Abstract
Several studies show that human papillomavirus (HPV) positive head and neck cancers (HNSCC) are typically characterized by low tumor and high regional node stages, intrinsically indicating high local metastatic potential. Despite this, the distant metastasis rates of HPV positive and negative HNSCC are similar. To date, majority of the studies focus on molecular characterization of HPV positive disease and on treatment outcome. Here we assessed the biological mechanisms of metastasis by combining in vitro and in vivo head and neck carcinoma xenograft models with patient data. We provide experimental evidence for a dual role of p16, a surrogate marker for HPV infections, in the metastasis process of HNSCC. We found that p16 regulates the invasiveness and metastatic potential of HNSCC cells by impairing angiogenesis. In parallel, we found that p16 is regulating the nodal spread by mediating lymphatic vessel formation through the upregulation of integrins. These findings not only provide understanding of the biology of the different dissemination patterns but also suggest that inhibition of lymphangiogenesis in HPV positive cancers and inhibition of angiogenesis in HPV negative cancers can form a treatment strategy against metastasis.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0678-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: HPV, P16, Head and neck cancer, Metastasis, Angiogenesis, Lymphangiogenesis
Background
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the sixth most common malignancy worldwide with 600,000 cases every year and is associated with high morbidity and mortality [1]. HNSCC patients are divided in two groups according to their etiology, namely high-risk human papilloma virus related (HPV) and the alcohol and tobacco related HNSCC [1–5].
Although recent studies show favorable local and survival outcome of HPV related HNSCC patients, the distant metastasis (DM) rate is similar for HPV positive and negative HNSCC patients [5, 6]. The frequency of distant recurrence in HNSCC is low but with the rarity of locoregional failure, the importance of DM on survival is now more prominent and the leading cause of death in HPV positive patients [6–8]. Even more striking is the unusual dissemination pattern to distal organs like liver and brain in HPV positive HNSCC, compared to HPV negative HNSCC where lung and bone are the most frequent locations for metastasis [9]. Moreover, it is reported that DM in HPV positive HNSCC can still be detected up to 5 years of follow-up [5, 6]. In contrast, DM rates in HPV negative HNSCC are stable after 2 years [5, 6, 9]. HPV positive HNSCC are characterized by low tumor (T) and high regional node (N) stages, intrinsically indicating high local metastatic potential [5, 7, 10]. The significance of T and N stages along with tobacco exposure as factors influencing the risk of recurrence and death in patients with HPV positive HNSCC have been explored in several studies [5, 11–15]. However, the biological assessment behind the unusual and somewhat paradoxical dissemination pattern remains largely unknown. In this paper, we assessed the biological mechanisms behind the clinical presentation of HPV related HNSCC by combining data from in vitro and in vivo HNSCC xenograft models with data of 241 HNSCC patients.
Main text
HPV/p16 positive and negative HNSCC show differences in nodal involvement
We determined the HPV and p16 status of 241 oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPC) patients treated with (chemo)radiation (c)RT. The human tumor samples were acquired according to protocols approved by the Ethical board of the University Hospitals Leuven (Leuven, Belgium) and implied consent of all the patients were obtained. Clinicopathological data were extracted from patient charts and the mean follow-up time was 4.19 years. HPV positive patients were characterized by lower T stages with 45% (26 out of 58; p = 0.025) of HPV positive patients showing T1/2 stage tumors whereas this was 29% (51 out of 175; p = 0.025) in the HPV negative group. Moreover, HPV positive tumors showed significantly higher (p = 0.014) nodal involvement with 72% (42 out of 58) of HPV positive patients showing N2/N3 tumors whereas this was only 54% (95 out of 175) in the HPV negative group. Although the relationship between p16 status and N stage was not significant, a trend to higher nodal involvement and p16 positivity was seen. Sixty-three% of p16 positive patients showed N2/N3 tumors, whereas this was only 54% in the p16 negative group (Table 1). These results are in concordance with other studies, showing that HPV positive HNSCC patients have higher N and lower T stages [5, 6, 10, 16].
Table 1.
