Abstract
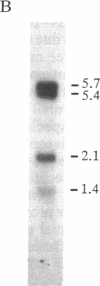
Iduronate 2-sulfatase (IDS, EC 3.1.6.13) is required for the lysosomal degradation of heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Mutations causing IDS deficiency in humans result in the lysosomal storage of these glycosaminoglycans and Hunter syndrome, an X chromosome-linked disease. We have isolated and sequenced a 2.3-kilobase cDNA clone coding for the entire sequence of human IDS. Analysis of the deduced 550-amino acid IDS precursor sequence indicates that IDS has a 25-amino acid amino-terminal signal sequence, followed by 8 amino acids that are removed from the proprotein. An internal proteolytic cleavage occurs to produce the mature IDS present in human liver shown to contain a 42-kDa polypeptide N-terminal to a 14-kDa polypeptide. The IDS sequence has strong sequence homology with other sulfatases (such as sea urchin arylsulfatase, human arylsulfatases A, B, and C, and human glucosamine 6-sulfatase), suggesting that the sulfatases comprise an evolutionarily related family of genes that arose by gene duplication and divergent evolution. The arylsulfatases have a greater homology with each other than with the non-arylsulfatases (IDS and glucosamine 6-sulfatase). The IDS cDNA detected RNA species of 5.7, 5.4, 2.1, and 1.4 kilobases in human placental RNA and revealed structural alterations and gross deletions of the IDS gene in many of the clinically severe Hunter syndrome patients studied.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bray Jeremy. Better safe than sorry. Nature. 1985 Mar 28;314(6009):310–310. doi: 10.1038/314310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James G. T. Essential arginine residues in human liver arylsulfatase A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Oct 1;197(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. D., van Etten R. L. Evidence of an essential histidine residue in rabbit liver aryl sulfatase A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Dec;171(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Altschul S. F., Kececioglu J. D. A tool for multiple sequence alignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4412–4415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama T., Gojobori T., Aota S., Ikemura T. Codon usage tabulated from the GenBank genetic sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14 (Suppl):r151–r197. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morreau H., Galjart N. J., Gillemans N., Willemsen R., van der Horst G. T., d'Azzo A. Alternative splicing of beta-galactosidase mRNA generates the classic lysosomal enzyme and a beta-galactosidase-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20655–20663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. V., Carey W. F., Morris C. P., Pollard A. C. Cystic fibrosis: prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection by DNA analysis. Med J Aust. 1989 Aug 7;151(3):126-7, 130-1. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1989.tb139595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima A., Kyle J. W., Miller R. D., Hoffmann J. W., Powell P. P., Grubb J. H., Sly W. S., Tropak M., Guise K. S., Gravel R. A. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of cDNA for human beta-glucuronidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):685–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters C., Schmidt B., Rommerskirch W., Rupp K., Zühlsdorf M., Vingron M., Meyer H. E., Pohlmann R., von Figura K. Phylogenetic conservation of arylsulfatases. cDNA cloning and expression of human arylsulfatase B. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3374–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. A., Freeman C., Nelson P. V., Morris C. P., Hopwood J. J. Human glucosamine-6-sulfatase cDNA reveals homology with steroid sulfatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):218–224. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Yamada K., Akasaka K., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Saito A., Sato M., Shimada H. cDNA cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression of the gene for arylsulfatase in the sea urchin (Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus) embryo. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):9–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Gieselmann V., Kreysing J., Schmidt B., Pohlmann R., Waheed A., Meyer H. E., O'Brien J. S., von Figura K. Cloning and expression of human arylsulfatase A. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1252–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Hille A., Seidel J., Rijnbout S., Waheed A., Schmidt B., Geuze H., von Figura K. Cloning and expression of human steroid-sulfatase. Membrane topology, glycosylation, and subcellular distribution in BHK-21 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13865–13872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Allen E., Marsh B., Mohandas T., Wang N., Taggart R. T., Shapiro L. J. Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurrence of deletions in STS deficiency: implications for X-Y interchange. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90447-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Marsh B., Allen E., Tsai S. P., Ellison J., Connolly L., Neiswanger K., Shapiro L. J. The human X-linked steroid sulfatase gene and a Y-encoded pseudogene: evidence for an inversion of the Y chromosome during primate evolution. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1123–1135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]