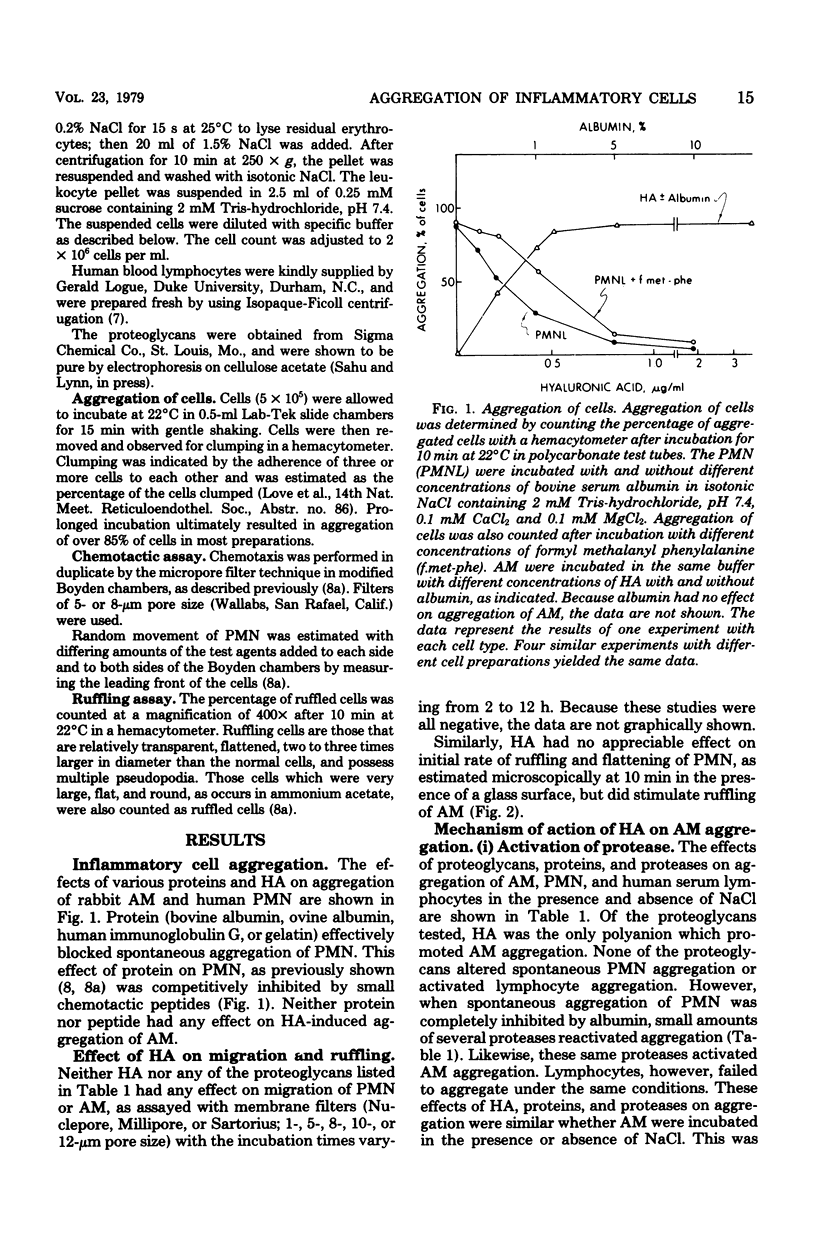
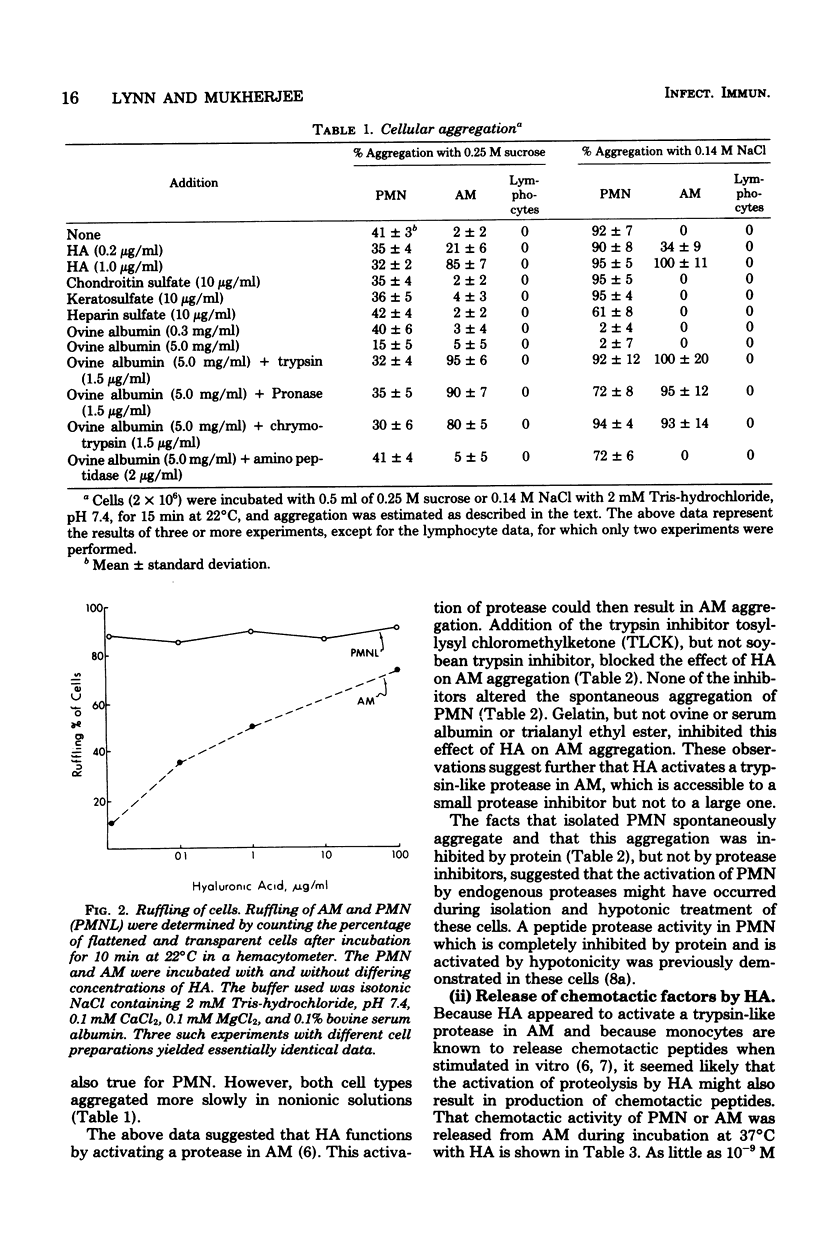
Abstract
A trypsin-like protease activity present in rabbit alveolar macrophages was shown to be activated by hyaluronic acid (HA) at 10(-9) M, but not by other proteoglycans. This activation of proteases by HA was accompanied by aggregation of alveolar macrophages and by the release of chemotactic activity. This chemotactic activity was destroyed by proteases and was less active for polymorphonuclear leukocytes than for alveolar macrophages. These effects of HA appear to be sepcific for alveolar macrophages, because no similar effects of HA on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes or lymphocytes could be observed. These observations suggest that HA, which is secreted into airways, plays a specific role in the macrophage-mediated chronic inflammatory processes in the distal lung.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki Y. Crystallization and characterization of a new protease in mitochondria of bone marrow cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):2026–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue M. L., Janoff A. Possible mechanisms of emphysema in cigarette smokers. Release of elastase from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by cigarette smoke condensate in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Feb;117(2):317–325. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E. Superoxide production by digitonin-stimulated guinea pig granulocytes. The effects of N-ethyl maleimide, divalent cations; and glycolytic and mitochondrial inhibitors on the activation of the superoxide generating system. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1088–1096. doi: 10.1172/JCI109008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauber J. H., Daniele R. P. Chemotactic activity of guinea pig alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Apr;117(4):673–684. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.4.