Correlation between patient characteristics, HPV and p16 status
| HPV negative | HPV positive | P | p16 negative | p16 positive | P | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | (%) | No. | (%) | No. | (%) | No. | (%) | |||
| No. of patients | ||||||||||
| 175 | 58 | 173 | 68 | |||||||
| Gender | p = 0.67b | p = 0.99b | ||||||||
| Male | 146 | 83 | 47 | 81 | 143 | 83 | 56 | 82 | ||
| Female | 29 | 17 | 11 | 19 | 30 | 17 | 12 | 18 | ||
| Age, years | p = 0.031a | p = 0.046a | ||||||||
| Median (Range) | 59 | (57–60) | 61 | (59–65) | 59 | (57–60) | 61 | (59–64) | ||
| Smoking history | p = 0.001b | p = 0.004b | ||||||||
| Never | 8 | 5 | 15 | 26 | 11 | 6 | 13 | 19 | ||
| Former | 20 | 11 | 11 | 19 | 22 | 13 | 11 | 16 | ||
| Current | 126 | 72 | 25 | 43 | 120 | 69 | 35 | 51 | ||
| Unknown | 21 | 12 | 7 | 12 | 20 | 12 | 9 | 13 | ||
| Treatment | p = 0.68b | p = 0.15b | ||||||||
| RT | 71 | 41 | 19 | 33 | 68 | 39 | 29 | 43 | ||
| RT + CT | 97 | 55 | 34 | 59 | 100 | 58 | 33 | 49 | ||
| RT + EGFR inhibitor | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 6 | ||
| Unknown | 2 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Nodal stage* | p = 0.014b | p = 0.07b | ||||||||
| N0/N1 | 80 | 45 | 16 | 28 | 78 | 45 | 25 | 37 | ||
| N2/N3 | 95 | 54 | 42 | 72 | 94 | 54 | 43 | 63 | ||
| Unknown | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Tumor stage* | p = 0.025b | p = 0.11b | ||||||||
| T1/2 | 51 | 29 | 26 | 45 | 60 | 35 | 22 | 32 | ||
| T3/4 | 122 | 70 | 31 | 53 | 112 | 65 | 45 | 66 | ||
| unknown | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Disease stage* | p = 0.28b | p = 0.18b | ||||||||
| I-II | 17 | 10 | 3 | 5 | 17 | 10 | 3 | 4 | ||
| III-IV | 157 | 90 | 54 | 93 | 155 | 90 | 65 | 96 | ||
| Unknown | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| HPV | p < 0.0001b | |||||||||
| Negative | 150 | 87 | 16 | 24 | ||||||
| Positive | 9 | 5 | 44 | 65 | ||||||
| Unknown | 14 | 8 | 8 | 12 | ||||||
| p16 | p < 0.0001b | |||||||||
| Negative | 150 | 86 | 9 | 16 | ||||||
| Positive | 16 | 9 | 44 | 76 | ||||||
| Unknown | 9 | 5 | 5 | 9 | ||||||
Abbreviations: RT radiotherapy, CT chemotherapy, EGFR epidermal growth factor
*International Union of Cancer Research 1982 classification; aANOVA; bchi square test.
As anticipated, low T stages resulted in better distant control (DC) rates with 5-year control rates of 83% and 70% (p = 0.04) for T1/T2 and T3/4 tumors respectively (Additional file 1: Figure S1A). N2/3 tumors (5-year DC 70%; p = 0.02) showed a higher risk to distant failure compared to N0/1 tumors (5-year DC rate 85%; p = 0.02) (Additional file 1: Figure S1B). No statistically significant difference was seen in DC rate between HPV positive and negative disease (5-year DC rate of 82% vs 5-year DC rate of 72% respectively; p = 0.20) (Additional file 1: Figure S1C). Although not significant, this 10% difference in DC rates suggests influence of the virus beyond local tumor control. Moreover, it indicates the presence of different dissemination patterns between HPV positive and negative HNSCC.
p16 represses the invasion and migration capacity of HPV positive HNSCC
To investigate the molecular mechanism behind these potential differences seen in metastasis in our patient cohort, we assessed the in vitro migration and invasion capacity of HNSCC cells. HPV/p16 positive SCC154 and SCC104 cells showed a significant lower migration rate compared to HPV/p16 negative SQD9, CAL27 and SC263 cells (Fig. 1a). In agreement with the migration assay, HPV/p16 positive cells showed reduced invasion abilities compared to the HPV/p16 negative cells (Fig. 1b).
