. S., Elango N., Mattia E., Au-Young J., Robbins P. W., Cabib E. Isolation of chitin synthetase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification of an enzyme by entrapment in the reaction product. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14966–14972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawyer F. C., Stoffel S., Saiki R. K., Myambo K., Drummond R., Gelfand D. H. Isolation, characterization, and expression in Escherichia coli of the DNA polymerase gene from Thermus aquaticus. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6427–6437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Wong H. C., Ting Y. E., Van Arsdell J. N., Chang S. Control of lysogeny and immunity of Bacillus subtilis temperate bacteriophage SP beta by its d gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):952–959. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.952-959.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhauser T. J., Ditta G., Helinski D. R. Broad-host-range plasmid cloning vectors for gram-negative bacteria. Biotechnology. 1988;10:287–332. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-409-90042-2.50021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swissa M., Aloni Y., Weinhouse H., Benizman M. Intermediatry steps in Acetobacter xylinum cellulose synthesis: studies with whole cells and cell-free preparations of the wild type and a celluloseless mutant. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1142–1150. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1142-1150.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki T., Horinouchi S., Fukaya M., Okumura H., Kawamura Y., Beppu T. Nucleotide sequence of the membrane-bound aldehyde dehydrogenase gene from Acetobacter polyoxogenes. J Biochem. 1989 Oct;106(4):541–544. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittman V., Wong H. C. Regulation of the penicillinase genes of Bacillus licheniformis: interaction of the pen repressor with its operators. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3206–3212. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3206-3212.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Chang S. Identification of a positive retroregulator that stabilizes mRNAs in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]