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramse M., Bingenheimer C., Schmidt W., Egbring R., Havemann K. Degradation products of fibrinogen by elastase-like neutral protease from human granulocytes. Characterization and effects on blood coagulation in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1027–1033. doi: 10.1172/JCI109001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gallin J. I., Fauci A. S. Immunologic reactivity of the lung: the in vivo and in vitro generation of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jan;117(1):15–23. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlander R. J., Rosse W. F., Logue G. L. Quantitative influence of antibody and complement coating of red cells on monocyte-mediated cell lysis. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1309–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI109048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn W. S., Mukherjee C. Motility of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Roles of hydroxy fatty acids, other lipids, and cations. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jun;91(3):581–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee C., Lynn W. S. Role of ions and extracellular protein in leukocyte motility and membrane ruffling. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):369–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Olsson I. The neutral proteases of human granulocytes. Isolation and partial characterization of granulocyte elastases. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector W. G., Ryan G. B. New evidence for the existence of long lived macrophages. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):860–860. doi: 10.1038/221860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilbert I., Gallacher A., Mehta J. M., Mandell B. Urate crystal-induced chemotactic factor: isolation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):815–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI108533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Turner S. R., Lynn W. S. New aspects of chemotaxis. Specific target-cell attraction by lipid and lipoprotein fractions of Escherichia coli chemotactic factor. Am J Pathol. 1975 Nov;81(2):401–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