Fig. 1.
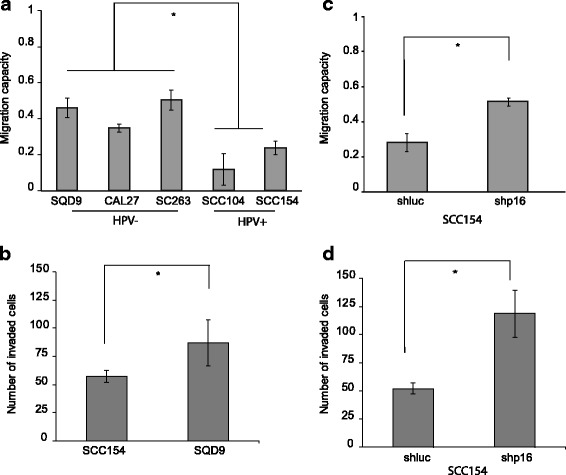
p16 represses the in vitro invasion and migration capacity of HPV positive HNSCC. a Migration capacity of HPV negative cells (SQD9, CAL27 and SC263) and HPV positive cells (SCC154, SCC104). b Invasion capacity of HPV negative SQD9 cells and HPV positive SCC154 cells. c Migration capacity of HPV positive SCC154 cells treated with shRNA for p16 (shp16) and control (shluc). d Invasion capacity of HPV positive SCC154 cells treated with shRNA for p16 (shp16) and control (shluc). (a-d) The result is shown as mean ± SEM of three experiments and p-values are calculated by two-sided t-test
The tumor suppressor p16 is a well-known cell cycle regulator and a good surrogate marker for HPV positive HNSCC [2, 3, 15]. Moreover, recent data ascribe a broader role for p16, including a role in migration and repression of angiogenesis [17–20]. Therefore, we also examined the influence of p16 on the migration and invasion capacity of HPV positive SCC154 cells manipulated with short hairpin RNA (shRNA) for p16 (shp16) and control shRNA (shluc). Downregulation of p16 expression increased migration and invasion capacities of the SCC154 cells (Fig. 1c and d). These data verify the presence of differences in dissemination patterns between HPV positive and negative HNSCC and suggest an active role of p16 in the metastatic cascade.
p16 suppresses migration and invasion through angiogenesis in HPV positive HNSCC
It is well known that angiogenesis, which is actively sustained in cancer cells by pro-angiogenic factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), is a conduit for cancer cell spread and metastasis and promotes aggressive tumor progression [18, 21, 22]. Moreover, the negative correlation between HPV/p16 and VEGFA is previously described in HNSCC [18]. Therefore, we assessed the relation between HPV, p16 and VEGFA in our patient cohort. HPV positive patients showed significantly lower VEGFA expression with 54% (28 out of 51) of patients showing no or low VEGFA expression compared to 32% (53 out of 161) in HPV negative group (Table 2). Although the negative correlation between VEGFA and p16 was less pronounced, a trend to significance was seen (Table 2).
Table 2.
Correlation between VEGF expression, HPV and p16 in HNSCC patients
| VEGF low | VEGF high | P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | (%) | No. | (%) | ||
| HPV | p=0.005b | ||||
| Negative | 53 | 65 | 108 | 82 | |
| Positive | 28 | 35 | 23 | 18 | |
| p16 | p=0.07b | ||||
| Negative | 53 | 66 | 99 | 77 | |
| Positive | 27 | 34 | 29 | 23 | |
bchi square test
We further investigated the relation between angiogenesis and p16 with in vivo xenografts injected with SCC154 HPV positive cells manipulated with shp16 or shluc. A higher number of blood vessels was detected in mice tumors with low p16 expression compared to control tumors (Fig. 2a). Furthermore, the increase in vascularization resulted in lower necrosis, higher number of mitotic cells and growth advantage of shp16 expressing tumors (Additional file 2: Figure S2A-C). We could not verify the involvement of p16 in suppression of metastasis in vivo due to the absence of a metastatic animal model. However, the growth advantage and the increased vascularization seen in shp16 mice tumors can explain the frequent occurrence of advanced T stages in HPV negative HNSCC patients.
Fig. 2.

Dual role of p16 in dissemination of HNSCC. a Blood vessel formation in SCC154 shp16 and SCC154 shluc xenograft mouse models assessed by CD31 staining (above the graph); n = 5. b Average number of lymphatic vessel formation in SCC154 shp16 and SCC154 shluc xenograft mouse models assessed by LYVE-1 staining (above the graph); n = 5. c Average score of alpha4 beta1 integrin staining in SCC154 shp16 and SCC154 shluc mouse xenograft models; n = 5. d Average score of alpha4 beta1 integrin staining in HPV positive SCC154 (n = 7) and HPV negative SQD9 (n = 10) mouse xenograft models. a-d P-values are calculated by two-sided t-test
p16 stimulates lymphangiogenesis and nodal spread in HPV positive HNSCC
These results still do not explain the occurrence of the similar distant relapse rates in HPV/p16 positive and negative HNSCC patients and certainly do not explain the highly significant association between HPV positivity and nodal involvement described in our and several other studies [5, 6, 10, 16]. This is especially important since it implicates the presence of a high local metastatic potential in HPV positive HNSCC. Interestingly lymphangiogenesis, like angiogenesis, promotes tumor metastasis by inducing the growth of new lymphatic vessels within the tumor and by enhancing cell trafficking to lymph nodes. Moreover, increased lymphatic vessel density in tumors is associated with increased metastasis to lymph nodes. [21, 23, 24]. Therefore, we assessed the lymphatic vessel formation by homologue lymphatic vessel hyaluronan (LYVE-1) immunostaining in shluc and shp16 mice tumors. We found that p16 suppression resulted in lower lymphatic vessel density in HPV/p16 positive xenografts suggesting a dual role of p16 in metastasis (Fig. 2b).
To understand the function of p16, we focused on integrins as these proteins are accepted as key regulators of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis [21, 23–27]. Moreover, the binding of p16 to integrins and loss of cell spread is previously documented [20, 28]. Integrins such as alpha4 beta1 are important modulators of lymphangiogenesis [21, 23, 24]. Therefore, we assessed the presence of alpha4 beta1 integrin in SCC154 shluc and SCC154 shp16 mice tumors. Although not statistically significant (p = 0.09), shluc tumors showed a higher percentage of integrin compared to shp16 tumors (Fig. 2c). In line with SCC154 shRNA xenografts, tumors from HPV/p16 positive SCC154 xenografts showed higher percentage of alpha4 beta 1 integrin compared to tumors from HPV/p16 negative SQD9 xenografts (Fig. 2d).
Conclusion
Taken together, we provide experimental evidence for a dual role of p16 in the metastasis process of HNSCC. We show that p16 on the one hand regulates vascular invasiveness and growth of the tumor cells by inhibiting angiogenesis; on the other hand, it stimulates nodal spread by enhancing lymphangiogenesis. These findings provide us a better understanding of the molecular principles underlying the dissemination patterns and clinical presentation of HNSCC. Importantly, it also opens different treatment opportunities for metastasis in HNSCC by the inhibition of vascularization (e.g. anti-angiogenic drugs) in HPV negative cancers and by the inhibition of lymphangiogenesis (e.g. alpha4 antagonist) in HPV positive cancers. However, further preclinical and clinical studies are necessary to confirm these results and to investigate the utility and specificity of these treatment approaches.
Additional files
HPV/p16 positive and negative HNSCC patients show differences in nodal involvement. (A) Distant control (DC) rates in HNSCC patients with different T stages presented by Kaplan-Meier curves. (B) Distant control (DC) rates in HNSCC patients with different N stages presented by Kaplan-Meier curves (C) Distant control (DC) rates in HNSCC patients with different HPV status by Kaplan-Meier curves. (A-C) P values are determined by log-rank tests. (PDF 411 kb)
Dual role of p16 in dissemination of HNSCC. (A) Average tumor necrosis in SCC154 shp16 and SCC154 shluc xenograft mouse models; n = 5. (B) Average number of mitotic cells in SCC154 shp16 and SCC154 shluc xenograft mouse models; n = 5. (C) Average tumor volume of SCC154 shp16 and SCC154 shluc xenograft mouse models assessed by caliper measurements; n = 5. (A-C) P-values are calculated by two-sided t-test. (PDF 351 kb)
Supplementary material and methods. Detailed description of the material and methods. (DOCX 19 kb)
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Esther Hauben from the Department of Pathology (UZ Leuven) for her input to the study.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Authors’ contributions
RD, MG were involved in the acquisition of data and analysis and interpretation of data. MB and KH were involved in the acquisition of data. RD and SN were involved in study concept. SN provided material support, study concept, design, and drafting of the manuscript. All authors were involved in writing the paper and had final approval of the submitted and published versions.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Funding
This study was supported by Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek and by Koning Boudewijnstichting Fonds Anhaive, Belgium.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The human tumor samples were acquired according to protocols approved by the Ethical board of the University Hospitals Leuven (Leuven, Belgium) and implied consent of all the patients were obtained (see also Additional file 3).
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- (c)RT
(Chemo)radiation therapy
- CT
Chemotherapy
- DC
Distant control
- DM
Distant metastasis
- EGFR
Epidermal growth factor
- HNSCC
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- HPV
Human papillomavirus
- LYVE-1
Homologue lymphatic vessel hyaluronan receptor
- N
Node
- OPC
Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma patients
- shRNA
short hairpin RNA
- shluc
shRNA luciferase
- shp16
shRNA p16
- T
Tumor
- VEGFA
Vascular endothelial growth factor A
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0678-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
References
- 1.Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. doi: 10.3322/caac.20006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lassen P. The role of human papillomavirus in head and neck cancer and the impact on radiotherapy outcome. Radiother Oncol. 2010;95:371–380. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.04.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:9–22. doi: 10.1038/nrc2982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Marur S, Forastiere AA. Head and neck cancer: changing epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:489–501. doi: 10.4065/83.4.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ang KK, Harris J, Wheeler R, Weber R, Rosenthal DI, Nguyen-Tan PF, et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:24–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0912217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.O'Sullivan B, Huang SH, Siu LL, Waldron J, Zhao H, Perez-Ordonez B, et al. Deintensification candidate subgroups in human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal cancer according to minimal risk of distant metastasis. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:543–550. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.44.0164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Spector ME, Gallagher KK, Bellile E, Chinn SB, Ibrahim M, Byrd S, et al. Patterns of nodal metastasis and prognosis in human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2014;36:1233–1240. doi: 10.1002/hed.23438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Spector ME, Gallagher KK, Light E, Ibrahim M, Chanowski EJ, Moyer JS, et al. Matted nodes: poor prognostic marker in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma independent of HPV and EGFR status. Head Neck. 2012;34:1727–1733. doi: 10.1002/hed.21997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang SH, Perez-Ordonez B, Liu FF, Waldron J, Ringash J, Irish J, et al. Atypical clinical behavior of p16-confirmed HPV-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma treated with radical radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82:276–283. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.08.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.O'Sullivan B, Huang SH, Perez-Ordonez B, Massey C, Siu LL, Weinreb I, et al. Outcomes of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer patients treated by radiotherapy alone using altered fractionation. Radiother Oncol. 2012;103:49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2012.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fakhry C, Westra WH, Li S, Cmelak A, Ridge JA, Pinto H, et al. Improved survival of patients with human papillomavirus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in a prospective clinical trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:261–269. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gillison ML, Zhang Q, Jordan R, Xiao W, Westra WH, Trotti A, et al. Tobacco smoking and increased risk of death and progression for patients with p16-positive and p16-negative oropharyngeal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2102–2111. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lowy DR, Munger K. Prognostic implications of HPV in oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:82–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1003607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Maxwell JH, Kumar B, Feng FY, Worden FP, Lee JS, Eisbruch A, et al. Tobacco use in human papillomavirus-positive advanced oropharynx cancer patients related to increased risk of distant metastases and tumor recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:1226–1235. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rischin D, Young RJ, Fisher R, Fox SB, Le QT, Peters LJ, et al. Prognostic significance of p16INK4A and human papillomavirus in patients with oropharyngeal cancer treated on TROG 02.02 phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4142–4148. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.29.2904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Quon H, Forastiere AA. Controversies in treatment deintensification of human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal carcinomas: should we, how should we, and for whom? J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:520–522. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.7746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Al-Ansari MM, Hendrayani SF, Tulbah A, Al-Tweigeri T, Shehata AI, Aboussekhra A. p16INK4A represses breast stromal fibroblasts migration/invasion and their VEGF-a-dependent promotion of angiogenesis through Akt inhibition. Neoplasia. 2012;14:1269–1277. doi: 10.1593/neo.121632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baruah P, Lee M, Wilson PO, Odutoye T, Williamson P, Hyde N, et al. Impact of p16 status on pro- and anti-angiogenesis factors in head and neck cancers. Br J Cancer. 2015;113:653–659. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chen YW, Chu HC, Ze-Shiang L, Shiah WJ, Chou CP, Klimstra DS, et al. p16 stimulates CDC42-dependent migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e69389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Romagosa C, Simonetti S, Lopez-Vicente L, Mazo A, Lleonart ME, Castellvi J. Ramon y Cajal S: p16(Ink4a) overexpression in cancer: a tumor suppressor gene associated with senescence and high-grade tumors. Oncogene. 2011;30:2087–2097. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Avraamides CJ, Garmy-Susini B, Varner JA. Integrins in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:604–617. doi: 10.1038/nrc2353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–936. doi: 10.1038/nature04478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Garmy-Susini B, Makale M, Fuster M, Varner JA. Methods to study lymphatic vessel integrins. Methods Enzymol. 2007;426:415–438. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)26018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jin H, Varner J. Integrins: roles in cancer development and as treatment targets. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:561–565. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Brooks PC, Stromblad S, Klemke R, Visscher D, Sarkar FH, Cheresh DA. Antiintegrin alpha v beta 3 blocks human breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J Clin Invest. 1995;96:1815–1822. doi: 10.1172/JCI118227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Friedlander M, Theesfeld CL, Sugita M, Fruttiger M, Thomas MA, Chang S, et al. Involvement of integrins alpha v beta 3 and alpha v beta 5 in ocular neovascular diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:9764–9769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.18.9764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hirakawa S, Kodama S, Kunstfeld R, Kajiya K, Brown LF, Detmar M. VEGF-A induces tumor and sentinel lymph node lymphangiogenesis and promotes lymphatic metastasis. J Exp Med. 2005;201:1089–1099. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fahraeus R, Lane DP. The p16(INK4a) tumour suppressor protein inhibits alphavbeta3 integrin-mediated cell spreading on vitronectin by blocking PKC-dependent localization of alphavbeta3 to focal contacts. EMBO J. 1999;18:2106–2118. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.8.2106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
HPV/p16 positive and negative HNSCC patients show differences in nodal involvement. (A) Distant control (DC) rates in HNSCC patients with different T stages presented by Kaplan-Meier curves. (B) Distant control (DC) rates in HNSCC patients with different N stages presented by Kaplan-Meier curves (C) Distant control (DC) rates in HNSCC patients with different HPV status by Kaplan-Meier curves. (A-C) P values are determined by log-rank tests. (PDF 411 kb)
Dual role of p16 in dissemination of HNSCC. (A) Average tumor necrosis in SCC154 shp16 and SCC154 shluc xenograft mouse models; n = 5. (B) Average number of mitotic cells in SCC154 shp16 and SCC154 shluc xenograft mouse models; n = 5. (C) Average tumor volume of SCC154 shp16 and SCC154 shluc xenograft mouse models assessed by caliper measurements; n = 5. (A-C) P-values are calculated by two-sided t-test. (PDF 351 kb)
Supplementary material and methods. Detailed description of the material and methods. (DOCX 19 kb)
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.


